|
SS Claymont Victory
SS ''Claymont Victory'' was a type Victory ship-based VC2-S-AP2 troop transport built for the U.S. Army Transportation Corps late in World War II. Launched in November 1944, it saw service in the European Theater of Operations during 1945 and in the immediate post-war period repatriating U.S. troops. After being briefly laid up in the U.S. ''Claymont Victory'' was purchased by Vereenigde Nederlandsche Scheepvaartmaatschapppij of the Netherlands and renamed ''Mariekerk''. In 1966 she was sold to Kavo Compañia Naviera S.A., of Greece and renamed ''Kavo Longos''. She was scrapped at Whampoa Dock, Hong Kong, in 1971. History Construction and operation SS ''Claymont Victory'' was laid down on September 25, 1944, as a U.S. MARCOM Type C2 ship-based VC2-S-AP2 hull by Bethlehem-Fairfield Shipyard of Baltimore, Maryland. Launched on November 18, 1944, she was then converted into a dedicated troopship, and delivered on December 15, 1944. She was operated on behalf of USAT by Easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claymont, Delaware
Claymont is a census-designated place (CDP) in New Castle County, Delaware. The estimated 2017 population of the 19703 ZIP code, which Claymont encompasses, was 15,292. History The community now known as Claymont started on the banks of Naamans Creek where it empties into the Delaware River. This once rich ecosystem has been occupied steadily since before 1200 A.D. and has undergone numerous cultural and economic changes, most of which are still evident in the architecture and living patterns of the community today. The first residents were aboriginal Indians of the Middle Woodland period (1100-1600 B.C.). Evidence of these early dwellers has been found along both sides of Naamans Creek. The Dutch named the creek and settlement after the Chief of the Lenape Indians who occupied the region. The settlement grew rapidly from the 17th century through the 20th century, first with gristmills, farms, and related ancillary industries, and later with lumber mills, a steel mill, and a chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
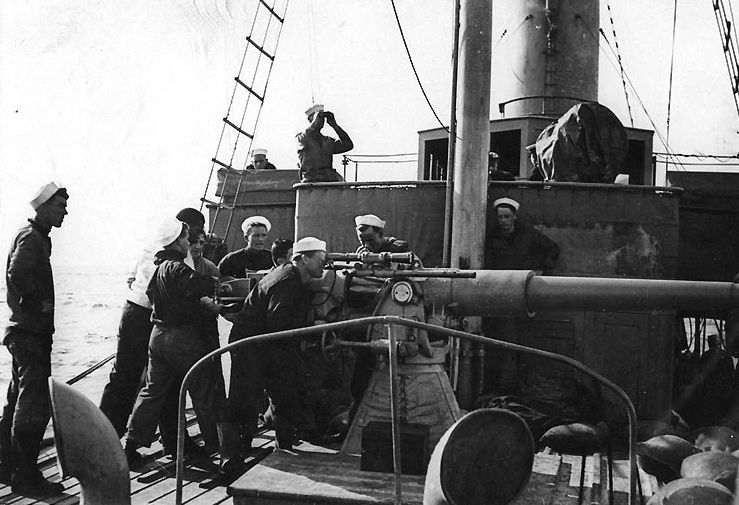
3"/50 Caliber Gun
The 3"/50 caliber gun (spoken "three-inch fifty-caliber") in United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile in diameter, and the barrel was 50 calibers long (barrel length is 3 in × 50 = ). Different guns (identified by Mark numbers) of this caliber were used by the U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard from 1890 through to 1994 on a variety of combatant and transport ship classes. The gun is still in use with the Spanish Navy on ''Serviola''-class patrol boats. Early low-angle guns The US Navy's first 3"/50 caliber gun (Mark 2) was an early model with a projectile velocity of per second. Low-angle (single-purpose/non-anti-aircraft) mountings for this gun had a range of 7000 yards at the maximum elevation of 15 degrees. The gun entered service around 1900 with the s, and was also fitted to s. By World War II these guns were found only on a few Coast Guard cutters and Defensively Equipped Merchant Ships. Low-angle 3"/50 caliber guns (Marks 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS American Victory
SS ''American Victory'' is a Victory ship which saw brief service in the Pacific Theater of Operations during the final months of World War II, Korean War from 1951–1954, and Vietnam War from 1966–1969. Built in June 1945, she carried ammunition and other cargo from Los Angeles to Southeast Asia, then ferried cargo, equipment and troops back to the U.S. after the war ended. She survived two typhoons and one hurricane. She circumnavigated the globe once. ''American Victory'' spent part of the period between 1946 and 1966 chartered to commercial carriers and the other part in two stints in U.S. reserve fleets. From 1966 to 1969 she delivered cargo to Southeast Asia in the Vietnam War, then three decades again in reserve. In April 1999, she was turned over to a preservation organization to serve as a museum ship. Today she is the main feature of the American Victory Ship & Museum, also known as the American Victory Mariners Memorial & Museum Ship in Tampa, Florida's Channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Maritime Victory
SS ''Maritime Victory'', hull number 821, VC2-S-AP2/WSAT, renamed USAT ''Pvt. Frederick C. Murphy'', was an American Army troop transport which saw duty just after World War II. The ''Maritime Victory'' was unusual in that as an AP2 vessel, the cargo holds were converted for troop berthing (though with reduced cargo-carrying ability) and topside cargo handling gear was retained. A total of 97 such VC2-S-AP2 conversions were planned, 84 completed. "In the summer of 1945, eighty-four VC2-S-AP2 Victory ships, including the Maritime Victory, were converted into troopships by MARITIME VICTORY the U.S. Maritime Commission in preparation for an assault on the Japanese home islands. The ship made several crossings of the Atlantic Ocean and was used to repatriate American troops from Europe after World War II. pp. 1-2 On 5 July 1946 the ship was returned to the U.S. Army. On 30 August 1946 it was put into the reserve fleet and renamed USAT ''Pvt. Frederick C. Murphy'' on 10 February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monrovia
Monrovia () is the capital city of the West African country of Liberia. Founded in 1822, it is located on Cape Mesurado on the Atlantic coast and as of the 2008 census had 1,010,970 residents, home to 29% of Liberia’s total population. As the nation's primate city, Monrovia is the country's economic, financial and cultural center; its economy is primarily centered on its harbor and its role as the seat of Liberian government. Etymology Monrovia is named in honor of U.S. President James Monroe, a prominent supporter of the colonization of Liberia and the American Colonization Society. Along with Washington, D.C., it is one of two world capitals to be named after a U.S. President. History Before 1816, the area around Cape Mesurado and the mouth of the Mesurado River was called Ducor. It had long been established as a crossroads and place of trade, and was inhabited by fishing, trading and farming communities of various ethnicities, including the Dey, Kru, Bassa, Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1269th Engineer Combat Battalion (United States)
The 1269th Engineer Combat Battalion was an engineer combat battalion that served in the United States Army in the European Theater of Operations during World War II. It saw action in France and Germany, serving notably with the Army's T-Force intelligence assault force in the capture of German atomic weapons facilities and personnel as part of Operation Big. History Formation The 1269th Engineer Combat Battalion was activated at Camp Chaffee, Arkansas on 30 March 1944. A senior cadre was organized under the command of Major Willard White. In April a core unit of 18-year-old ASTP volunteers and Army Air Corps trainees arrived for five months of combat engineer basic training. Many of that group were promoted to round out NCO cadre vacancies, after which replacements were brought in to fill the unit to T/O strength. The battalion moved by train to Camp Kilmer, New Jersey, arriving 18 October 1944. In the ETO France The battalion departed New York POE on 27 October and cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Port Of Embarkation
The Boston Port of Embarkation (BPOE) was a United States Army command responsible for the movement of troops and supplies from the United States to overseas commands. In World War I it was a sub-port of the New York Port of Embarkation. During World War II it became an independent Port of Embarkation with the second greatest number of passengers embarked and third greatest tonnage of cargo embarked by east coast Ports of Embarkation. In passengers it was exceeded on the east coast only by New York and in cargo only by New York and the Hampton Roads Port of Embarkation. Within three months after entry of the United States into World War II Boston was being established as a sub-port of New York.During the period the New York sub-port at Charleston became the independent Charleston Port of Embarkation and the San Francisco Port of Embarkation sub-port at Seattle became the independent Seattle Port of Embarkation. Sub-ports of San Francisco were being established at Portland, Oregon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VJ Day
Victory over Japan Day (also known as V-J Day, Victory in the Pacific Day, or V-P Day) is the day on which Imperial Japan surrendered in World War II, in effect bringing the war to an end. The term has been applied to both of the days on which the initial announcement of Japan's surrender was made – 15 August 1945, in Japan, and because of time zone differences, 14 August 1945 (when it was announced in the United States and the rest of the Americas and Eastern Pacific Islands) – as well as to 2 September 1945, when the surrender document was signed, officially ending World War II. 15 August is the official V-J Day for the United Kingdom, while the official US commemoration is 2 September. The name, V-J Day, had been selected by the Allies after they named V-E Day for the victory in Europe. On 2 September 1945, formal surrender occurred aboard the battleship USS ''Missouri'' in Tokyo Bay. In Japan, 15 August usually is known as the ; the official name for the day, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" (French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Cliffs Of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, deposited during the Late Cretaceous. The cliffs, on both sides of the town of Dover in Kent, stretch for eight miles (13 km). The White Cliffs of Dover form part of the North Downs. A section of coastline encompassing the cliffs was purchased by the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust in 2016. The cliffs are part of the Dover to Kingsdown Cliffs Site of Special Scientific Interest and Special Area of Conservation. The point where Great Britain is closest to continental Europe, on a clear day the cliffs are visible from France (approximately away). A celebrated UK landmark, the cliffs have featured on commemorative postage stamps issued by the Royal Mail, including in their Great Britain commem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
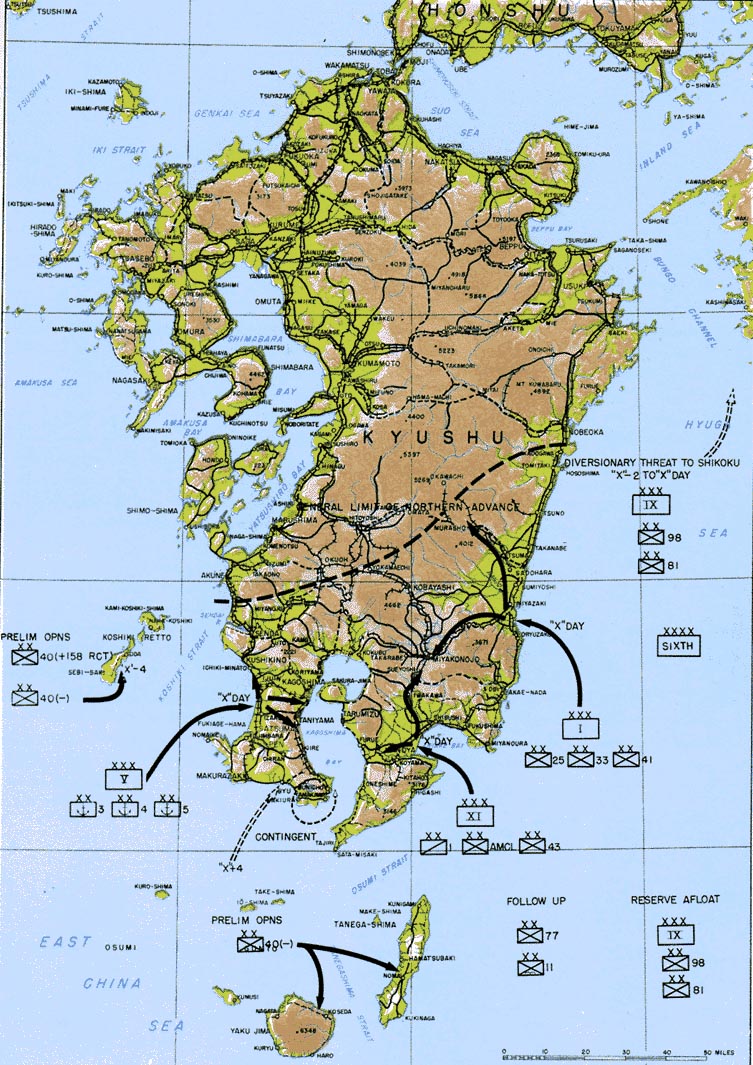
Operation Downfall
Operation Downfall was the proposed Allied plan for the invasion of the Japanese home islands near the end of World War II. The planned operation was canceled when Japan surrendered following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet declaration of war, and the invasion of Manchuria. The operation had two parts: Operation Olympic and Operation Coronet. Set to begin in November 1945, Operation Olympic was intended to capture the southern third of the southernmost main Japanese island, Kyūshū, with the recently captured island of Okinawa to be used as a staging area. In early 1946 would come Operation Coronet, the planned invasion of the Kantō Plain, near Tokyo, on the main Japanese island of Honshu. Airbases on Kyūshū captured in Operation Olympic would allow land-based air support for Operation Coronet. If Downfall had taken place, it would have been the largest amphibious operation in history, surpassing D-Day. Japan's geography made this invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean Theater Of World War II
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)