|
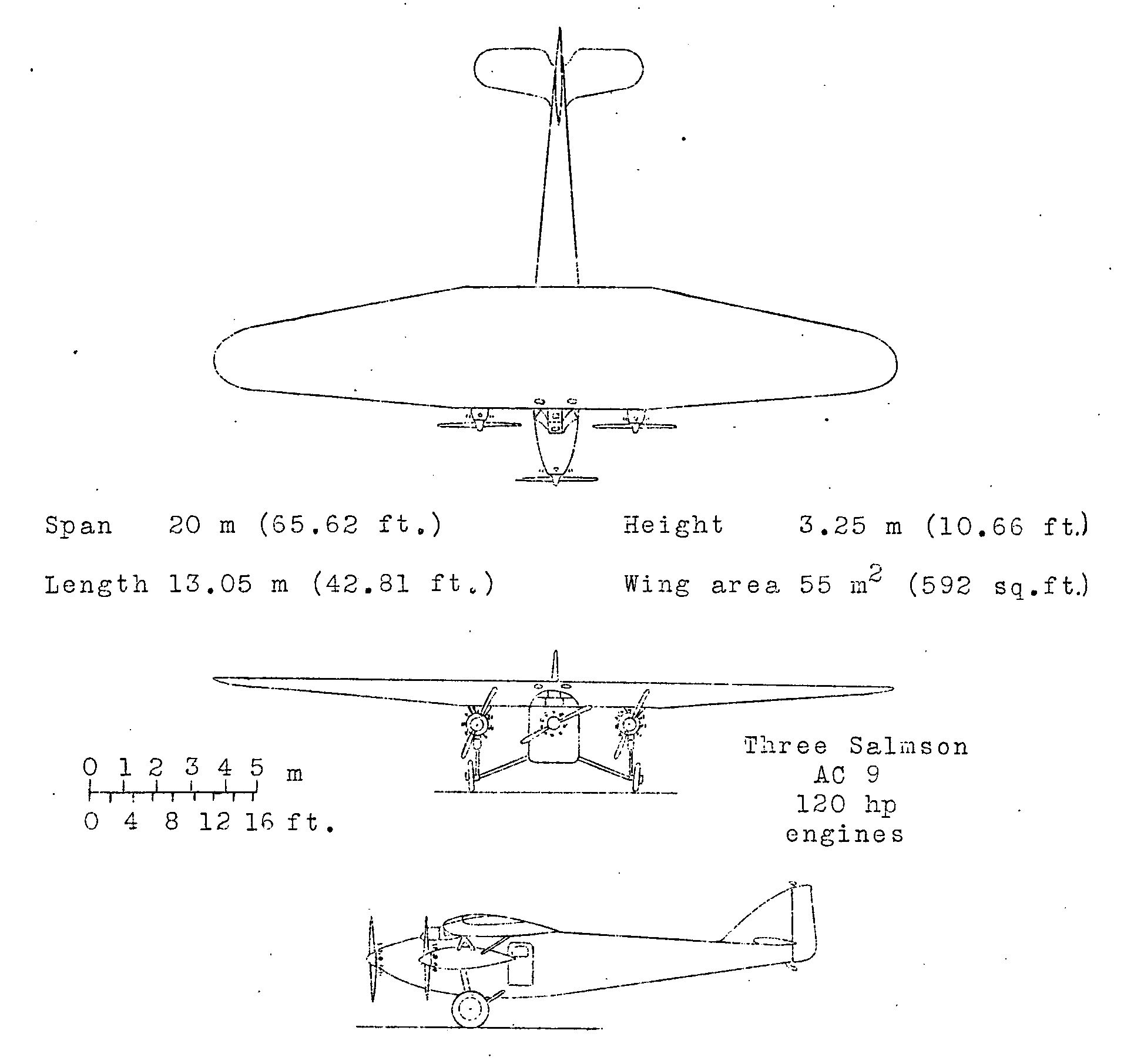
SPCA 218
The SPCA 40T, also designated the SPCA VII, was a mailplane designed and produced by the French aircraft manufacturer Société Provençale de Constructions Aéronautiques (SPCA). The 40T was a high-wing monoplane of conventional layout with a thick-sectioned, cantilever wing.''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft'', p. 2860. Both the flight deck and cargo bay were fully enclosed, the latter could be adapted to seat up to five passengers.Taylor 1989, p. 835. It was furnished with a fixed undercarriage that consisted of divided main units with spatted wheels along with a tailskid. Metal construction was used throughout the airframe. On 21 December 1929, the type performed its maiden flight. A total of three aircraft were produced; the third being equipped with more powerful engines and the first two being subsiquently rebuilt to the same standard. During the first half of the 1930s, it was operated by the Services Aeriens de Madagascar. Design and development The SPCA 40T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Configuration
The wing configuration or planform of a fixed-wing aircraft (including both glider (aircraft), gliders and powered aeroplanes) is its arrangement of lifting and related surfaces. Aircraft designs are often classified by their wing configuration. For example, the Supermarine Spitfire is a conventional low wing cantilever monoplane of straight elliptical planform with moderate aspect ratio and slight dihedral. Many variations have been tried. Sometimes the distinction between them is blurred, for example the wings of many modern combat aircraft may be described either as cropped compound deltas with (forwards or backwards) swept trailing edge, or as sharply tapered swept wings with large leading edge root extensions (or LERX). Some are therefore duplicated here under more than one heading. This is particularly so for variable geometry and combined (closed) wing types. Most of the configurations described here have flown (if only very briefly) on full-size aircraft. A few theoret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension. A stay is sometimes used as a synonym for strut, but some sources distinguish that struts are braces for holding compressive forces apart, while stays are braces for keeping stretching forces together. Human anatomy Part of the functionality of the clavicle is to serve as a strut between the scapula and sternum, resisting forces that would otherwise bring the upper limb close to the thorax. Keeping the upper limb away from the thorax is vital for its range of motion. Complete lack of clavicles may be seen in cleidocranial dysostosis, and the abnormal proximity of the shoulders to the median plane in cases of this genetic condition exemplifies the clavicle's importance as a strut. Architecture and construction Strut is a common name in timber framing for a support or brace of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or afterend. Often rudders are shaped to minimize hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is operated by pedals via mechanical linkages or hydraulics. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, on the front part of an aircraft, spacecraft, or submersible, from which a pilot controls the vehicle. The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that enable the pilot to fly the aircraft. In most airliners, a door separates the cockpit from the aircraft cabin. After the September 11, 2001 attacks, all major airlines fortified their cockpits against access by hijackers. Etymology The word cockpit seems to have been used as a nautical term in the 17th century, without reference to cock fighting. It referred to an area in the rear of a ship where the cockswain's station was located, the cockswain being the pilot of a smaller "boat" that could be dispatched from the ship to board another ship or to bring people ashore. The word "cockswain" in turn derives from the old English terms for "boat-servant" (''coque'' is the French word for "shell"; and ''swain'' was old English for boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longeron
In engineering, a longeron or stringer is a load-bearing component of a framework. The term is commonly used in connection with aircraft fuselages and automobile chassis. Longerons are used in conjunction with stringers to form structural frameworks. Aircraft In an aircraft fuselage, stringers are attached to formers (also called frames) and run in the longitudinal direction of the aircraft. They are primarily responsible for transferring the aerodynamic loads acting on the skin onto the frames and formers. In the wings or horizontal stabilizer, longerons run spanwise (from wing root to wing tip) and attach between the ribs. The primary function here also is to transfer the bending loads acting on the wings onto the ribs and spar. The terms "longeron" and "stringer" are sometimes used interchangeably. Historically, though, there is a subtle difference between the two terms. If the longitudinal members in a fuselage are few in number (usually 4 to 8) and run all along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulkhead (partition)
A bulkhead is an upright wall within the hull (watercraft), hull of a ship, within the fuselage of an airplane, or a car. Other kinds of partition elements within a ship are deck (ship), decks and deckheads. Etymology The word ''bulki'' meant "cargo" in Old Norse. During the 15th century sailors and builders in Europe realized that walls within a vessel would prevent cargo from shifting during passage. In shipbuilding, any vertical panel was called a head. So walls installed abeam (side-to-side) in a vessel's hull were called "bulkheads". Now, the term bulkhead applies to every vertical panel aboard a ship, except for the hull itself. History Bulkheads were known to the ancient Greeks, who employed bulkheads in triremes to support the back of rams. By the Athenian trireme era (500 BC), the hull was strengthened by enclosing the bow behind the ram, forming a bulkhead compartment. Instead of using bulkheads to protect ships against rams, Greeks preferred to reinforce the hull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girder
A girder () is a Beam (structure), beam used in construction. It is the main horizontal support of a structure which supports smaller beams. Girders often have an I-beam cross section composed of two load-bearing ''flanges'' separated by a stabilizing ''web'', but may also have a box girder, box shape, Z shape, or other forms. Girders are commonly used to build bridges. A girt is a vertically aligned girder placed to resist shear loads. Small steel girders are Rolling (metalworking), rolled into shape. Larger girders (1 m/3 feet deep or more) are made as plate girders, welded or bolted together from separate pieces of steel plate. The Warren truss, Warren type girder replaces the solid web with an open latticework truss between the flanges. This arrangement combines strength with economy of materials, minimizing weight and thereby reducing loads and expense. Patented in 1848 by its designers James Warren (engineer), James Warren and Willoughby Theobald Monzani, its st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracing (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, bracing comprises additional structural members which stiffen the functional airframe to give it rigidity and strength under load. Bracing may be applied both internally and externally, and may take the form of struts, which act in compression or tension as the need arises, and/or wires, which act only in tension. In general, bracing allows a stronger, lighter structure than one which is unbraced, but external bracing in particular adds drag which slows down the aircraft and raises considerably more design issues than internal bracing. Another disadvantage of bracing wires is that they require routine checking and adjustment, or rigging, even when located internally. During the early years of aviation, bracing was a universal feature of all forms of aeroplanes, including the monoplanes and biplanes, which were then equally common. Today, bracing in the form of lift struts is still used for some light commercial designs where a high wing and light weight are more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 194. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', p. 10 (27th revised edition) The term derives from the French language verb which means " to feather an arrow". Most aircraft feature an empennage incorporating vertical and horizontal stabilising surfaces which stabilise the flight dynamics of yaw and pitch, as well as housing control surfaces. In spite of effective control surfaces, many early aircraft that lacked a stabilising empennage were virtually unflyable. Even so-called "tailless aircraft" usually have a tail fin (usually a vertical stabiliser). Heavier-than-air aircraft without any kind of empennage (such as the Northrop B-2) are rare, and generally use specially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called rolling or banking. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Boul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trailing Edge
The trailing edge of an aerodynamic surface such as a wing is its rear edge, where the airflow separated by the leading edge meets.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 521. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Essential flight control surfaces are attached here to control the direction of the departing air flow, and exert a controlling force on the aircraft. Such control surfaces include ailerons on the wings for roll control, elevator (aircraft), elevators on the tailplane controlling Aircraft principal axes, pitch, and the rudder on the fin controlling Aircraft principal axes, yaw. Elevators and ailerons may be combined as elevons on tailless aircraft. The shape of the trailing edge is of prime importance in the aerodynamic function of any aerodynamic surface. A sharp trailing edge is always employed in an airfoil. George Batchelor has written about: :“ ... the remarkable controlling influence exerted by the sharp trailing edge of an aerof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |