|
SPON1
Spondin-1 (also known as F-spondin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SPON1'' gene. It is secreted by cells of the floor plate and may be involved in axon guidance Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they mana ... The protein contains 807 amino acids and is structurally composed of six thrombospondin domains, one reelin domain, and one spondin domain. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Extracellular matrix proteins {{gene-11-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombospondin
Thrombospondins (TSPs) are a family of secreted glycoproteins with antiangiogenic functions. Due to their dynamic role within the extracellular matrix they are considered matricellular proteins. The first member of the family, thrombospondin 1 (THBS1), was discovered in 1971 by Nancy L. Baenziger. Types The thrombospondins are a family of multifunctional proteins. The family consists of thrombospondins 1-5 and can be divided into 2 subgroups: A, which contains TSP-1 and TSP-2, and B, which contains TSP-3, TSP-4 and TSP-5 (also designated cartilage oligomeric protein or COMP). TSP-1 and TSP-2 are homotrimers, consisting of three identical subunits, whereas TSP-3, TSP-4 and TSP-5 are homopentamers. TSP-1 and TSP-2 are produced by immature astrocytes during brain development, which promotes the development of new synapses. Thrombospondin 1 Thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) is encoded by THBS1. It was first isolated from platelets that had been stimulated with thrombin, and so was desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
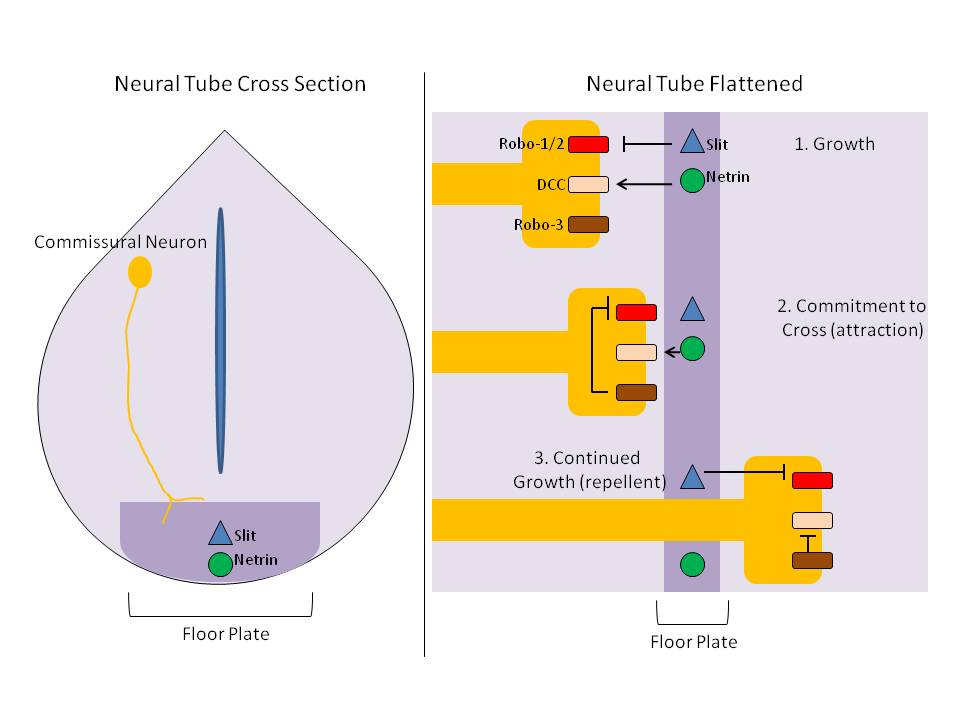
Floor Plate
The floor plate is a structure integral to the developing nervous system of vertebrate organisms. Located on the ventral midline of the embryonic neural tube, the floor plate is a specialized glial structure that spans the anteroposterior axis from the midbrain to the tail regions. It has been shown that the floor plate is conserved among vertebrates, such as zebrafish and mice, with homologous structures in invertebrates such as the fruit fly ''Drosophila'' and the nematode ''C. elegans''. Functionally, the structure serves as an organizer to ventralize tissues in the embryo as well as to guide neuronal positioning and differentiation along the dorsoventral axis of the neural tube. Induction Induction of the floor plate during embryogenesis of vertebrate embryos has been studied extensively in chick and zebrafish and occurs as a result of a complex signaling network among tissues, the details of which have yet to be fully refined. Currently there are several competing lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Guidance
Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they manage to find their way so accurately is an area of ongoing research. Axon growth takes place from a region called the growth cone and reaching the axon target is accomplished with relatively few guidance molecules. Growth cone receptors respond to the guidance cues. Mechanisms Growing axons have a highly motile structure at the growing tip called the growth cone, which responds to signals in the extracellular environment that instruct the axon in which direction to grow. These signals, called guidance cues, can be fixed in place or diffusible; they can attract or repel axons. Growth cones contain receptors that recognize these guidance cues and interpret the signal into a chemotropic response. The general theoretical framework is that wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reelin
Reelin, encoded by the ''RELN'' gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this important role in early development, reelin continues to work in the adult brain. It modulates synaptic plasticity by enhancing the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation. It also stimulates dendrite and dendritic spine development and regulates the continuing migration of neuroblasts generated in adult neurogenesis sites like the subventricular and subgranular zones. It is found not only in the brain but also in the liver, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, Fallopian tube, breast and in comparatively lower levels across a range of anatomical regions. Reelin has been suggested to be implicated in pathogenesis of several brain diseases. The expression of the protein has been found to be significantly lower in schizophrenia and psycho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |