|
SR-BI
Scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SRB1) also known as SR-BI is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SCARB1'' gene. SR-BI functions as a receptor for high-density lipoprotein. Function Scavenger receptor class B, type I (SR-BI) is an integral membrane protein found in numerous cell types/tissues, including enterocytes, the liver and adrenal gland. It is best known for its role in facilitating the uptake of cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins in the liver. This process drives the movement of cholesterol from peripheral tissues towards the liver, where cholesterol can either be secreted via the bile duct or be used to synthesise steroid hormones. This movement of cholesterol is known as reverse cholesterol transport and is a protective mechanism against the development of atherosclerosis, which is the principal cause of heart disease and stroke. SR-BI is crucial in carotenoid and vitamin E uptake in the small intestine. SR-B1 is upregulated in times of vit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Cholesterol Transport
Reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) is a multistep process comprising removal of excess cholesterol from cells in the body and delivery to the liver for excretion into the small intestine. Enhancing reverse cholesterol transport is considered a potential strategy for preventing and treating atherosclerosis and associated diseases such as cardiovascular disease and stroke. Atherosclerosis is caused by the build-up in arterial blood vessels of atherosclerotic plaques. These consist mostly of foam cells, which are macrophages overloaded with cholesterol and other lipids. Foam cells and other cells in peripheral tissues can hand over their excess cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. These will transport the cholesterol via the lymph and then the blood stream to the liver, from where it will be excreted with bile into the small intestine. Reverse cholesterol transport thereby works against the build-up of atherosclerotic plaques from dying foam cells. In more deta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
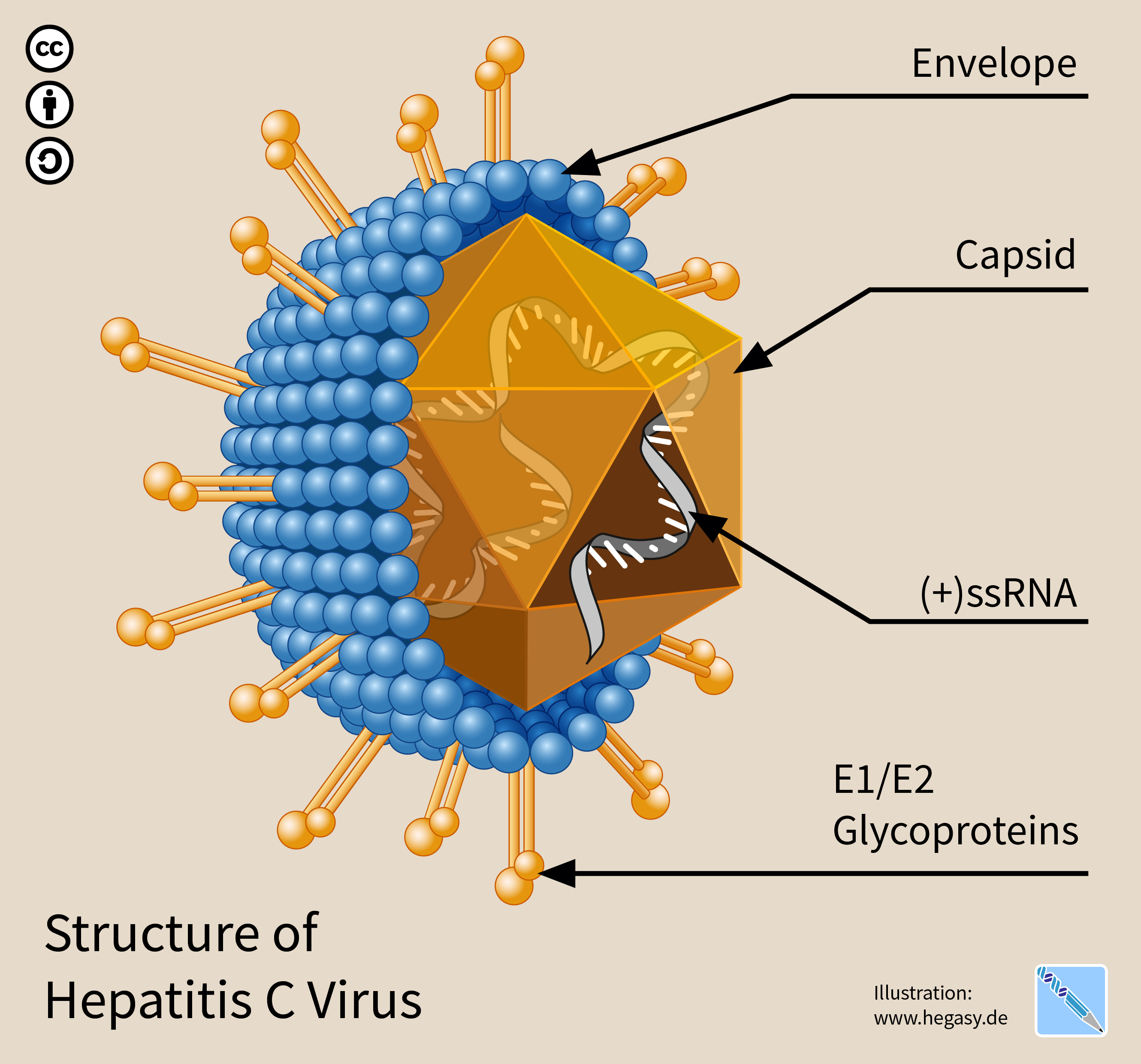
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA). HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. HDL particles are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol", because they transport fat molecules out of artery walls, reduce macrophage accumulation, and thus help prevent or even regress atherosclerosis. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldfish
The goldfish (''Carassius auratus'') is a freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae of the order Cypriniformes. It is commonly kept as a pet in indoor aquariums, and is one of the most popular aquarium fish. Goldfish released into the wild have become an invasive pest in parts of North America and Australia. Native to China, the goldfish is a relatively small member of the carp family (which also includes the Prussian carp and the crucian carp). It was first selectively bred for color in imperial China more than 1,000 years ago, where several distinct breeds were developed. Goldfish breeds vary greatly in size, body shape, fin configuration, and coloration (various combinations of white, yellow, orange, red, brown, and black are known). History Various species of carp (collectively known as Asian carp) have been bred and reared as food fish for thousands of years in East Asia. Some of these normally gray or silver species have a tendency to produce red, oran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogenes
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells undergo a preprogrammed rapid cell death () if critical functions are altered and then malfunction. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they predispose the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including ''co-suppression'', ''post-transcriptional gene silencing'' (PTGS), and ''quelling''. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SiRNA
Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20–24 base pairs in length, similar to microRNA (miRNA), and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading messenger RNA (mRNA) after transcription, preventing translation. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License It was discovered in 1998 by Andrew Fire at the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington, D.C. and Craig Mello at the University of Massachusetts in Worcester. Structure Naturally occurring siRNAs have a well-defined structure that is a short (usually 20 to 24- bp) double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) with phosphorylated 5' ends and hydroxylated 3' ends with two overhanging nucleotides. The Dicer enzyme catalyzes prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at the same time, such that the average size of cells remains constant in the population. Cell division can occur without cell growth, producing many progressively smaller cells (as in cleavage of the zygote), while cell growth can occur without cell division to produce a single larger cell (as in growth of neurons). Thus, cell proliferation is not synonymous with either cell growth or cell division, despite these terms sometimes being used interchangeably. Stem cells undergo cell proliferation to produce proliferating "transit amplifying" daughter cells that later differentiate to construct tissues during normal development and tissue growth, during tissue regeneration after da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD81
CD81 molecule, also known as CD81 (Cluster of Differentiation 81), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CD81'' gene. It is also known as 26 kDa cell surface protein, TAPA-1 (Target of the Antiproliferative Antibody 1), and Tetraspanin-28 (Tspan-28). Gene The gene is located on the plus strand of the short arm of chromosome 11 (11p15.5). It is 20,103 bases in length and encodes a protein of 236 amino acids (predicted molecular weight 25.809 kDa). The protein does not appear to be post translationally modified and has four transmembrane domains. Both the N-terminus and C-terminus lie on the intracellular side of the membrane. The gene is expressed in hemopoietic, endothelial, and epithelial cells. It is absent from erythrocytes, platelets, and neutrophils. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spawn (biology)
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is known as spawning. The vast majority of aquatic and amphibious animals reproduce through spawning. These include the following groups: * Bony fishes * Crustaceans (such as crabs, shrimps, etc.) *Mollusks (such as oysters, octopus, squid) *Echinoderms (such as sea urchins, sea stars, sea cucumbers, etc.) * Amphibians (such as frogs, toads, salamanders, newts) * Aquatic insects (such as dragonflies, mayflies, mosquitoes) *Coral, which are living colonies of tiny, aquatic organisms—not plants, as they are sometimes perceived to be. Corals, while appearing sedentary or botanical by nature, actually spawn by releasing clouds of sperm and egg cells into the water column, where the two mix. As a general rule, aquatic or semiaquatic reptiles, birds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |