|
SPAD S.A
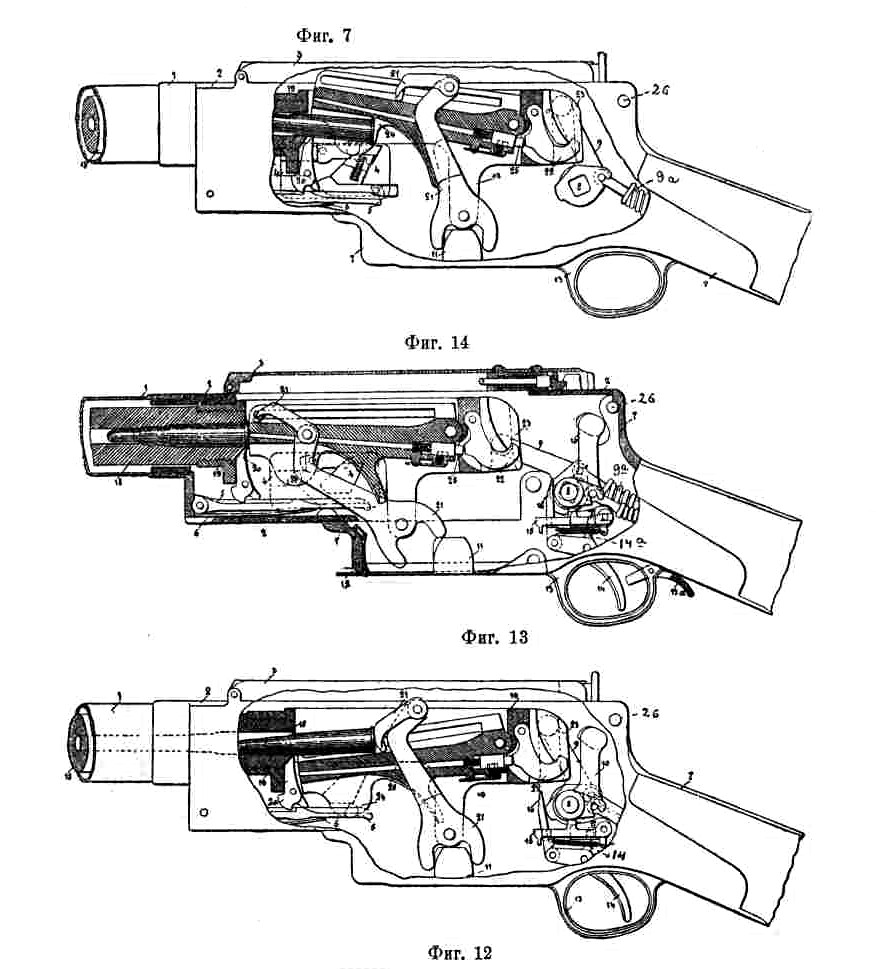
The SPAD S.A (also called S.A.L.) was a French two-seat tractor biplane first flown in 1915. It was used by France and Russia in the early stages of the First World War in the fighter and reconnaissance roles. It was a unique aircraft that carried its observer in a nacelle ahead of wing, engine and propeller. Design and development The SPAD A.1 prototype was the first aircraft produced by SPAD following its reorganization from the pre-war Deperdussin company. The chief designer, Louis Béchereau, had been involved in designing that firm's successful monocoque racing monoplanes, and many design details were carried over from the Deperdussins. The aircraft was designed to carry not only its pilot in the normal position, but also an observer in a streamlined nacelle ahead of the propeller. This configuration was an attempt to combine the advantages of the tractor and the pusher types, giving the observer a clear field of view to the front and sides without the drag penalty of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Société Pour L'Aviation Et Ses Dérivés
Groupe Lactalis S.A. (doing business as Lactalis) is a French multinational dairy products corporation, owned by the Besnier family and based in Laval, Mayenne, France. The company's former name was Besnier S.A. Lactalis is the largest dairy products group in the world, and is the second largest food products group in France, behind Danone. It owns brands such as Parmalat, Président, Kraft Natural Cheese, Siggi's Dairy, Skånemejerier, Rachel's Organic, and Stonyfield Farm. History André Besnier started a small cheesemaking company in 1933 and launched its '' Président'' brand of Camembert in 1968. In 1990, it acquired Group Bridel (2,300 employees, 10 factories, fourth-largest French dairy group) with a presence in 60 countries. In 1992, it acquired United States cheese company Sorrento. In 1999, ''la société Besnier'' became ''le groupe Lactalis'' owned by Belgian holding company BSA International SA. In 2006, they bought Italian group Galbani, and in 2008, bought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somme-Vesle
Somme-Vesle () is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France. See also *Communes of the Marne department The following is a list of the 610 communes in the French department of Marne. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Sommevesle {{ChâlonsChampagne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deperdussin TT
The Deperdussin TT was a French monoplane built by ''Société Pour les Appareils Deperdussin'', later to become S.P.A.D. Introduced in 1912, the type was one widely used by the French Air Force (then ''Aviation Militaire'') before the First World War. In February 1914, an experiment was made to install a machine gun on the aircraft, but this did not see service. A number were used by the Naval Wing of the British Royal Flying Corps, one being fitted with floats and flown from Lake Windemere.Thetford 1982, p. 411. Operators ; *Belgian Air Force ; *French Air Force ; * Paraguayan Air Force ; *Portuguese Air Force ; *Imperial Russian Air Service ; *Serbian Air Force ; *Spanish Air Force ; *Ottoman Air Force ; *Royal Flying Corps ** No. 3 Squadron RFC *Royal Naval Air Service The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deperdussin Monocoque
The Deperdussin Monocoque was an early racing aircraft built in 1912 by the Aéroplanes Deperdussin, a French aircraft manufacturer started in 1911 and reorganized as the Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés ( SPAD) in 1913. It is so named because of the method of construction of its fuselage. The aircraft is noted for winning the Gordon Bennett Trophy in 1912 and 1913, and for raising the world speed record for aircraft to . Background The usual method of construction of an aircraft's fuselage at this time was to use a wire braced box-girder covered in fabric. The first use of monocoque construction in aviation is attributed to Eugene Ruchonnet, a Swiss marine engineer who had built an aircraft nicknamed the ''Cigare'' in 1911, which had a fuselage constructed by building up several layers of thin wood, each lamination applied at right angle to the one underneath. Design The Deperdussin Monocoque was a mid-wing monoplane with parallel-chord wings with the spars mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madsen Machine Gun
The Madsen is a light machine gun that Julius A. Rasmussen and Theodor Schouboe designed and proposed for adoption by Colonel Herman Madsen, Vilhelm Herman Oluf Madsen, the Minister of War (Denmark), Danish Minister of War, and that the Royal Danish Army adopted in 1902. It was the world's first true light machine gun produced in quantity and Madsen was able to sell it in 12 calibres to over 34 countries. The gun saw extensive combat usage for over 100 years, with continued use in limited quantities worldwide into the 2010s. The Madsen was produced by DISA (company), Compagnie Madsen A/S (later operating as Dansk Rekyl Riffel Syndikat A/S and then Dansk Industri Syndikat A/S). Design details The design dates to 1880s, with the Danish Self Loading rifle M.1888 (; ), being a precursor design. In 1883 Captain Vilhelm Herman Oluf Madsen (a Danish artillery officer), and (a weapons technician at the Danish Arsenal), began working on a recoil-operated self-loading rifle; Madsen de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotchkiss M1909 Benét–Mercié Machine Gun
Hotchkiss may refer to: Places Canada * Hotchkiss, Alberta * Hotchkiss, Calgary United States * Hotchkiss, Colorado * Hotchkiss, Virginia * Hotchkiss, West Virginia Business and industry * Automobiles Hotchkiss, a French automobile manufacturer * Hotchkiss et Cie, a French armaments manufacturer * Hotchkiss Ordnance Company, an English armaments manufacturer Military * Hotchkiss H35, a French tank of World War II * Hotchkiss gun ** Hotchkiss machine gun, including a list of variants * Hotchkiss M201, a French light transport vehicle Other uses * Hotchkiss (surname) * Hotchkiss drive, a form of automobile power transmission and suspension. * Hotchkiss Bicycle Railroad in Smithville, Burlington County, New Jersey, U.S. * Hotchkiss School, a private school in Lakeville, Connecticut, U.S. * Rebecca Hotchkiss, a character on the NBC/DirecTV daytime drama ''Passions'' See also * Hodgkin, a surname {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M1895 Colt–Browning Machine Gun
The Colt–Browning M1895, nicknamed "potato digger" because of its unusual operating mechanism, is an air-cooled, belt-fed, gas-operated machine gun that fires from a closed bolt with a cyclic rate of 450 rounds per minute. Based on an 1889 design by John Browning and his brother Matthew S. Browning, it was the first successful gas-operated reloading, gas-operated machine gun to enter service. Operating mechanism Filed for patent in 1892, the M1895's operating mechanism is one of John Browning, John and Matthew S. Browning's early patents for automatic rifles; they had previously been working on lever-action rifles for Winchester such as the Winchester rifle#Model 1886, Winchester 1886. In a typical lever-action design, the operating lever lies under the rear of the gun, typically below the stock, and is hinged near the breech area. It is operated by rotating the lever down and forward, which causes the breechblock to slide rearward away from the barrel and eject the spent rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces (, VVS SSSR; literally "Military Air Forces of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics"; initialism VVS, sometimes referred to as the "Red Air Force") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces were formed from components of the Imperial Russian Air Service in 1917, and faced their greatest test during World War II. The groups were also involved in the Korean War, and dissolved along with the Soviet Union itself in 1991–92. Former Soviet Air Forces' assets were subsequently divided into several air forces of former Republics of the Soviet Union, Soviet republics, including the new Russian Air Force. The "Air March, March of the Pilots" was its marching song. Origins The first military aviation branch of Russia or any of the Soviet Union's constituent states was the short-lived Imperial Russian Air Service, founded in 1912 and disbanded in 1917 with the onset of the Bolshevik Revolution and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Air Force
The French Air and Space Force (, , ) is the air force, air and space force of the French Armed Forces. Formed in 1909 as the ("Aeronautical Service"), a service arm of the French Army, it became an independent military branch in 1934 as the French Air Force (). On 10 September 2020, it assumed its current name, the French Air and Space Force, to reflect an "evolution of its mission" into the area of outer space. The number of aircraft in service with the French Air and Space Force varies depending on the source; the Ministry of Armed Forces (France), Ministry of Armed Forces gives a figure of 658 aircraft in 2014. According to 2025 data, this figure includes 207 combat aircraft: 99 Dassault Mirage 2000 and 108 Dassault Rafale. the French Air and Space Force employs a total of 40,500 regular personnel, with a military reserve forces of France, reserve element of 5,187 in 2014. The Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force (CEMAAE) is a direct subordinate of the Chief of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
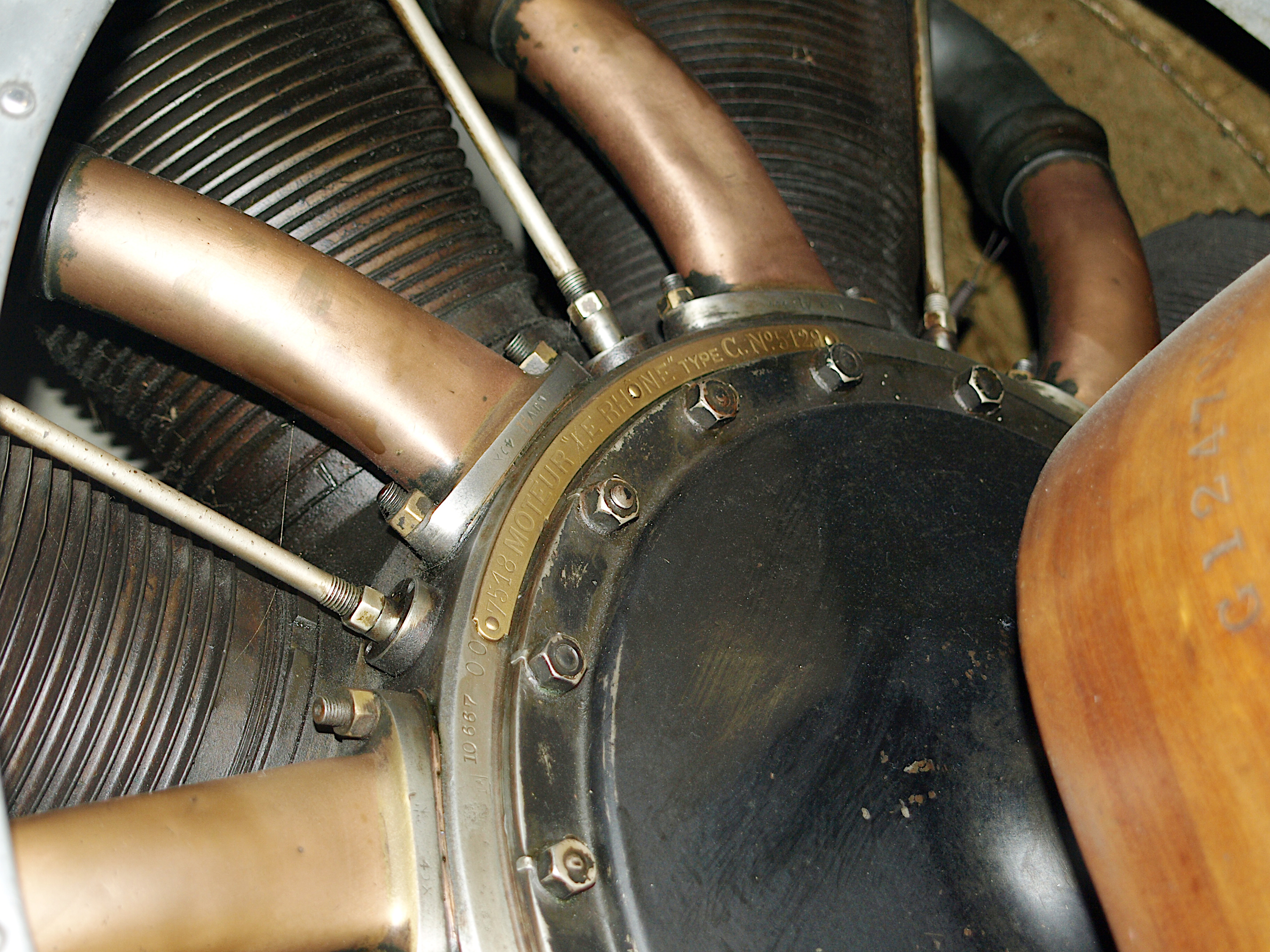
Le Rhône 9J
The Le Rhône 9J is a nine-cylinder Rotary engine, rotary aircraft engine produced in France by Gnome et Rhône. Also known as the Le Rhône 110 hp in a reference to its nominal power rating, the engine was fitted to a number of military aircraft types of the World War I, First World War. Le Rhône 9J engines were produced under license in Great Britain by W. H. Allen, Sons & Company Ltd., W.H. Allen Son & Company of Bedford, and in Germany by Motorenfabrik Oberursel where it was sold as the Oberursel Ur.II.Lumsden 2003, p. 161. In common with other Le Rhône series engines, the 9J featured highly visible copper Inlet manifold, induction pipes and used a single push-pull rod to operate its two overhead valves. The main visual difference between the 9J and the earlier, less powerful Le Rhône 9C engine is that the copper intake manifold tubing (with round section lower ends) on the 110 hp 9J is attached to the crankcase behind the cylinders, whereas on the 9C (8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Rhône 9C
The Le Rhône 9C is a nine-cylinder Rotary engine, rotary aircraft engine produced in France by '' Société des Moteurs Le Rhône'' / Gnome et Rhône. Also known as the Le Rhône 80 hp in a reference to its nominal power rating, the engine was fitted to many military aircraft types during the World War I, First World War. Le Rhône 9C engines were also produced under license in Great Britain, the United States and Sweden. Design and development First marketed in 1912, the 80 horsepower 9C was the first of the Le Rhône, Rhône series rotary engines to have nine cylinders. In common with earlier seven cylinder Le Rhône series engines, the 9C featured copper Inlet manifold, induction pipes and used a single push-pull rod to operate its two Overhead valve, overhead valves. Unlike the later 110 horsepower 9J, the induction pipes and push rods were located on the front of the engine. Prior to the outbreak of World War One, aircraft powered by the Rhône 9C set nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |