|
Safety Factor
In engineering, a factor of safety (FoS) or safety factor (SF) expresses how much stronger a system is than it needs to be for its specified maximum load. Safety factors are often calculated using detailed analysis because comprehensive testing is impractical on many projects, such as bridges and buildings, but the structure's ability to carry a load must be determined to a reasonable accuracy. Many systems are intentionally built much stronger than needed for normal usage to allow for emergency situations, unexpected loads, misuse, or degradation (reliability engineering, reliability). Margin of safety (MoS or MS) is a related measure, expressed as a relative change. Definition There are two definitions for the factor of safety (FoS): * The ratio of a structure's absolute strength (structural capability) to actual applied load; this is a measure of the Reliability engineering, reliability of a particular design. This is a calculated value, and is sometimes referred to, for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability is defined as the probability that a product, system, or service will perform its intended function adequately for a specified period of time, OR will operate in a defined environment without failure. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The ''reliability function'' is theoretically defined as the probability of success. In practice, it is calculated using different techniques, and its value ranges between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates no probability of success while 1 indicates definite success. This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets, or through reliability testing and reliability modeling. Availability, testability, maintainability, and maintenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. One person might consider a failure what another person considers a success, particularly in cases of direct competition or a zero-sum game. Similarly, the degree of success or failure in a situation may be differently viewed by distinct observers or participants, such that a situation that one considers to be a failure, another might consider to be a success, a qualified success or a neutral situation. It may also be difficult or impossible to ascertain whether a situation meets criteria for failure or success due to ambiguous or ill-defined definition of those criteria. Finding useful and effective criteria or heuristics to judge the success or failure of a situation may itself be a significant task. Sociology Cultural historian Scot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size of the vessel, the contents, working pressure, mass constraints, and the number of items required. Pressure vessels can be dangerous, and fatal accidents have occurred in the history of their development and operation. Consequently, pressure vessel design, manufacture, and operation are regulated by engineering authorities backed by legislation. For these reasons, the definition of a pressure vessel varies from country to country. The design involves parameters such as maximum safe operating pressure and temperature, safety factor, corrosion allowance and minimum design temperature (for brittle fracture). Construction is tested using nondestructive testing, such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and pressure tests. Hydrostatic pressure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redundancy (engineering)
In engineering and systems theory, redundancy is the intentional duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the goal of increasing reliability of the system, usually in the form of a backup or fail-safe, or to improve actual system performance, such as in the case of GNSS receivers, or multi-threaded computer processing. In many safety-critical systems, such as fly-by-wire and hydraulic systems in aircraft, some parts of the control system may be triplicated, which is formally termed triple modular redundancy (TMR). An error in one component may then be out-voted by the other two. In a triply redundant system, the system has three sub components, all three of which must fail before the system fails. Since each one rarely fails, and the sub components are designed to preclude common failure modes (which can then be modelled as independent failure), the probability of all three failing is calculated to be extraordinarily small; it is often outweighed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Mode And Effects Analysis
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended Goal, objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. One person might consider a failure what another person considers a success, particularly in cases of direct competition or a zero-sum game. Similarly, the degree of success or failure in a situation may be differently viewed by distinct observers or participants, such that a situation that one considers to be a failure, another might consider to be a success, a qualified success or a neutral situation. It may also be difficult or impossible to ascertain whether a situation meets criteria for failure or success due to ambiguous or ill-defined definition of those criteria. Finding useful and effective criteria or heuristics to judge the success or failure of a situation may itself be a significant task. Sociology Cultural historian Sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Analysis (engineering)
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. One international standard definition of risk is the "effect of uncertainty on objectives". The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas (business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security, privacy, etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and general guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Definitions of risk Oxford English Dictionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment (systems)
An open system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which defines the concept. An open system is contrasted with the concept of an isolated system which exchanges neither energy, matter, nor information with its environment. An open system is also known as a flow system. The concept of an open system was formalized within a framework that enabled one to interrelate the theory of the organism, thermodynamics, and evolutionary theory. This concept was expanded upon with the advent of information theory and subsequently systems theory. Today the concept has its applications in the natural and social sciences. In the natural sciences an open system is one whose border is permeable to both energy and mass. By contrast, a closed system is permeable to energy but not to matter. The definition of an open system assumes that ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wear
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology. Wear in machine elements, together with other processes such as fatigue and creep, causes functional surfaces to degrade, eventually leading to material failure or loss of functionality. Thus, wear has large economic relevance as first outlined in the Jost Report. Abrasive wear alone has been estimated to cost 1–4% of the gross national product of industrialized nations. Wear of metals occurs by plastic displacement of surface and near-surface material and by detachment of particles that form wear debris. The particle size may vary from millimeters to nanometers. This process may occur by contact with other metals, nonmetallic solids, flowing liquids, solid particles or liquid droplets entrained in flowing gasses. The wear rate is affected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Load
A structural load or structural action is a mechanical load (more generally a force) applied to Structural engineering#Structural elements, structural elements. A load causes stress (physics), stress, deformation (engineering), deformation, displacement (vector), displacement or acceleration in a structure. Structural analysis, a discipline in engineering, analyzes the effects of loads on structures and structural elements. Excess load may cause structural failure, so this should be considered and controlled during the design of a structure. Particular mechanical structures—such as aircraft, satellites, rockets, space stations, ships, and submarines—are subject to their own particular structural loads and actions. Engineers often evaluate structural loads based upon published regulations, contracts, or specifications. Accepted technical standards are used for acceptance testing and inspection. Types In civil engineering, specified loads are the best estimate of the actual l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accuracy
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''. ''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their ''true value''. ''Precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines a related measure: ''trueness'', "the closeness of agreement between the arithmetic mean of a large number of test results and the true or accepted reference value." While ''precision'' is a description of '' random errors'' (a measure of statistical variability), ''accuracy'' has two different definitions: # More commonly, a description of ''systematic errors'' (a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency, such as the mean). In this definition of "accuracy", the concept is independent of "precision", so a particular set of data can be said to be accurate, precise, both, or neither. This concept corresponds to ISO's ''trueness''. # A combination of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Breaking is often accompanied by a sharp snapping sound. When used in materials science, it is generally applied to materials that fail when there is little or no plastic deformation before failure. One proof is to match the broken halves, which should fit exactly since no plastic deformation has occurred. Brittleness in different materials Polymers Mechanical characteristics of polymers can be sensitive to temperature changes near room temperatures. For example, poly(methyl methacrylate) is extremely brittle at temperature 4˚C, but experiences increased ductility with increased temperature. Amorphous polymers are polymers that can behave differently at different temperatures. They may behave like a glass at low temperatures (the gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
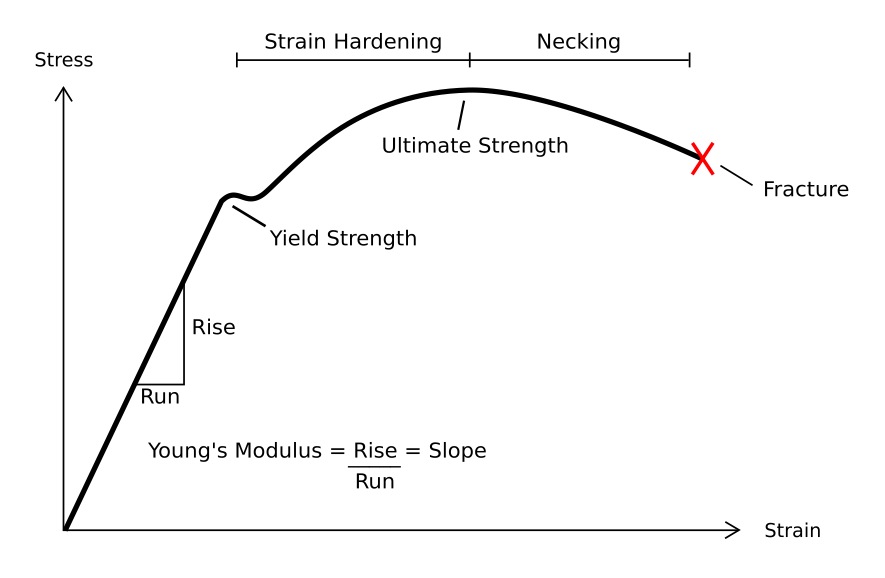
Plastic Deformation
In engineering, deformation (the change in size or shape of an object) may be ''elastic'' or ''plastic''. If the deformation is negligible, the object is said to be ''rigid''. Main concepts Occurrence of deformation in engineering applications is based on the following background concepts: * ''Displacements'' are any change in position of a point on the object, including whole-body translations and rotations ( rigid transformations). * ''Deformation'' are changes in the relative position between internals points on the object, excluding rigid transformations, causing the body to change shape or size. * ''Strain'' is the ''relative'' ''internal'' deformation, the dimensionless change in shape of an infinitesimal cube of material relative to a reference configuration. Mechanical strains are caused by mechanical stress, ''see stress-strain curve''. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |