|
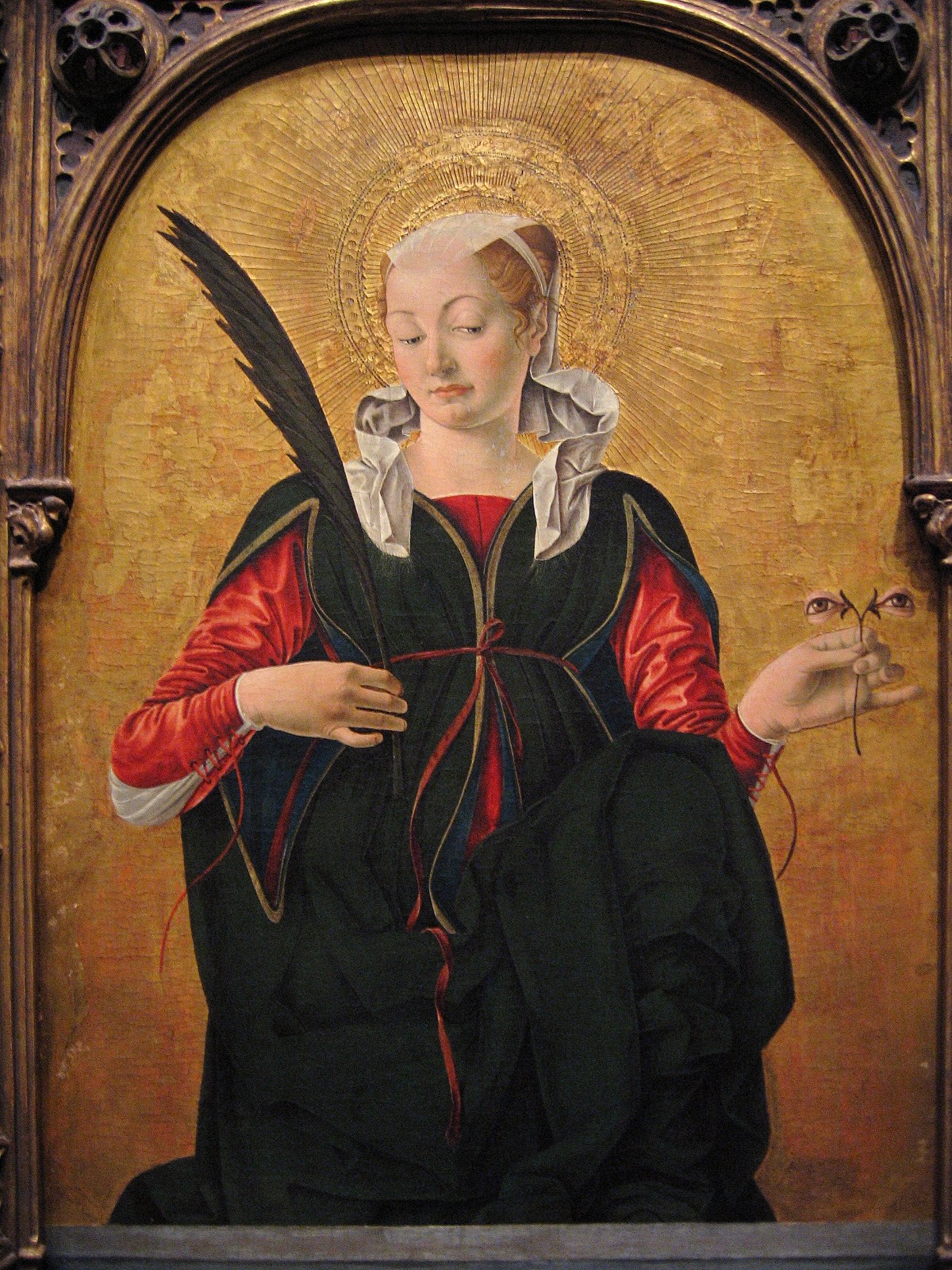
Saint Florian (Francesco Del Cossa)
Saint Floriano is a tempera and gold panel painting (79 × 55 cm) by Francesco del Cossa, created circa1472 and on display at the National Gallery of Art in Washington. The work was the upper left panel of the ./ Background Francesco del Cossa was newly arrived in Bologna when he received from a commission from the Griffoni family for an altarpiece for the chapel in the Basilica of San Petronio, made in collaboration of another painter from Ferrara, Ercole de' Roberti. The altarpiece was for dedication of the ''Chapel of St. Vincent Ferrer;'' the saint having been canonized in 1448 and his cult promoted by the Dominican Order. The work remained in the chapel until 1725–1730, when it was disassembled and sold in separate lots.. The two upper panels of Saint Florian and Saint Lucy ended up in Gubbio in the collections of Count Ugo Beni around 1858. In 1882 they were put up for sale with the other assets of the Count and purchased by Joseph Spiridon, who placed them on the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Del Cossa
Francesco del Cossa (c. 1430 – c. 1477) was an Italian Renaissance painter of the School of Ferrara, who after 1470 worked in Bologna. Cossa is best known for his frescoes, especially his collaboration with Cosimo Tura on a cycle of the months in the Palazzo Schifanoia of the Este family, rulers of Ferrara. Otherwise, his paintings are mostly of religious subjects, with some portraits and drawings attributed to him. He also designed stained glass. Biography The son of a stonemason in Ferrara, little is known about his early works, although it is known that he travelled outside of Ferrara in his late twenties or early thirties. One of the first records we have of him is in 1456 when he was an assistant to his father, Cristofano del Cossa, at that time employed in painting the carvings and statues on the high altar in the chapel of the bishop's palace at Ferrara. One of his followers was Leonardo Scaletti of Faenza. Allegorical frescoes in the Palazzo Schifanoia In con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gubbio
Gubbio () is an Italian town and ''comune'' in the far northeastern part of the Italian province of Perugia ( Umbria). It is located on the lowest slope of Mt. Ingino, a small mountain of the Apennines. History The city's origins are very ancient. The hills above the town were already occupied in the Bronze Age. As ''Ikuvium'', it was an important town of the Umbri in pre-Roman times, made famous for the discovery there in 1444 of the Iguvine Tablets, a set of bronze tablets that together constitute the largest surviving text in the Umbrian language. After the Roman conquest in the 2nd century BC – it kept its name as ''Iguvium'' – the city remained important, as attested by its Roman theatre, the second-largest surviving in the world. Gubbio became very powerful in the beginning of the Middle Ages. The town sent 1000 knights to fight in the First Crusade under the lead of Girolamo Gabrielli, and according to an undocumented local tradition, they were the first to penetra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collections Of The National Gallery Of Art
Collection or Collections may refer to: * Cash collection, the function of an accounts receivable department * Collection (church), money donated by the congregation during a church service * Collection agency, agency to collect cash * Collections management (museum) ** Collection (museum), objects in a particular field forms the core basis for the museum ** Fonds in archives ** Private collection, sometimes just called "collection" * Collection (Oxford colleges), a beginning-of-term exam or Principal's Collections * Collection (horse), a horse carrying more weight on his hindquarters than his forehand * Collection (racehorse), an Irish-bred, Hong Kong based Thoroughbred racehorse * Collection (publishing), a gathering of books under the same title at the same publisher * Scientific collection, any systematic collection of objects for scientific study Collection may also refer to: Computing * Collection (abstract data type), the abstract concept of collections in compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
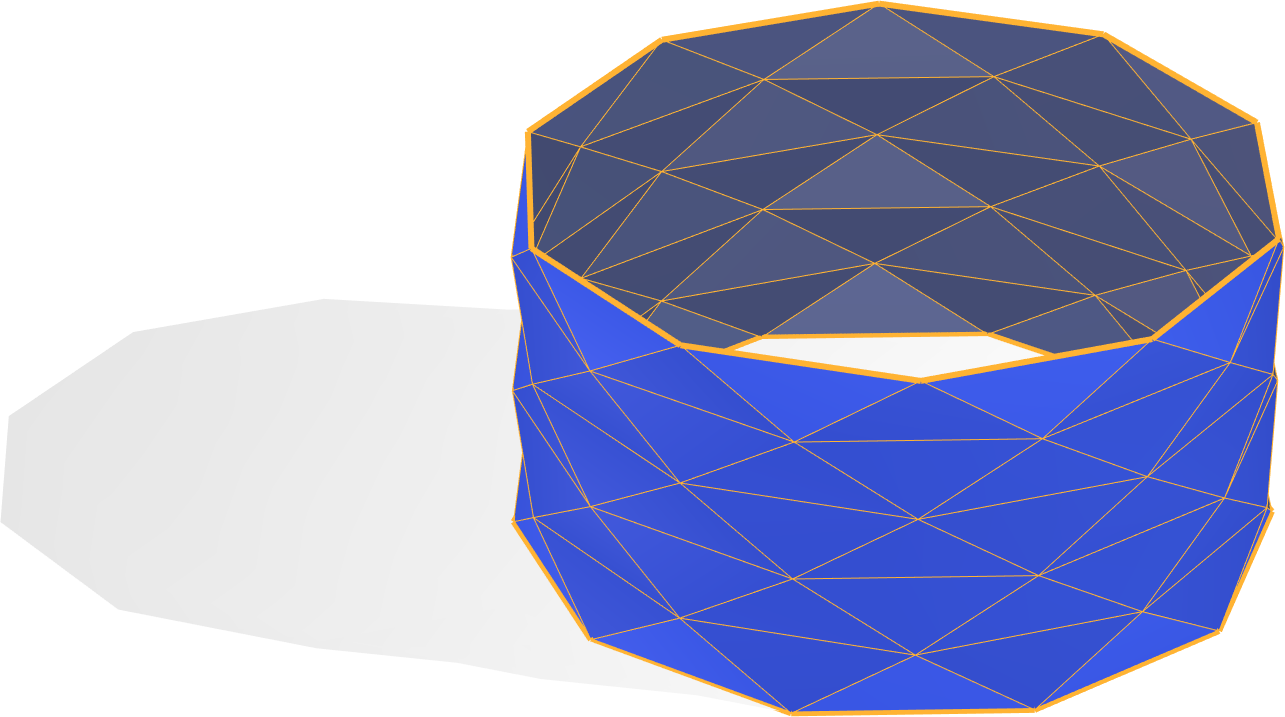
Yoshimura Buckling
In mechanical engineering, Yoshimura buckling is a triangular mesh buckling pattern found in thin-walled cylinders under compression along the axis of the cylinder, producing a corrugated shape resembling the Schwarz lantern. The same pattern can be seen on the sleeves of '' Mona Lisa''. This buckling pattern is named after Yoshimaru Yoshimura, the Japanese researcher who provided an explanation for its development in a paper first published in Japan in 1951, and later republished in the United States in 1955. Unknown to Yoshimura, the same phenomenon had previously been studied by Theodore von Kármán and Qian Xuesen in 1941. The crease pattern for folding the Schwarz lantern from a flat piece of paper, a tessellation of the plane by isosceles triangle In geometry, an isosceles triangle () is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. Sometimes it is specified as having ''exactly'' two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having ''at least'' two sides of equa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piero Della Francesca
Piero della Francesca (, also , ; – 12 October 1492), originally named Piero di Benedetto, was an Italian painter of the Early Renaissance. To contemporaries he was also known as a mathematician and geometer. Nowadays Piero della Francesca is chiefly appreciated for his art. His painting is characterized by its serene humanism, its use of geometric forms and perspective. His most famous work is the cycle of frescoes '' The History of the True Cross'' in the church of San Francesco in the Tuscan town of Arezzo. Biography Early years Piero was born Piero di Benedetto in the town of Borgo Santo Sepolcro, modern-day Tuscany, to Benedetto de' Franceschi, a tradesman, and Romana di Perino da Monterchi, members of the Florentine and Tuscan Franceschi noble family. His father died before his birth, and he was called Piero della Francesca after his mother, who was referred to as "la Francesca" due to her marriage into the Franceschi family (similar to how Lisa Gherardini became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyptych
A polyptych ( ; Greek: ''poly-'' "many" and ''ptychē'' "fold") is a painting (usually panel painting) which is divided into sections, or panels. Specifically, a "diptych" is a two-part work of art; a "triptych" is a three-part work; a tetraptych or quadriptych has four parts, and so on. Historically, polyptychs typically displayed one "central" or "main" panel that was usually the largest of the attachments; the other panels are called "side" panels, or "wings". Sometimes, as evident in the Ghent and Isenheim works (see below), the hinged panels can be varied in arrangement to show different "views" or "openings" in the piece. The upper panels often depict static scenes, while the lower register, the predella, often depict small narrative scenes. Polyptychs were most commonly created by early Renaissance painters, the majority of whom designed their works to be altarpieces in churches and cathedrals. The polyptych form of art was also quite popular among ukiyo-e printmakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Where extending above a roof, a parapet may simply be the portion of an exterior wall that continues above the edge line of the roof surface, or may be a continuation of a vertical feature beneath the roof such as a fire wall or party wall. Parapets were originally used to defend buildings from military attack, but today they are primarily used as guard rails, to conceal rooftop equipment, reduce wind loads on the roof, and to prevent the spread of fires. In the Bible the Hebrews are obligated to build a parapet on the roof of their houses to prevent people falling (Deuteronomy 22:8). Parapet types Parapets may be plain, embattled, perforated or panelled, which are not mutually exclusive terms. *Plain parapets are upward extensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roberto Longhi
Roberto Longhi (28 December 1890 – 3 June 1970) was an Italian academic, art historian, and curator. The main subjects of his studies were the painters Caravaggio and Piero della Francesca. Early life and career Longhi was born in December 1890 in Alba in Piedmont. His parents were from Emilia. He studied with Pietro Toesca, in Turin, and Adolfo Venturi in Rome. The latter made him book reviews editor of the journal ''L'Arte'' in 1914. Between 1913 and 1917, Longhi, primarily an essayist, published text in ''L'Arte'' and ''La Voce'' on Mattia Preti, Piero della Francesca, Orazio Borgianni and Orazio Gentileschi. Over the course of his career Longhi developed a fascination with Caravaggio and his followers. his book ''Quesiti caravaggeschi'' uestions on Caravaggio(1928–34), was followed by ''Ultimi studi caravaggeschi'' atest Caravaggio studies(1943). In 1951, Longhi curated a ground-breaking exhibition on Caravaggio at the Royal Palace in Milan, ''Mostra di Caravaggio e d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tondo (art)
A tondo (plural "tondi" or "tondos") is a Renaissance term for a circular work of art, either a painting or a sculpture. The word derives from the Italian ''rotondo,'' "round." The term is usually not used in English for small round paintings, but only those over about 60 cm (two feet) in diameter, thus excluding many round portrait miniatures – for sculpture the threshold is rather lower. A circular or oval relief sculpture is also called a roundel. History Artists have created tondi since Greek antiquity. The circular paintings in the centre of painted vases of that period are known as tondi, and the inside of the broad low winecup called a '' kylix'' also lent itself to circular enframed compositions. The style was revived in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, particularly in Italy, where it may have developed from the smaller desco da parto or birthing tray. Since then it has been less common. In Ford Madox Brown's painting '' The Last of England'', the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel H
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the biblical judges to the United Kingdom of Israel under Saul, and again in the monarchy's transition from Saul to David. He is venerated as a prophet in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In addition to his role in the Hebrew scriptures, Samuel is mentioned in Jewish rabbinical literature, in the Christian New Testament, and in the second chapter of the Quran (although Islamic texts do not mention him by name). He is also treated in the fifth through seventh books of ''Antiquities of the Jews'', written by the Jewish scholar Josephus in the first century. He is first called "the Seer" in 1 Samuel 9:9. Biblical account Family Samuel's mother was Hannah and his father was Elkanah. Elkanah lived at Ramathaim in the district of Zuph. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Lucy
Lucia of Syracuse (283–304), also called Saint Lucia ( la, Sancta Lucia) better known as Saint Lucy, was a Roman people, Roman Christian martyr who died during the Diocletianic Persecution. She is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church, Catholic, Anglicanism, Anglican, Lutheranism, Lutheran, and Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches. She is one of eight women (including Mary, mother of Jesus, the Virgin Mary) explicitly commemorated by Catholics in the Canon of the Mass. Her traditional feast day, known in Europe as Saint Lucy's Day, is observed by Western Christianity, Western Christians on 13 December. Lucia of Syracuse was honored in the Middle Ages and remained a well-known saint in early modern England. She is one of the best known virgin martyrs, along with Agatha of Sicily, Agnes of Rome, Saint Cecilia, Cecilia of Rome and Catherine of Alexandria. Sources The oldest record of her story comes from the fifth-century ''Acts of the Martyrs''. The single fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington D
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines * New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |