|
SN2005ap
SN 2005ap was an extremely energetic type Ic supernova in the galaxy SDSS J130115.12+274327.5. With a peak absolute magnitude of around −22.7, it is the second-brightest superluminous supernova yet recorded, twice as bright as the previous record holder, SN 2006gy, though SN 2005ap was eventually surpassed by ASASSN-15lh. It was initially classified as type II-L, but later revised to type Ic. It was discovered on 3 March 2005, on unfiltered optical images taken with the 0.45 m ROTSE-IIIb (Robotic Optical Transient Search Experiment) telescope, which is located at the McDonald Observatory in West Texas, by Robert Quimby, as part of the Texas Supernova Search that also discovered SN 2006gy. Although it was discovered before SN 2006gy, it was not recognized as being brighter until October 2007. As it occurred 4.7 billion light years from Earth, it was not visible to the naked eye. Although SN 2005ap was twice as bright at its peak than SN 2006gy, it was not as energetic o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Supernova Search
Texas Supernova Search (TSS) is one of many ongoing projects to identify and record supernova events. The project is led by Robert Quimby and to date has found 35 supernovae, 29 of which they were the first to report on. In addition they have discovered twelve (extragalactic) novae (in M31 and M33, including a probable LBV) and six dwarf novae. The project's most notable successes are SN 2005ap and SN 2006gy, the two most powerful supernovae yet recorded. SN 2005ap was an extremely energetic type II supernova A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when .... It is reported to be the brightest supernova yet recorded, twice as bright as the previous record holder, SN 2006gy. Although SN 2005ap was twice as bright at its peak than SN 2006gy it was not as energetic overall as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCP 06F6
SCP 06F6 is (or was) an astronomical object of unknown type, discovered on 21 February 2006 in the constellation BoötesSpace 'firefly' resembles no known object ''New Scientist News'', 16 September 2008 during a survey of CL 1432.5+3332.8 with the 's Wide Field Channel.Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 2006gy
SN 2006gy was an extremely energetic supernova, also referred to as a hypernova or quark-nova, that was discovered on September 18, 2006. It was first observed by Robert Quimby and P. Mondol,IAU Circular No. 8754 , accessed May 8, 2007 and then studied by several teams of astronomers using facilities that included the Chandra, , and Keck [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and transiting extrasolar planets, or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, a cataclysmic variable star, a supernova or a microlensing event or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of the light curve, together with other observations, can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces it or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the apparent magnitude of a variable star over time are commonly used to visualise and analyse their behaviour. Although the categorisation of variable star types is increasingly done from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonald Observatory
McDonald Observatory is an astronomical observatory located near unincorporated community of Fort Davis in Jeff Davis County, Texas, United States. The facility is located on Mount Locke in the Davis Mountains of West Texas, with additional facilities on Mount Fowlkes, approximately to the northeast. The observatory is part of The University of Texas at Austin. It is an organized research unit of the College of Natural Sciences. The observatory produces '' StarDate'', a daily syndicated radio program consisting of short segments related to astronomy that airs on both National Public Radio and commercial radio stations — about 400 affiliates in all. History McDonald Observatory was originally endowed by the Texas banker William Johnson McDonald (1844–1926), who left about $1 million — the bulk of his fortune — to The University of Texas at Austin to endow an astronomical observatory. The provision of the will was challenged by McDonald's relatives, but after a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernovae
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appeari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIMBAD
SIMBAD (the Set of Identifications, Measurements and Bibliography for Astronomical Data) is an astronomical database of objects beyond the Solar System. It is maintained by the Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS), France. SIMBAD was created by merging the Catalog of Stellar Identifications (CSI) and the Bibliographic Star Index as they existed at the Meudon Computer Centre until 1979, and then expanded by additional source data from other catalogues and the academic literature. The first on-line interactive version, known as Version 2, was made available in 1981. Version 3, developed in the C language and running on UNIX stations at the Volgograd Observatory, was released in 1990. Fall of 2006 saw the release of Version 4 of the database, now stored in PostgreSQL, and the supporting software, now written entirely in Java. JP11 is a star catalogue containing about 4,000 objects. Currently it exists only as a part of the SIMBAD database. , SIMBAD contains infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre De Données Astronomiques De Strasbourg
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Jay County, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Loire, formerly Centre, France * Centre (de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aladin Sky Atlas
Aladin is an interactive software sky atlas, created in France. It's allowing the user to visualize digitized astronomical images, superimpose entries from astronomical catalogues or databases, and interactively access related data and information from the SIMBAD database, the VizieR service and other archives for all known sources in the field. Created in 1999, Aladin has become a widely used VO portal capable of addressing challenges such as locating data of interest, accessing and exploring distributed datasets, visualizing multi-wavelength data. Compliance with existing or emerging VO standards, interconnection with other visualisation or analysis tools, ability to easily compare heterogeneous data are key topics allowing Aladin to be a powerful data exploration and integration tool as well as a science enabler. Aladin is developed and maintained by the Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS) and released under the GNU GPL v3. See also * Centre national de la re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBC News
NBC News is the news division of the American broadcast television network NBC. The division operates under NBCUniversal Television and Streaming, a division of NBCUniversal, which is, in turn, a subsidiary of Comcast. The news division's various operations report to the president of NBC News, Noah Oppenheim. The NBCUniversal News Group also comprises MSNBC, the network's 24-hour general news channel, business and consumer news channels CNBC and CNBC World, the Spanish language Noticias Telemundo and United Kingdom–based Sky News. NBC News aired the first regularly scheduled news program in American broadcast television history on February 21, 1940. The group's broadcasts are produced and aired from 30 Rockefeller Plaza, NBCUniversal's headquarters in New York City. The division presides over America's number-one-rated newscast, '' NBC Nightly News'', the world's first of its genre morning television program, '' Today'', and the longest-running television series in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
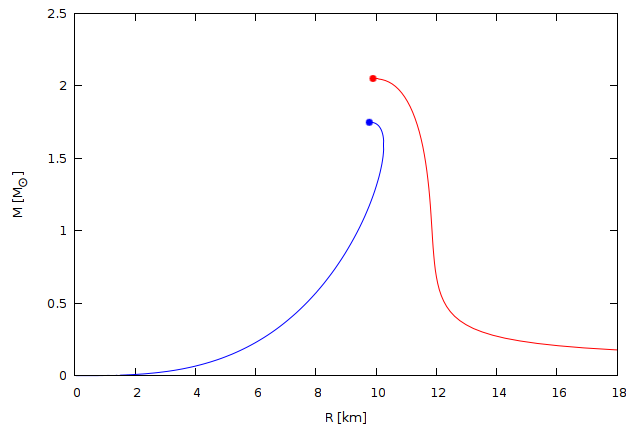
Quark Star
A quark star is a hypothetical type of compact, exotic star, where extremely high core temperature and pressure has forced nuclear particles to form quark matter, a continuous state of matter consisting of free quarks. Background Some massive stars collapse to form neutron stars at the end of their life cycle, as has been both observed and explained theoretically. Under the extreme temperatures and pressures inside neutron stars, the neutrons are normally kept apart by a degeneracy pressure, stabilizing the star and hindering further gravitational collapse. However, it is hypothesized that under even more extreme temperature and pressure, the degeneracy pressure of the neutrons is overcome, and the neutrons are forced to merge and dissolve into their constituent quarks, creating an ultra-dense phase of quark matter based on densely packed quarks. In this state, a new equilibrium is supposed to emerge, as a new degeneracy pressure between the quarks, as well as repulsive e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |