|
ST-148 (D2L Antagonist)
ST-148 is a drug which acts as a subtype selective antagonist for dopamine receptors, with reasonable selectivity for the D2L subtype. See also * Aripiprazole * WAY-100635 WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the ... References {{Dopaminergics Dopamine antagonists Dimethylamino compounds Naphthylamines Sulfonamides 2-Methoxyphenyl compounds Piperazines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Receptor
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein (dopamine receptor-interacting proteins) interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors. Dopamine receptors are implicated in many neurological processes, including motivational and incentive salience, cognition, memory, learning, and fine motor control, as well as modulation of neuroendocrine signaling. Abnormal dopamine receptor signaling and dopaminergic nerve function is implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders. Thus, dopamine receptors are common neurologic drug targets; antipsychotics are often dopamine receptor antagonists while psychostimulants are typically indirect agonists of dopamine receptors. Subtypes The existence of multiple types of receptors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D2L Receptor
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''DRD2'' gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon H. Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined. Function D2 receptors are coupled to Gi subtype of G protein. This G protein-coupled receptor inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity. In mice, regulation of D2R surface expression by the neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) in the dentate gyrus is involved in exploration, synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Studies have shown potential roles for D2R in retrieval of fear memories in the prelimbic cortex and in discr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aripiprazole
Aripiprazole, sold under the brand name Abilify, among others, is an atypical antipsychotic primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and irritability associated with autism spectrum disorder; other uses include as an add-on treatment for major depressive disorder and tic disorders. Aripiprazole is taken by mouth or via injection into a muscle. A Cochrane review found low-quality evidence of its effectiveness at treating schizophrenia. Common side effects include restlessness, insomnia, transient weight gain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dizziness, and mild sedation. Serious side effects may include neuroleptic malignant syndrome, tardive dyskinesia, and anaphylaxis. It is not recommended for older people with dementia-related psychosis due to an increased risk of death. In pregnancy, there is evidence of possible harm to the fetus. It is not recommended in women who are breastfeeding. It has not been very well studied in people younger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAY-100635
WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135. In light of its dopaminergic activity, conclusions drawn from studies that employ WAY-100635 as a selective 5-HT1A antagonist may need to be re-evaluated. Human PET studies In human PET studies WAY-100635 shows high binding in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, raphe nucleus and amygdaloid nucleus, while lower in thalamus and basal ganglia. One study described a single case with relatively high binding in the cerebellum. In relating its binding to subject variables one Swedish study found WAY-100635 binding in raphe brain region correlating with self-transcendence and spiritual acceptance personality traits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Antagonists
A dopamine antagonist, also known as an anti-dopaminergic and a dopamine receptor antagonist (DRA), is a type of Pharmaceutical drug, drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism. Most antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists, and have been used in treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and stimulant psychosis. Several other dopamine antagonists are antiemetics used in the treatment of nausea and vomiting. Receptor pharmacology Dopamine receptors are all G protein–coupled receptors, and are divided into two classes based on which G-protein they are coupled to. The D1-like class of dopamine receptors is coupled to Gαs/olf and stimulates Adenylyl cyclase, adenylate cyclase production, whereas the D2-like class is coupled to Gαi/o and thus inhibits adenylate cyclase production. D1-like receptors: D1 and D5 D1-like receptor, D1-like receptors – D1 and D5 are always found post-synaptically. The genes coding these receptors lack introns, so there are no splice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylamino Compounds
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005. Structure and synthesis The molecule consists of a nitrogen atom with two methyl substituents and one hydrogen. Dimethylamine is a base (chemistry), weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3--CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79). Dimethylamine reacts with acids to form salts, such as dimethylamine hydrochloride, an odorless white solid with a melting point of 171.5 °C. Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthylamines
Naphthylamine or aminonaphthalene can refer to either of two isomeric chemical compounds: * 1-Naphthylamine (1-aminonaphthalene) * 2-Naphthylamine (2-aminonaphthalene) {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
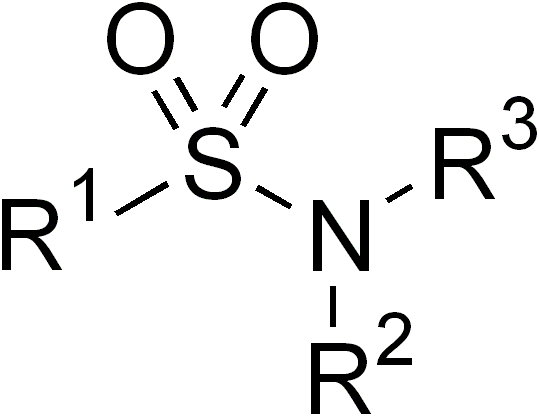
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the Chemical structure, structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for Sulfonamide (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |