|
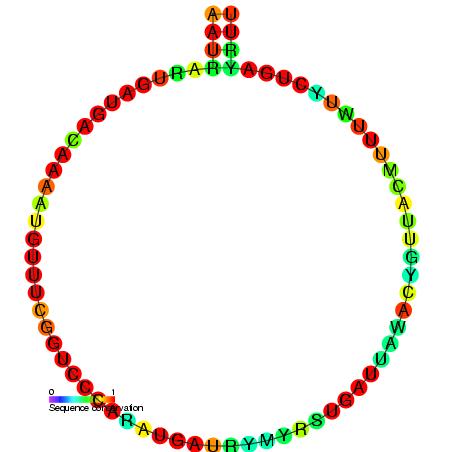
SNORD116
In molecular biology, SNORD116 (also known as HBII-85) is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA. SNORD116 belongs to the C/D box class of snoRNAs which contain the conserved sequence motifs known as the C box (UGAUGA) and the D box (CUGA). Most of the members of the box C/D family function in directing site-specific 2'-O-methylation of substrate RNAs. In the human genome, there are 29 tandemnly repeated copies of SNORD116, followed by 48 copies of another C/D box snoRNA, SNORD115, in the Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) region of chromosome 15. Unlike most other snoRNAs, SNORD116 is expressed prevalently in the brain (but is absent in PWS patients) and lacks any significant complementarity with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SnoRNA
In molecular biology, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes or the guide RNAs (gRNAs) used by Cas9 for CRISPR gene editing. snoRNA guided modifications After transcription, nascent rRNA molecules (termed pre-rRNA) undergo a series of processing steps to generate the mature rRNA molecule. Prior to cleavage by exo- and endonucleases, the pre-rRNA undergoes a complex pattern of nucleoside modifications. These include methylations and pseudouridylations, guided by snoRNAs. *Methylation is the attachment or substitution of a methyl group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
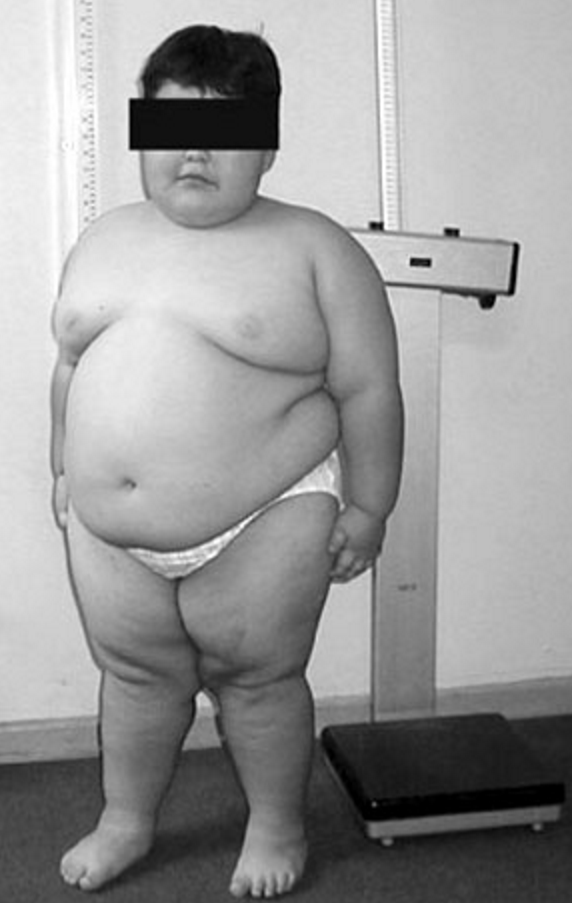
Prader–Willi Syndrome
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a rare genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. In newborns, symptoms include hypotonia, weak muscles, poor feeding, and slow development. Beginning in childhood, those affected become constantly hungry, which often leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mild to moderate intellectual impairment and Behavioural problems, behavioral problems are also typical of the disorder. Often, affected individuals have a narrow forehead, small hands and feet, short height, and light skin and hair. Most are Infertility, unable to have children. About 74% of cases occur when part of the father's chromosome 15 is deleted. In another 25% of cases, the affected person has Uniparental disomy, two copies of the maternal chromosome 15 from the mother and lacks the paternal copy. As parts of the chromosome from the mother are turned off through Genomic imprinting, imprinting, they end up with no working copies of certain genes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not Translation (genetics), translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important list of RNAs, types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, Extracellular RNA, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long noncoding RNA, long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent Transcriptomics, transcriptomic and Bioinformatics, bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have unknown functions, if any. There is no consensus on how much of non-coding transcription is functional: some believe most ncRNAs to be non-functional "junk RNA", spurious transcriptions, while others expect that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen#Compounds, hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and biology. In biological systems, methylation is Catalysis, catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of Protein#Functions, protein function, and RNA processing. ''In vitro'' methylation of tissue samples is also a way to reduce some histology#Histological Artifacts, histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals and can regulate gene expression, RNA processing, and protein function. It is a key pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the Human mitochondrial genetics, mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of non-coding DNA, DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of RNA#Regulatory RNA, regulatory RNAs. It also includes Promoter (biology), promoters and their associated Cis-regulatory element, gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as Scaffold/matrix attachment region, scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and Origin of replication, origins of repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperphagia
Polyphagia, or hyperphagia, is an abnormally strong, incessant sensation of hunger or desire to eat often leading to overeating. In contrast to an increase in appetite following exercise, polyphagia does not subside after eating and often leads to rapid intake of excessive quantities of food. Polyphagia is not a disorder by itself; rather, it is a symptom indicating an underlying medical condition. It is frequently a result of abnormal blood glucose levels (both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia), and, along with polydipsia and polyuria, it is one of the "3 Ps" commonly associated with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Etymology The word ''polyphagia'' () uses combining forms of '' poly-'' + '' -phagia'', from the Greek words πολύς (polys), "very much" or "many", and φᾰ́γω (phago), "eating" or "devouring". Underlying conditions and possible causes Polyphagia is one of the most common symptoms of diabetes mellitus. It is associated with hyperthyroidism and endocrine di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between Prokaryote, prokaryotes and Eukaryote, eukaryotes. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementarity (molecular Biology)
In molecular biology, complementarity describes a relationship between two structures each following the lock-and-key principle. In nature complementarity is the base principle of DNA replication and transcription as it is a property shared between two DNA or RNA sequences, such that when they are aligned antiparallel to each other, the nucleotide bases at each position in the sequences will be complementary, much like looking in the mirror and seeing the reverse of things. This complementary base pairing allows cells to copy information from one generation to another and even find and repair damage to the information stored in the sequences. The degree of complementarity between two nucleic acid strands may vary, from complete complementarity (each nucleotide is across from its opposite) to no complementarity (each nucleotide is not across from its opposite) and determines the stability of the sequences to be together. Furthermore, various DNA repair functions as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD115
Small means of insignificant size. Small may also refer to: Science and technology * SMALL, an ALGOL-like programming language * ''Small'' (journal), a nano-science publication * <small>, an HTML element that defines smaller text Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Small, in the British children's show Big & Small Other uses * Small (surname) * List of people known as the Small * "Small", a song from the album ''The Cosmos Rocks'' by Queen + Paul Rodgers See also * Smal (other) Smal may refer to: People * (1927-2001), Dutch musician * Georges Smal (1928–1988), Belgian writer * Gert Smal (born 1961), South African rugby player * Gijs Smal (born 1997), Dutch football player * (born 1939), Belgian politician; a memb ... * Smalls (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandem Repeat
In genetics, tandem repeats occur in DNA when a pattern of one or more nucleotides is repeated and the repetitions are directly adjacent to each other, e.g. ATTCG ATTCG ATTCG, in which the sequence ATTCG is repeated three times. Several protein domains also form tandem repeats within their amino acid primary structure, such as armadillo repeats. However, in proteins, perfect tandem repeats are rare in naturally proteins, but they have been added to designed proteins. Tandem repeats constitute about 8% of the human genome. They are implicated in more than 50 lethal human diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington's disease, and several cancers. Terminology All tandem repeat arrays are classifiable as satellite DNA, a name originating from the fact that tandem DNA repeats, by nature of repeating the same nucleotide sequences repeatedly, have a unique ratio of the two possible nucleotide base pair combinations, conferring them a specific mass density that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |