|
Saint Petersburg Dam
The Saint Petersburg Flood Prevention Facility Complex (), unofficially the Saint Petersburg Dam, is a long complex of dams for flood control near Saint Petersburg, Russia. The dam extends from Lomonosov, Russia, Lomonosov northward to Kotlin Island (and the city of Kronstadt), then turns east toward Cape Lisiy Nos near Sestroretsk. The complex is intended to protect Saint Petersburg from storm surges by separating the Neva Bay from the rest of the Gulf of Finland. The dam's tunnel also serves as the final leg of the Saint Petersburg Ring Road. The northern and southern parts of the dam act like two giant bridges, providing access from the mainland to Kotlin Island and Kronstadt. Historically, storm surges from the gulf have caused Floods in Saint Petersburg, over 300 floods of varying severity within the city, some with devastating effects. The dam has the capability to protect the city from water rising up to . Its first use to hold back the incoming Baltic water into Neva B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
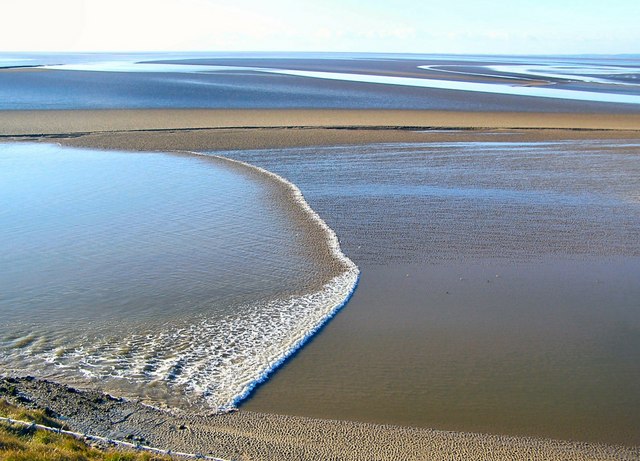
Aerial View Of Navigation Pass S-1 Of Saint Petersburg Dam
Aerial may refer to: Music *Aerial (album), ''Aerial'' (album), by Kate Bush, and that album's title track *Aerials (song), "Aerials" (song), from the album ''Toxicity'' by System of a Down Bands *Aerial (Canadian band) *Aerial (Scottish band) *Aerial (Swedish band) Recreation and sport *Aerial (dance move) *Aerial (skateboarding) *Front aerial, gymnastics move performed in acro dance * Aerial cartwheel * Aerial silk, a form of acrobatics * Aerial skiing Technology *Aerial (radio), a radio ''antenna'' or transducer that transmits or receives electromagnetic waves **Aerial (television), an over-the-air television reception antenna *Aerial photography Other uses *Aerial, Georgia, a community in the United States *Aerial (magazine), ''Aerial'' (magazine), a poetry magazine *Aerials (film), ''Aerials'' (film), a 2016 Emirati science-fiction film *''Aerial'', a BBC Two '1991–2001' idents, TV ident for BBC Two from 1997 to 2001 See also * Arial * Ariel (disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Of Russia
Voice of Russia (), commonly abbreviated VOR, was the Russian government's international radio broadcasting service from 1993 until 2014, when it was reorganised as Radio Sputnik. Its interval signal was a chime version of 'Majestic' chorus from the ''Great Gate of Kiev'' portion of '' Pictures at an Exhibition'' by Mussorgsky. History Russian president Boris Yeltsin issued a decree on 22 December 1993 which reorganised Radio Moscow under a new name: Voice of Russia. On 9 December 2013, Russian president Vladimir Putin issued a presidential decree dissolving the Voice of Russia as an agency, and merging it with RIA Novosti to form the '' Rossiya Segodnya'' international news agency. Margarita Simonyan, editor-in-chief of the Rossiya Segodnya, said in March 2014 that "We will stop using obsolete radio broadcasting models, when the signal is transmitted without any control and when it is impossible to calculate who listens to it and where." The Voice of Russia ceased shortwav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin () was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is considered by many to be the greatest Russian poet,Short biography from University of Virginia . Retrieved 24 November 2006.Allan Reid, "Russia's Greatest Poet/Scoundrel" Retrieved 2 September 2006. as well as the founder of modern Russian literature [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Garden
The Summer Garden () is a historic public garden that occupies an eponymous island between the Neva, Fontanka, Moika, and the Swan Canal in downtown Saint Petersburg, Russia and shares its name with the adjacent Summer Palace of Peter the Great. Its inception dates back to the early 18th century when Russia took these lands from Sweden in the Great Northern War. Being a monument of landscape architecture featuring original and copied sculptures of classical mythology characters, a former royal palace and a monument to the fable author Ivan Krylov, the garden is now a branch of the Saint Petersburg-based national art treasury Russian Museum. Landscape design Original The park was personally designed by Tsar Peter in 1704, supposedly, with the assistance of the Dutch gardener and physician Nicolaas Bidloo. Starting from 1712, the planting of the Summer Garden was further elaborated by the Dutch gardener Jan Roosen, who was the chief gardener of the park till 1726. The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Griboyedov
Alexander Sergeyevich Griboyedov (; 15 January 179511 February 1829) was a Russian diplomat, playwright, poet, and composer. His one notable work is the 1823 verse comedy '' Woe from Wit''. He was Russia's ambassador to Qajar Persia, where he and all the embassy staff were massacred by an angry mob in the aftermath of the ratification of the Treaty of Turkmenchay (1828), which confirmed the cession to Russia of Persia's northern territories comprising Transcaucasia and parts of the North Caucasus. Griboyedov played a pivotal role in the ratification of the treaty. The immediate cause for the incident was Griboyedov giving refuge to Armenians who had escaped from the harems of the Persian shah and his son. Early life Griboyedov was born in Moscow, the exact year unknown, with biographers debating whether it was in 1790 or 1795. His mother who dreamed of providing him with a career made sure Griboyedov received the best education. He received a master's degree in philology from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Bore
A tidal bore, often simply given as bore in context, is a tidal phenomenon in which the leading edge of the incoming tide forms a wave (or waves) of water that travels up a river or narrow bay, reversing the direction of the river or bay's current. It is a strong tide that pushes up the river, against the current. Description Bores occur in relatively few locations worldwide, usually in areas with a large tidal range (typically more than between high and low tide) and where incoming tides are funneled into a shallow, narrowing river or lake via a broad bay. The funnel-like shape not only increases the tidal range, but it can also decrease the duration of the flood tide, down to a point where the flood appears as a sudden increase in the water level. A tidal bore takes place during the flood tide and never during the ebb tide. A tidal bore may take on various forms, ranging from a single breaking wavefront with a somewhat like a hydraulic jumpto undular bores, compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seiche
A seiche ( ) is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water. Seiches and seiche-related phenomena have been observed on lakes, reservoirs, swimming pools, bays, harbors, caves, and seas. The key requirement for formation of a seiche is that the body of water be at least partially bounded, allowing the formation of the standing wave. The term was promoted in 1890 by the Swiss hydrologist François-Alphonse Forel, who was the first to make scientific observations of the effect in Lake Geneva. The word had apparently long been used in the region to describe oscillations in alpine lakes. According to Wilson (1972), this Swiss French dialect word comes from the Latin word meaning "dry", i.e., as the water recedes, the beach dries. The French word or (dry) descends from the Latin. Seiches in harbours can be caused by ''long-period'' or '' infragravity waves'', which are due to subharmonic nonlinear wave interaction with the wind waves, having periods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the world's largest brackish water basin. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. It is a Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea and marginal sea of the Atlantic with limited water exchange between the two, making it an inland sea. The Baltic Sea drains through the Danish straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia (divided into the Bothnian Bay and the Bothnian Sea), the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within the smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrometeorology
Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere for academic research, commercial gain or operational forecasting purposes. Whilst traditionally meteorologists and hydrologists sit within separate organisations, hydrometeorlogists may work in joint project teams, virtual teams, deal with specific incidents or be permanently co-located to deliver specific objectives. Hydrometeorlogists typically have a foundation in one or other discipline before undertaking additional training and specialist forecaster training depending on requirements. The cross over skills and knowledge between the two disciplines can bring organisational benefits in terms of efficiencies in terms of using tools and data available, and provide benefits in terms of enhanced lead times ahead of hydrometeological hazards occurring. UNESCO has several programs and activities in place that deal with the study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake Baikal, and the List of lakes by area, 14th largest freshwater lake by area in the world. It is comparable in size to Lake Ontario. ''Ladoga Lacus'', a methane lake on Saturn's moon Titan (moon), Titan, is named after the lake. Etymology In one of Nestor the Chronicler, Nestor's chronicles from the 12th century a lake called "the Great Nevo" is mentioned, a clear link to the Neva River and possibly further to Finnish language, Finnish ''nevo'' 'sea' or ''neva'' 'bog, quagmire'.:ru:Поспелов, Евгений Михайлович, Evgeny Pospelov: ''Geographical names of the world. Toponymic dictionary.'' Second edition. Astrel, Moscow 2001, pp. 106f. Ancient Norse sagas and Hanseatic treaties both mention a city made of lakes named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neva
The Neva ( , ; , ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it is the fourth-largest river in Europe in terms of average discharge (after the Volga, the Danube and the Rhine). The Neva is the only river flowing from Lake Ladoga. It flows through the city of Saint Petersburg, the three smaller towns of Shlisselburg, Kirovsk and Otradnoye, and dozens of settlements. It is navigable throughout and is part of the Volga–Baltic Waterway and White Sea–Baltic Canal. It is the site of many major historical events, including the Battle of the Neva in 1240 which gave Alexander Nevsky his name, the founding of Saint Petersburg in 1703, and the Siege of Leningrad by the German army during World War II. The river played a vital role in trade between Byzantium and Scandinavia. Etymology The earliest people in recorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |