|
SWER
Single-wire earth return (SWER) or single-wire ground return is a single-wire transmission line which supplies single-phase electric power from an electrical grid to remote areas at lowest cost. The earth (or sometimes a body of water) is used as the return path for the current, to avoid the need for a second wire (or ''neutral wire'') to act as a return path. Single-wire earth return is principally used for rural electrification, but also finds use for larger isolated loads such as water pumps. It is also used for high-voltage direct current over submarine power cables. Electric single-phase railway traction, such as light rail, uses a very similar system. It uses resistors to earth to reduce hazards from rail voltages, but the primary return currents are through the rails. History Lloyd Mandeno, OBE (1888–1973) fully developed SWER in New Zealand around 1925 for rural electrification. Although he termed it "Earth Working Single Wire Line", it was often called "Mandeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloyd Mandeno
Lloyd Mandeno (3 October 1888 – 30 December 1973) was a New Zealand electrical engineer, inventor and local politician. He was born in Rangiaowhia, Waikato, New Zealand, on 3 October 1888. He is credited with nine hydroelectric installations and numerous inventions. He served on electric power boards, regional councils and as a deputy mayor. Mandeno was born at Rangiaowhia, near Te Awamutu in the Waikato region to a farming family. He studied at St John's Collegiate School in Auckland and started at Auckland University College in 1905. The following year he transferred to University of Canterbury, Canterbury College from where he graduated in 1912 with a Bachelor of Engineering degree. He married Constance Mary Woodward at Mangere in 1913. Mandeno invented, developed and successfully promoted widespread use of "single wire earth-return" (SWER) grids for rural electrification in New Zealand.Mandeno, L. (1947)"Rural Power Supply Especially in Back Country Areas". ''Proceeding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Electrical circuits may be connected to ground for several reasons. Exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment are connected to ground to protect users from electrical shock hazards. If internal insulation fails, dangerous voltages may appear on the exposed conductive parts. Connecting exposed conductive parts to a "ground" wire which provides a low-impedance path for current to flow back to the incoming neutral (which is also connected to ground, close to the point of entry) will allow circuit breakers (or RCDs) to interrupt power supply in the event of a fault. In electric power distribution systems, a protective earth (PE) conductor is an essential part of the safety provided by the earthing system. Connection to ground also limits the build-up of static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahora Bassa (HVDC) - KNP - 001
The Cahora Bassa lake—in the Portuguese colonial era (until 1974) known as Cabora Bassa, from Nyungwe language, Nyungwe ''Kahoura-Bassa'', meaning "finish the job"—is Africa's fourth-largest artificial lake, situated in the Tete Province in Mozambique. In Africa, only Lake Volta in Ghana, Lake Kariba on the Zambezi upstream of Cahora Bassa, and Egypt's Lake Nasser are bigger in terms of surface water. History Portuguese period The Cahora Bassa System started in the late 1960s as a project of the Portugal, Portuguese in the Overseas Province of Mozambique. Southern African governments were also involved in an agreement stating that Portugal would build and operate a Cahora_Bassa_Dam, hydroelectric generating station at Cabora Bassa (as it was then called in Portuguese language, Portuguese) together with Cahora Bassa (HVDC), the high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system required to bring electricity to the border of South Africa. South Africa, on the other hand, und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Midwest
The Upper Midwest is a northern subregion of the U.S. Census Bureau's Midwestern United States. Although the exact boundaries are not uniformly agreed upon, the region is usually defined to include the states of Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota and Wisconsin; some definitions include North Dakota, South Dakota, and parts of Nebraska and Illinois. Definitions The National Centers for Environmental Information considers the Upper Midwest climate region to include Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin. The United States Geological Survey uses two different Upper Midwest regions: *The USGS Upper Midwest Environmental Sciences Center considers it to be the six states of Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota and Wisconsin, which comprise the watersheds of the Upper Mississippi River and upper Great Lakes. *The USGS Mineral Resources Program considers the area to contain Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota and Wisconsin. The Association for Institutional Research in the Uppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
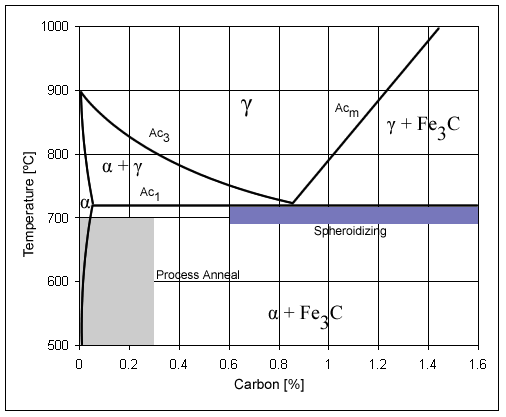
High-carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states: * no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, or any other element to be added to obtain a desired alloying effect; * the specified minimum for copper does not exceed 0.40%; * or the specified maximum for any of the following elements does not exceed: manganese 1.65%; silicon 0.60%; and copper 0.60%. As the carbon content percentage rises, steel has the ability to become harder and stronger through heat treating; however, it becomes less ductile. Regardless of the heat treatment, a higher carbon content reduces weldability. In carbon steels, the higher carbon content lowers the melting point. The term may be used to reference steel that is not stainless steel; in this use carbon steel may include all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number 8 Wire
Number 8 wire is a gauge of wire on the British Standard Wire Gauge that has entered into the cultural lexicon of New Zealand. Use for farm fencing Early farm fences in New Zealand were generally used to protect crops, gardens, and orchards from farm animals, rather than to contain the stock. Fencing methods used were post-and-rail fences, ditch-and-bank fences, stone walls, and hedges, but all proved too expensive to install and maintain to fence entire properties and tended to be unreliable. To prevent stock straying, boundary keepers were employed to patrol boundaries. In the 1850s, heavy annealed iron wire became available for fences, but this wire was very thick and only came in short lengths, was hard to work and to keep taut, and was expensive to use. In England, in 1855, Henry Bessemer patented the Bessemer process that led to the mass production of low-cost high-quality steel, leading to the large scale production of affordable lighter gauge steel wire. The introducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split-phase Electric Power
A split-phase or single-phase three-wire system is a type of single-phase electric power distribution. It is the alternating current (AC) equivalent of the original Edison Machine Works three-wire direct-current system. Its primary advantage is that, for a given capacity of a distribution system, it saves conductor material over a single-ended single-phase system. The system is common in North America for residential and light commercial applications. Two AC lines are supplied to the premises that are out of phase by 180 degrees with each other (when both measured with respect to the neutral), along with a common neutral. The neutral conductor is connected to ground at the transformer center tap. Circuits for lighting and small appliance power outlets use circuits connected between one line and neutral. High-demand applications, such as ovens, are often powered using AC circuits—these are connected between the two AC lines. These loads are either hard-wired or use out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below a meter (3 ft), the deepest is greater than . Similarly, the area of individual permafrost zones may be limited to narrow mountain summits or extend across vast Arctic regions. The ground beneath glaciers and ice sheets is not usually defined as permafrost, so on land, permafrost is generally located beneath a so-called active layer of soil which freezes and thaws depending on the season. Around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface is underlain by permafrost, covering a total area of around . This includes large areas of Alaska, Canada, Greenland, and Siberia. It is also located in high mountain regions, with the Tibetan Plateau being a prominent example. Only a minority of permafrost exists in the Southern Hemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phantom Loop
In telecommunications and electrical engineering, a phantom circuit is an electrical circuit derived from suitably arranged wires with one or more conductive paths being a circuit in itself and at the same time acting as one conductor of another circuit. Phantom group A phantom group is composed of three circuits that are derived from two single-channel circuits to form a ''phantom circuit''. Here the phantom circuit is a third circuit derived from two suitably arranged pairs of wires, called side circuits, with each pair of wires being a circuit in itself and at the same time acting as one conductor of the third circuit. The "side circuits" within phantom circuits can be coupled to their respective voltage drops by center-tapped transformers, usually called " repeating coils". The center taps are on the line side of the side circuits. Current from the phantom circuit is split evenly by the center taps. This cancels crosstalk from the phantom circuit to the side circuits. Pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Thus all circuits are networks, but not all networks are circuits (although networks without a closed loop are often referred to as "open circuits"). A resistive network is a network containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive networks is less complicated than analysis of networks containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant ( DC) sources, the result is a DC network. The effective resistance and current distribution properties of arbitrary resistor networks can be modeled in terms of their graph measures and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductor (material)
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow of negatively charged electrons generates electric current, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in some cases. In order for current to flow within a closed electrical circuit, one charged particle does not need to travel from the component producing the current (the current source) to those consuming it (the loads). Instead, the charged particle simply needs to nudge its neighbor a finite amount, who will nudge ''its'' neighbor, and on and on until a particle is nudged into the consumer, thus powering it. Essentially what is occurring is a long chain of momentum transfer between mobile charge carriers; the Drude model of conduction describes this process more rigorously. This momentum transfer model makes metal an ideal choice fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |