|
STRETCH Assembly Program
STRETCH Assembly Program (STRAP) was the assembler for the IBM 7030 Stretch computer. The first version (STRAP-1) was a subset cross assembler that ran on the IBM 704, IBM 709, and IBM 7090 The IBM 7090 is a second-generation transistorized version of the earlier IBM 709 vacuum tube mainframe computer that was designed for "large-scale scientific and technological applications". The 7090 is the fourth member of the IBM 700/7000 se ... computers. The final version (STRAP-2) ran natively. External links IBM Reference Manual 704-709-7090 Programming Package for the IBM 7030 Data Processing System(PDF) STRAP I - assembler for IBM 7030/709 Assemblers IBM software IBM 700/7000 series {{super-compu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Language
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book '' The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
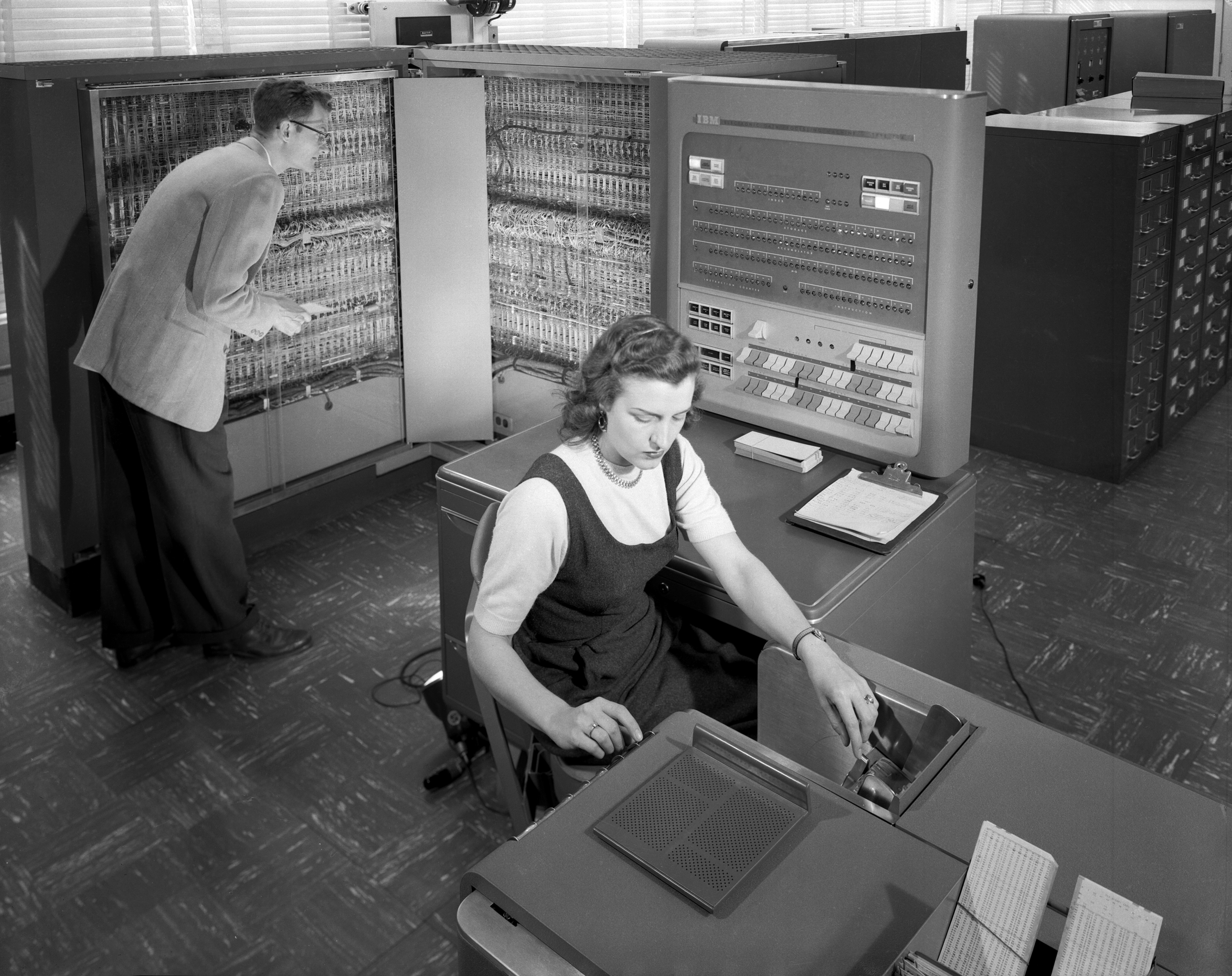
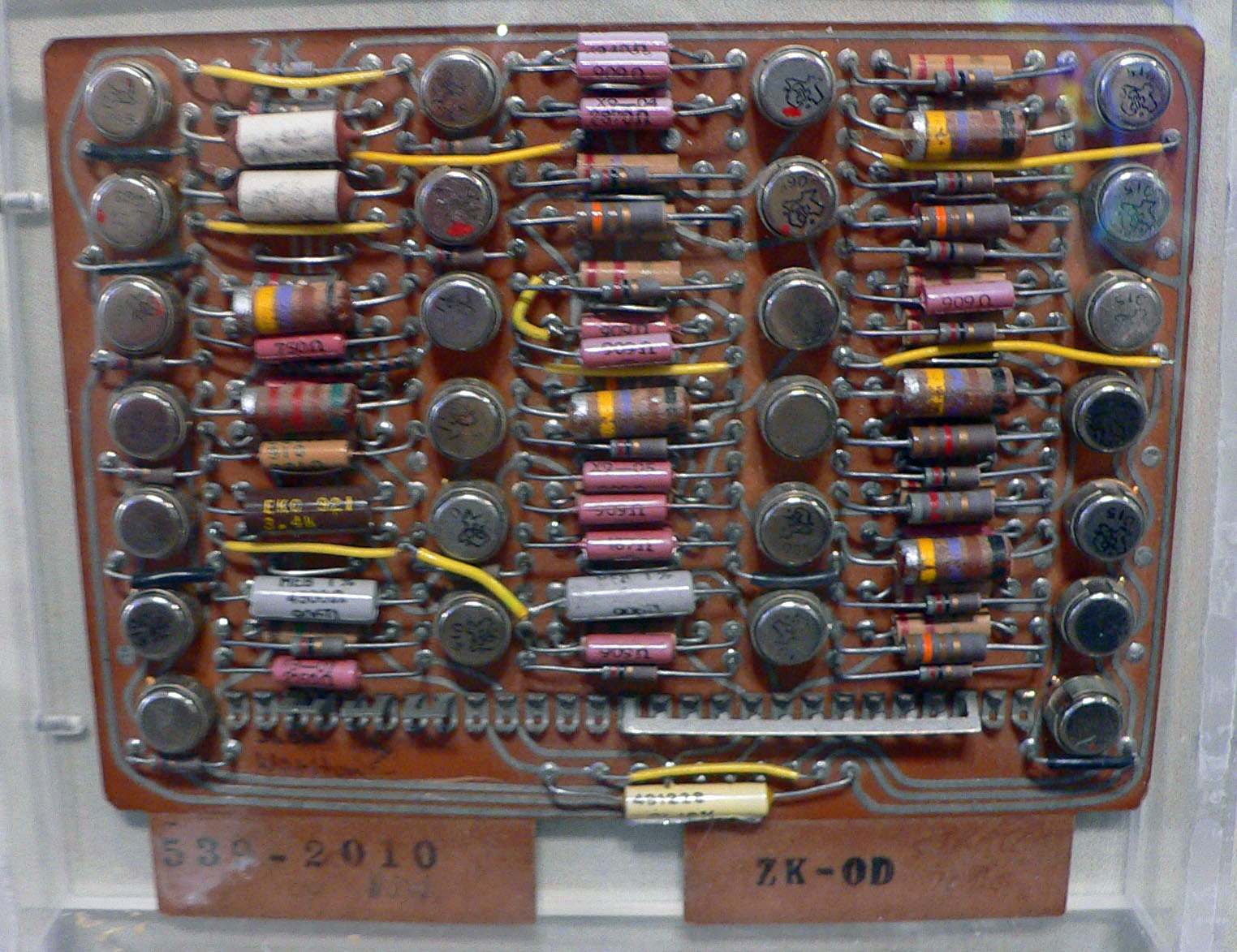
IBM 7030 Stretch
The IBM 7030, also known as Stretch, was IBM's first transistorized supercomputer. It was the fastest computer in the world from 1961 until the first CDC 6600 became operational in 1964."Designed by Seymour Cray, the CDC 6600 was almost three times faster than the next fastest machine of its day, the IBM 7030 Stretch." Originally designed to meet a requirement formulated by Edward Teller at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, the first example was delivered to Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1961, and a second customized version, the IBM 7950 Harvest, to the National Security Agency in 1962. The Stretch at the Atomic Weapons Research Establishment at Aldermaston, England was heavily used by researchers there and at AERE Harwell, but only after the development of the S2 Fortran Compiler which was the first to add dynamic arrays, and which was later ported to the Ferranti Atlas of Atlas Computer Laboratory at Chilton. The 7030 was much slower than expected and failed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Assembler
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an ''assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book ''The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digital Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 704
The IBM 704 is a large digital mainframe computer introduced by IBM in 1954. It was the first mass-produced computer with hardware for floating-point arithmetic. The IBM 704 ''Manual of operation'' states: The type 704 Electronic Data-Processing Machine is a large-scale, high-speed electronic calculator controlled by an internally stored program of the single address type. The 704 at that time was thus regarded as "pretty much the only computer that could handle complex math". The 704 was a significant improvement over the earlier IBM 701 in terms of architecture and implementation. Like the 701, the 704 uses vacuum-tube logic circuitry, but increased the instruction size from 18-bit to 36-bit, the same as the memory's word size. Changes from the 701 include the use of magnetic-core memory instead of Williams tubes, floating-point arithmetic instructions, 15-bit addressing and the addition of three index registers. To support these new features, the instructions w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 709
The IBM 709 was a computer system, initially announced by IBM in January 1957 and first installed during August 1958. The 709 was an improved version of its predecessor, the IBM 704, and was the third of the IBM 700/7000 series of scientific computers. The improvements included overlapped input/output, indirect addressing, and three "convert" instructions which provided support for decimal arithmetic, leading zero suppression, and several other operations. The 709 had 32,768 words of 36-bit magnetic core memory and could execute 42,000 add or subtract instructions per second. It could multiply two 36-bit integers at a rate of 5000 per second. An optional hardware emulator executed old IBM 704 programs on the IBM 709. This was the first commercially available emulator. Registers and most 704 instructions were emulated in 709 hardware. Complex 704 instructions such as floating point trap and input-output routines were emulated in 709 software. The FORTRAN Assembly Program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 7090
The IBM 7090 is a second-generation transistorized version of the earlier IBM 709 vacuum tube mainframe computer that was designed for "large-scale scientific and technological applications". The 7090 is the fourth member of the IBM 700/7000 series scientific computers. The first 7090 installation was in December 1959. In 1960, a typical system sold for $2.9 million (equivalent to $ million in ) or could be rented for $63,500 a month (). The 7090 uses a 36-bit word length, with an address space of 32,768 words (15-bit addresses). It operates with a basic memory cycle of 2.18 μs, using the IBM 7302 Core Storage core memory technology from the IBM 7030 (Stretch) project. With a processing speed of around 100 Kflop/s, the 7090 is six times faster than the 709, and could be rented for half the price. An upgraded version, the 7094 was up to twice as fast. Both the 7090 and the 7094 were withdrawn from sale on July 14, 1969, but systems remained in service for more than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assemblers
Assembler may refer to: Arts and media * Nobukazu Takemura, avant-garde electronic musician, stage name Assembler * Assemblers, a fictional race in the ''Star Wars'' universe * Assemblers, an alternative name of the superhero group Champions of Angor Biology * Assembler (bioinformatics), a program to perform genome assembly *Assembler (nanotechnology), a conjectured construction machine that would manipulate and build with individual atoms or molecules Computing * Assembler (computing), a computer program which translates assembly language to machine language ** Assembly language, a more readable interpretation of a processor's machine code, allowing easier understanding and programming by humans, sometimes erroneously referenced as 'assembler' after the program which translates it Other uses * a worker on an assembly line See also * Assemble (other) * Assembly (other) * Constructor (other) Constructor may refer to: Science and technology * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |