|
Sagnac Experiment
The Sagnac effect, also called Sagnac interference, named after French physicist Georges Sagnac, is a phenomenon encountered in interferometry that is elicited by rotation. The Sagnac effect manifests itself in a setup called a ring interferometer or Sagnac interferometer. A beam of light is split and the two beams are made to follow the same path but in opposite directions. On return to the point of entry the two light beams are allowed to exit the ring and undergo interference (wave propagation), interference. The relative phases of the two exiting beams, and thus the position of the interference fringes, are shifted according to the angular velocity of the apparatus. In other words, when the interferometer is at rest with respect to a inertial frame of reference, nonrotating frame, the light takes the same amount of time to traverse the ring in either direction. However, when the interferometer system is spun, one beam of light has a longer path to travel than the other in order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hendrik Lorentz
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz ( ; ; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch theoretical physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for their discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. He derived the Lorentz transformation of the special theory of relativity, as well as the Lorentz force, which describes the combined electric and magnetic forces acting on a charged particle in an electromagnetic field. Lorentz was also responsible for the Lorentz oscillator model, a classical model used to describe the anomalous dispersion observed in dielectric materials when the driving frequency of the electric field was near the resonant frequency of the material, resulting in abnormal refractive indices. According to the biography published by the Nobel Foundation, "It may well be said that Lorentz was regarded by all theoretical physicists as the world's leading spirit, who completed what was left unfinished by his predecessors and prepar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Von Laue
Max Theodor Felix von Laue (; 9 October 1879 – 24 April 1960) was a German physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1914 "for his discovery of the X-ray diffraction, diffraction of X-rays by crystals". In addition to his scientific endeavors with contributions in optics, crystallography, Quantum mechanics, quantum theory, superconductivity, and the theory of relativity, Laue had a number of administrative positions which advanced and guided Science and technology in Germany, German scientific research and development during four decades. A strong objector to Nazism, he was instrumental in re-establishing and organizing German science after World War II. Biography Early years Laue was born in Pfaffendorf, now part of Koblenz, Germany, to Julius Laue and Minna Zerrenner. In 1898, after passing his ''Abitur'' in Strasbourg, Strassburg, he began his compulsory year of military service, after which in 1899 he started to study mathematics, physics, and chemistry at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
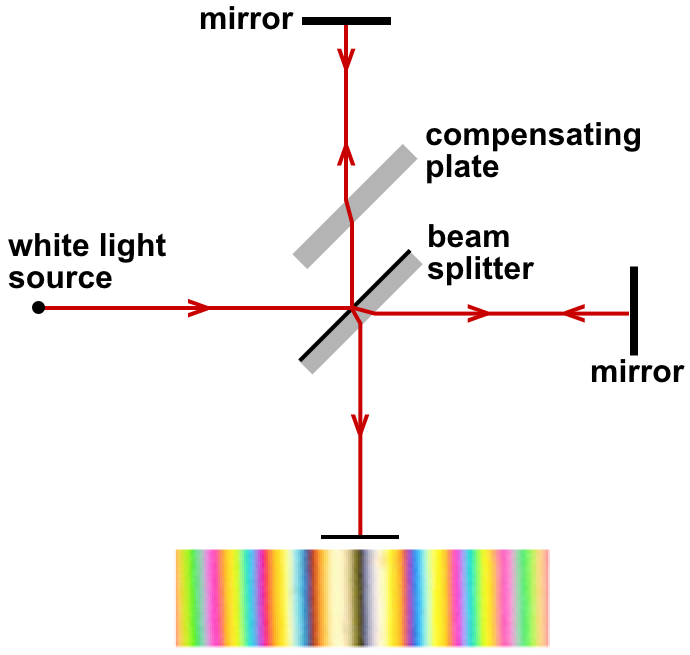
Albert Abraham Michelson
Albert Abraham Michelson ( ; December 19, 1852 – May 9, 1931) was an American physicist known for his work on measuring the speed of light and especially for the Michelson–Morley experiment. In 1907, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics, becoming the first American to win the Nobel Prize in a science. He was the founder and the first head of the physics departments of Case School of Applied Science (now Case Western Reserve University) and the University of Chicago. Life Michelson was born in Strelno, Posen, Kingdom of Prussia (modern-day Strzelno, Poland), to Jewish parents, the son of Samuel Michelson and his wife, Rozalia Przyłubska. He moved to the US with his parents in 1855, at the age of two. He grew up in the mining towns of Murphy's Camp, California, and Virginia City, Nevada, where his father was a merchant. His family was non-religious, and Michelson himself was a lifelong agnostic. He spent his high school years in San Francisco in the home of his aunt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Lodge
Sir Oliver Joseph Lodge (12 June 1851 – 22 August 1940) was an English physicist whose investigations into electromagnetic radiation contributed to the development of Radio, radio communication. He identified electromagnetic radiation independent of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, Heinrich Hertz's proof. At his 1894 Royal Institution lectures ("''The Work of Hertz and Some of His Successors''"), Lodge's demonstrations on methods to transmit and detect radio waves included an improved early radio receiver he named the "coherer". His work led to him holding key patents in early radio communication, his "syntonic" (or tuning) patents. Lodge was appointed the assistant professor of applied mathematics at Bedford College, London in 1879, became the chair of physics at the University of Liverpool, University College Liverpool in 1881, and was the principal of the University of Birmingham from 1900 to 1919. Lodge was also pioneer of Spiritualism (movement), spiritualism. His pseudoscientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aether Drag Hypothesis
In the 19th century, the theory of the luminiferous aether as the hypothetical Transmission medium, medium for the propagation of light waves was widely discussed. The aether hypothesis arose because physicists of that era could not conceive of light waves propagating without a physical medium in which to do so. When experiments failed to detect the hypothesized luminiferous aether, physicists conceived explanations for the experiments' failure which preserved the hypothetical aether's existence. The aether drag hypothesis proposed that the luminiferous aether is dragged by or entrained within moving matter. According to one version of this hypothesis, no relative motion exists between Earth and aether. According to another version, the Earth does move relative to the aether and the measured speed of light should depend on the speed of this motion ("aether wind"), which should be measurable by instruments at rest on Earth's surface. In 1818, Augustin-Jean Fresnel proposed that the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminiferous Aether
Luminiferous aether or ether (''luminiferous'' meaning 'light-bearing') was the postulated Transmission medium, medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum (space completely filled with matter) of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 19th century, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. The ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelson–Morley Experiment
The Michelson–Morley experiment was an attempt to measure the motion of the Earth relative to the luminiferous aether, a supposed medium permeating space that was thought to be the carrier of light waves. The experiment was performed between April and July 1887 by American physicists Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and published in November of the same year. The experiment compared the speed of light in perpendicular directions in an attempt to detect the relative motion of matter, including their laboratory, through the luminiferous aether, or "aether wind" as it was sometimes called. The result was negative, in that Michelson and Morley found no significant difference between the speed of light in the direction of movement through the presumed aether, and the speed at right angles. This result is generally considered to be the first strong evidence against some aether theories, as well as initiating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Reference Frame
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called an inertial space or a Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference in which objects exhibit inertia: they remain at rest or in uniform motion relative to the frame until acted upon by external forces. In such a frame, the laws of nature can be observed without the need to correct for acceleration. All frames of reference with zero acceleration are in a state of constant rectilinear motion (straight-line motion) with respect to one another. In such a frame, an object with zero net force acting on it, is perceived to move with a constant velocity, or, equivalently, Newton's first law of motion holds. Such frames are known as inertial. Some physicists, like Isaac Newton, originally thought that one of these frames was absolute — the one approximated by the fixed stars. However, this is not required for the definition, and it is now known that those stars are in fact moving, relative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Rotation
In physics, the concept of absolute rotation—rotation independent of any external reference—is a topic of debate about relativity, cosmology, and the nature of physical laws. For the concept of absolute rotation to be scientifically meaningful, it must be measurable. In other words, can an observer distinguish between the rotation of an observed object and their own rotation? Newton suggested two experiments to resolve this problem. One is the effects of centrifugal force upon the shape of the surface of water rotating in a bucket, equivalent to the phenomenon of rotational gravity used in proposals for human spaceflight. The second is the effect of centrifugal force upon the tension in a string joining two spheres rotating about their center of mass. Classical mechanics Newton's bucket argument Newton suggested the shape of the surface of the water indicates the presence or absence of absolute rotation relative to absolute space: rotating water has a curved surface, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |