|
STAC3
SH3 and cysteine-rich domain-containing protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STAC3 gene. STAC3 has been shown to be associated with the a special form of myopathy known as Native American myopathy (NAM), a neuromuscular disorder characterized by weakness, arthrogryposis, kyphoscoliosis, short stature, cleft palate, ptosis and susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia during anesthesia. It was first identified through a genetic screen in zebrafish and was shown to be a component of the excitation contraction coupling Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as ... machinery, followed by it being mapped to the region of the human genome which had been shown to be associated with the defects observed in NAM. References {{Reflist Human proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrogryposis
Arthrogryposis (AMC) describes congenital joint contracture in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning "curving of joints" (', "joint"; ', late Latin form of late Greek ', "hooking"). Children born with one or more joint contractures have abnormal fibrosis of the muscle tissue causing muscle shortening, and therefore are unable to perform active extension and flexion in the affected joint or joints. AMC has been divided into three groups: amyoplasia, distal arthrogryposis, and syndromic. Amyoplasia is characterized by severe joint contractures and muscle weakness. Distal arthrogryposis mainly involves the hands and feet. Types of arthrogryposis with a primary neurological or muscle disease belong to the syndromic group. Signs and symptoms Often, every joint in a patient with arthrogryposis is affected; in 84% all limbs are involved, in 11% only the legs, and in 4% only the arms are involved. Every joint in the body, when affected, displ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both a coronal and sagittal plane. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. This musculoskeletal disorder often leads to other issues in patients, such as under-ventilation of lungs, pulmonary hypertension, difficulty in performing day-to-day activities, psychological issues emanating from anxiety about acceptance among peers, especially in young patients. It can also be seen in syringomyelia, Friedreich's ataxia, spina bifida, kyphoscoliotic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (kEDS), and Duchenne muscular dystrophy due to asymmetric weakening of the paraspinal muscles. Signs and symptoms The following are clear signs of Kyphoscoliosis: * Abnormal hunch along with a presence of S or C-like shape. * * Presence of associated disorders like hypertension, neurological disorders * Abnormal gait Kyphosis Kyphosis by itself refers to an excessive convex curvature of the spine occurring in the thoracic and sacral regions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyelid can cause other conditions, such as amblyopia or astigmatism. This is why it is especially important for this disorder to be treated in children at a young age, before it can interfere with vision development. The term is from Greek 'fall, falling'. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms typically seen in this condition include: * The eyelid(s) may appear to droop. * Droopy eyelids can give the face a false appearance of being fatigued, disinterested, or even sinister. * The eyelid may not protect the eye as effectively, allowing it to dry out. * Sagging upper eyelids can partially block the person's field of view. * Obstructed vision may ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Screen
A genetic screen or mutagenesis screen is an experimental technique used to identify and select individuals who possess a phenotype of interest in a mutagenized population. Hence a genetic screen is a type of phenotypic screen. Genetic screens can provide important information on gene function as well as the molecular events that underlie a biological process or pathway. While genome projects have identified an extensive inventory of genes in many different organisms, genetic screens can provide valuable insight as to how those genes function. Basic screening Forward genetics (or a forward genetic screen) starts with a phenotype and then attempts to identify the causative mutation and thus gene(s) responsible for the phenotype. For instance, the famous screen by Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and Eric Wieschaus mutagenized fruit flies and then set out to find the genes causing the observed mutant phenotypes. Successful forward genetic screens often require a defined geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
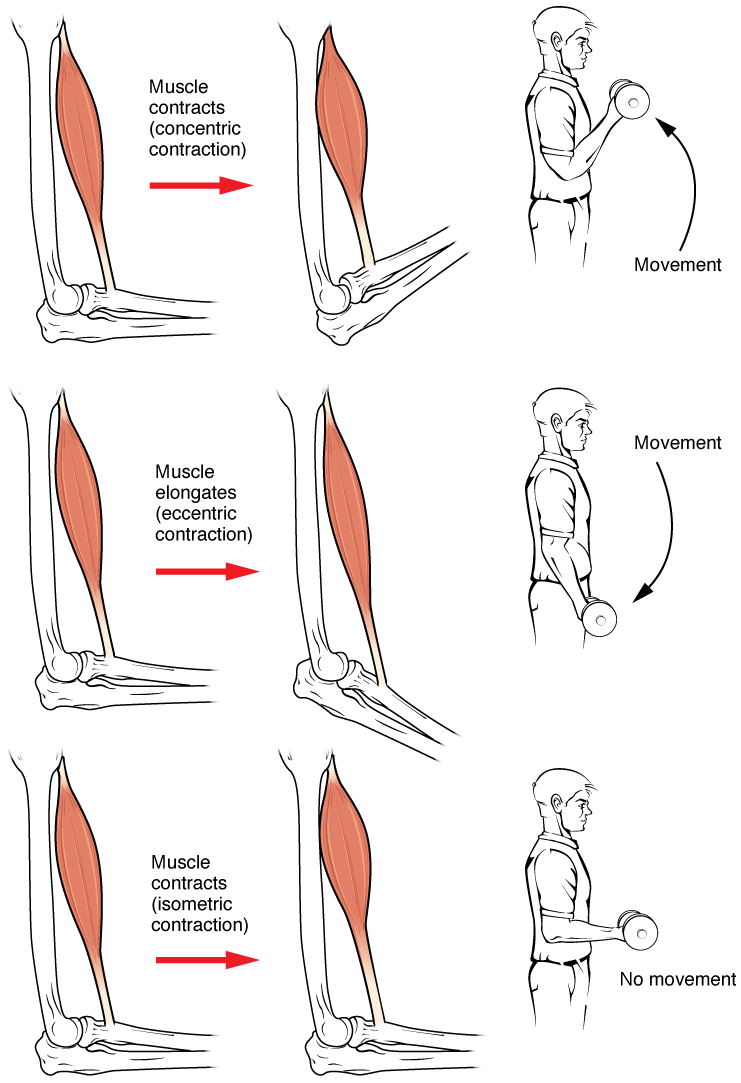
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |