|
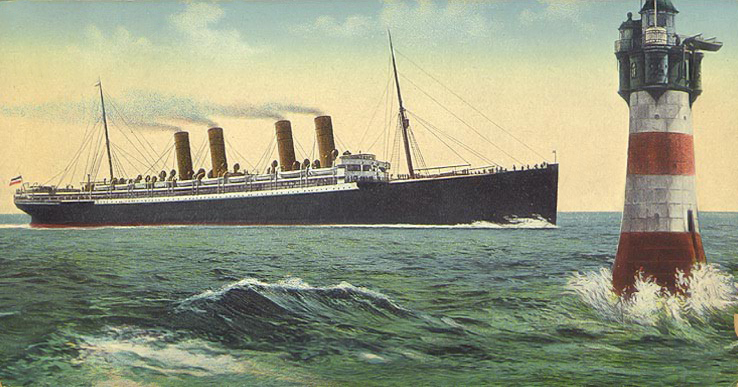
SS Kaiser Wilhelm II
The second SS ''Kaiser Wilhelm II'', named for the German Emperor, was a 19,361- gross register ton passenger ship built at Stettin, Germany (now Szczecin, Poland). The ship was completed in the spring of 1903. At the time of her launch she was larger by 1,900 tons than any other German ship and was surpassed in the weight of her hull and machinery only by the British liners ''RMS Cedric'' and ''RMS Celtic''. The ship was seized by the U.S. Government during World War I, and subsequently served as a transport ship under the name USS ''Agamemnon''. A famous photograph taken by Alfred Stieglitz called ''The Steerage'', as well as descriptions of the conditions of travel in the lowest class, have conflicted with her otherwise glitzy reputation as a high class, high speed trans-Atlantic liner. Design The ''Kaiser Wilhelm II'' was built with a full double-bottom along the hull. She was divided into 26 watertight compartments via 16 transverse bulkheads and one longitudinal bulkhead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Stieglitz
Alfred Stieglitz (January 1, 1864 – July 13, 1946) was an American photographer and modern art promoter who was instrumental over his 50-year career in making photography an accepted art form. In addition to his photography, Stieglitz was known for the New York art galleries that he ran in the early part of the 20th century, where he introduced many avant-garde European artists to the U.S. He was married to painter Georgia O'Keeffe. Early life and education Stieglitz was born in Hoboken, New Jersey, the first son of German Jewish immigrants Edward Stieglitz (1833–1909) and Hedwig Ann Werner (1845–1922). His father was a lieutenant in the Union Army and worked as a wool merchant. He had five siblings, Flora (1865–1890), twins Julius (1867–1937) and Leopold (1867–1956), Agnes (1869–1952) and Selma (1871–1957). Alfred Stieglitz, seeing the close relationship of the twins, wished he had a soul mate of his own during his childhood. Stieglitz attended Charli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Riband
The Blue Riband () is an unofficial accolade given to the passenger liner crossing the Atlantic Ocean in regular service with the record highest average speed. The term was borrowed from horse racing and was not widely used until after 1910. The record is based on average speed rather than passage time because ships follow different routes. Also, eastbound and westbound speed records are reckoned separately, as the more difficult westbound record voyage, against the Gulf Stream and the prevailing weather systems, typically results in lower average speeds.Kludas states that only westbound records counted for the Blue Riband, though this contradicts the other main sources on the subject (e.g. Lee, Gibbs, Bonsor, and contemporary news sources) which are clear that records in both directions qualified for the accolade. Of the 35 Atlantic liners to hold the Blue Riband, 25 were British, followed by five German, three American, as well as one each from Italy and France. Thirteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Wiegand
Johann Heinrich Christoph Wiegand (17 August 1855 in Bremen – 29 March 1909 in Bad Homburg vor der Höhe) was a lawyer who served as general director of the Norddeutscher Lloyd shipping company during a period of great expansion. Life and career Wiegand was born in Bremen, where his father, originally from the Upper Weser region, owned a profitable nursery and landscaping business. A teacher persuaded him to allow his son to study at the '' gymnasium'' and then go to university.Georg Bessell, ''Norddeutscher Lloyd, 1857–1957: Geschichte einer bremischen Reederei'', Bremen: Schünemann, 957 , p. 66 . He studied law at the universities of Erlangen, Bonn, Berlin and Strassburg, passed the bar at Lübeck and earned a Doctor of Law degree by examination at Göttingen in 1879, and went into practice as a lawyer in Bremen that same year.Paul August Ferdinand Neubaur, ''Der Norddeutsche Lloyd: 50 Jahre der Entwickelung, 1857–1907'' volume 2 Leipzig: Grunow, 1907, p. 606. He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transatlantic Crossing
Transatlantic crossings are passages of passengers and cargo across the Atlantic Ocean between Europe or Africa and the Americas. The majority of passenger traffic is across the North Atlantic between Western Europe and North America. Centuries after the dwindling of sporadic Viking trade with Markland, a regular and lasting transatlantic trade route was established in 1566 with the Spanish West Indies fleets, following the voyages of Christopher Columbus. By sea Prior to the 19th century, transatlantic crossings were undertaken in sailing ships, and the journeys were time-consuming and often perilous. The first trade route across the Atlantic was inaugurated by Spain a few decades after the European Discovery of the Americas, with the establishment of the West Indies fleets in 1566, a convoy system that regularly linked its territories in the Americas with Spain for over two centuries. Portugal created a similar maritime route between its ports in Brazil and the Portu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Stieglitz (American - The Steerage - Google Art Project
Alfred Stieglitz (January 1, 1864 – July 13, 1946) was an American photographer and modern art promoter who was instrumental over his 50-year career in making photography an accepted art form. In addition to his photography, Stieglitz was known for the New York art galleries that he ran in the early part of the 20th century, where he introduced many avant-garde European artists to the U.S. He was married to painter Georgia O'Keeffe. Early life and education Stieglitz was born in Hoboken, New Jersey, the first son of German Jewish immigrants Edward Stieglitz (1833–1909) and Hedwig Ann Werner (1845–1922). His father was a lieutenant in the Union Army and worked as a wool merchant. He had five siblings, Flora (1865–1890), twins Julius (1867–1937) and Leopold (1867–1956), Agnes (1869–1952) and Selma (1871–1957). Alfred Stieglitz, seeing the close relationship of the twins, wished he had a soul mate of his own during his childhood. Stieglitz attended Charlier I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Class Drawing Room (Gesellschaftszimmer) Of The Kaiser Wilhelm II
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1). First or 1st may also refer to: *World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement Arts and media Music * 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and record producer Albums * ''1st'' (album), a 1983 album by Streets * ''1st'' (Rasmus EP), a 1995 EP by The Rasmus, frequently identified as a single * ''1ST'', a 2021 album by SixTones * ''First'' (Baroness EP), an EP by Baroness * ''First'' (Ferlyn G EP), an EP by Ferlyn G * ''First'' (David Gates album), an album by David Gates * ''First'' (O'Bryan album), an album by O'Bryan * ''First'' (Raymond Lam album), an album by Raymond Lam * ''First'', an album by Denise Ho Songs * "First" (Cold War Kids song), a song by Cold War Kids * "First" (Lindsay Lohan song), a song by Lindsay Lohan * "First", a song by Everglow from ''Last Melody'' * "First", a song by Lauren Daigle * "First", a song by Niki & Gabi * "First", a song by Jonas Brothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Kronprinz Wilhelm
SS ''Kronprinz Wilhelm'' was a German ocean liner built for Norddeutscher Lloyd, a shipping company now part of Hapag-Lloyd, by the AG Vulcan shipyard in Stettin, Germany (now Szczecin, Poland), in 1901. She was named after Crown Prince Wilhelm, son of the German Emperor Wilhelm II, and was a sister ship of . She had a varied career, starting off as a world-record-holding passenger liner, then becoming an auxiliary warship from 1914–1915 for the Imperial German Navy, sailing as a commerce raider for a year, and then interned in the United States when she ran out of supplies. When the US entered World War I, she was seized and served as a United States Navy troop transport until she was decommissioned and turned over to the United States Shipping Board, where she remained in service until she was scrapped in 1923. German passenger liner (1901–1914) ''Kronprinz Wilhelm'' was launched on 30 March 1901. Her registered length was , her beam was and her depth was . Her tonnag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Kaiser Wilhelm Der Grosse
''Kaiser Wilhelm der Grosse'' ( Ger. orth. ''Kaiser Wilhelm der Große'') was a German transatlantic ocean liner named after Wilhelm I, German Emperor, the first monarch of the German Empire. The liner was built in Stettin (now Szczecin, Poland) for the Norddeutscher Lloyd (NDL), and entered service in 1897. It was the first liner to have four funnels and is considered to be the first "superliner." The first of four sister ships built between 1903 and 1907 for NDL (the others being , and ), she marked the beginning of a change in the way maritime supremacy was demonstrated in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century. The ship began a new era in ocean travel and the novelty of having four funnels was quickly associated with size, strength, speed and above all luxury. Quickly established on the Atlantic, she gained the Blue Riband for Germany, a notable prize for the fastest trip from Europe to America which had been previously dominated by the British. In 1900, she was da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Poppe
Johann Georg Poppe (12 September 1837 – 18 August 1915), often called Johannes Poppe by English-speaking writers, was a prominent architect in Bremen during the German Gründerzeit and an influential interior designer of ocean liners for the Norddeutscher Lloyd. He worked in an eclectic mixture of historical revival styles sometimes called "Bremen Baroque architecture, Baroque".Alain Dewerpe, "Du style français. Les conventions nationales du paquebot comme produit matériel et imaginaire social, 1900–1935" in Bénédicte Zimmmermann, Claude Didry and Peter Wagner, eds., ''Le travail et la nation: histoire croisée de la France et de l'Allemagne'', Paris: Maison des sciences de l'homme, 1999, , pp. 281–310p. 303 Life and career Poppe was born in Bremen into a family with a heritage as architects;E. Gildemeister, "Das Wohnhaus", in Architekten- und Ingenieurverein, Bremen, ''Bremen und seine Bauten'', Bremen: Schünemann, 1900, , pp. 408–74p. 433 his father wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watertight Compartments
Floodability is the susceptibility of a ship's construction to flooding. It also refers to the ability to intentionally flood certain areas of the hull for damage control purposes, or to increase stability, which is particularly important in combat vessels, which often face the possibility of serious hull breach due to enemy action, and which rely on well-trained damage controlmen to equalize and then stop flooding of the hull. Floodability is reduced by dividing the volume of the hull into watertight compartments with decks and bulkheads (which also increase the strength of ships), use of double bottom (or double hull), and by other means. If a ship's hull is divided into watertight compartments, any flooding resulting from a breach of the hull can be contained in the compartments where the flooding occurs. In most cases, the watertight compartments are fitted with a system of automatic doors, which can be triggered either remotely or locally as soon as flooding is detecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)




.jpg)