 |
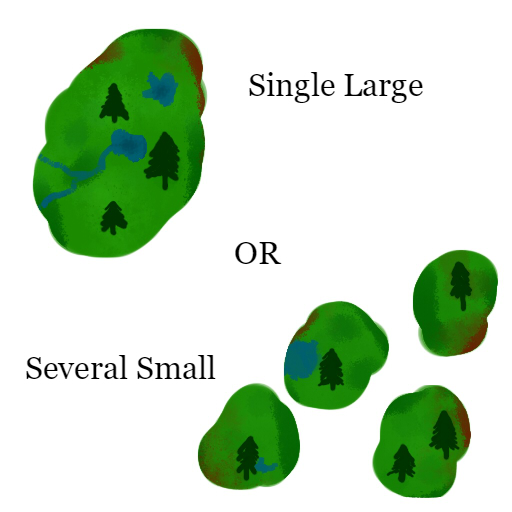
SLOSS Debate
The SLOSS debate was a debate in ecology and conservation biology during the 1970's and 1980's as to whether a single large or several small (SLOSS) reserves were a superior means of conserving biodiversity in a habitat fragmentation, fragmented habitat. Since its inception, multiple alternate theories have been proposed. There have been applications of the concept outside of the original context of habitat conservation. History In 1975, Jared Diamond suggested some "rules" for the design of protected areas, based on Robert MacArthur and E. O. Wilson's book ''The Theory of Island Biogeography''. One of his suggestions was that a single large reserve was preferable to several smaller reserves whose total areas were equal to the larger. Since species richness increases with habitat (ecology), habitat area, as established by the Species–area relationship, species area curve, a larger block of habitat would support more species than any of the smaller blocks. This idea was popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Bruce D
The English language name Bruce arrived in Scotland with the Normans, from the place name Brix, Manche in Normandy, France, meaning "the willowlands". Initially promulgated via the descendants of king Robert the Bruce (1274−1329), it has been a Scottish surname since medieval times; it is now a common male given name. The variant ''Lebrix'' and ''Le Brix'' are French language, French variations of the surname. Note: A few people are notable in more than one field, and therefore appear in more than one section. Arts and entertainment Film and television * Bruce Altman (born 1955), American actor * Bruce Baillie (1931–2020), American filmmaker * Bruce Bennett (1906–2007), American actor and athlete * Bruce Berman (born 1952), American film producer * Bruce Boa (1930–2004), Canadian actor * Bruce Boxleitner (born 1950), American actor * Bruce Campbell (born 1958), American actor, director, writer, producer and author * Bruce Conner (1933–2008), American artist and filmma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and other consequences that may arise from expression of wikt:deleterious, deleterious dominance (genetics), recessive traits resulting from incestuous sexual relationships and consanguinity. Animals avoid inbreeding only rarely. Inbreeding results in homozygous, homozygosity which can increase the chances of offspring being affected by recessive phenotypic trait, traits. In extreme cases, this usually leads to at least temporarily decreased Fitness (biology), biological fitness of a population (called inbreeding depression), which is its ability to survive and reproduce. An individual who inherits such deleterious traits is colloquially referred to as ''inbred''. The avoidance of expression of such deleterious recessive allel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as random genetic drift, allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the Allele frequency, frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable (due to the law of large numbers). In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Metapopulations
A metapopulation consists of a group of spatially separated populations of the same species which interact at some level. The term metapopulation was coined by Richard Levins in 1969 to describe a model of population dynamics of insect pests in agricultural fields, but the idea has been most broadly applied to species in naturally or artificially habitat fragmentation, fragmented habitats. In Levins' own words, it consists of "a population of populations". A metapopulation is generally considered to consist of several distinct populations together with areas of suitable habitat which are currently unoccupied. In classical metapopulation theory, each population cycles in relative independence of the other populations and eventually goes extinct as a consequence of demographic stochasticity (fluctuations in population size due to random demographic events); the smaller the population, the more chances of inbreeding depression and prone to extinction. Although individual populations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Conservation Genetics
Conservation genetics is an interdisciplinary subfield of population genetics that aims to understand the dynamics of genes in a population for the purpose of natural resource management, conservation of genetic diversity, and the prevention of species extinction. Scientists involved in conservation genetics come from a variety of fields including population genetics, research in natural resource management, molecular ecology, molecular biology, evolutionary biology, and systematics. The genetic diversity within species is one of the three fundamental components of biodiversity (along with species diversity and ecosystem diversity), so it is an important consideration in the wider field of conservation biology. Genetic diversity Genetic diversity is the total amount of genetic variability within a species. It can be measured in several ways, including: observed heterozygosity, expected heterozygosity, the mean number of alleles per locus, the percentage of loci that are po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Metapopulation
A metapopulation consists of a group of spatially separated populations of the same species which interact at some level. The term metapopulation was coined by Richard Levins in 1969 to describe a model of population dynamics of insect pests in agricultural fields, but the idea has been most broadly applied to species in naturally or artificially fragmented habitats. In Levins' own words, it consists of "a population of populations". A metapopulation is generally considered to consist of several distinct populations together with areas of suitable habitat which are currently unoccupied. In classical metapopulation theory, each population cycles in relative independence of the other populations and eventually goes extinct as a consequence of demographic stochasticity (fluctuations in population size due to random demographic events); the smaller the population, the more chances of inbreeding depression and prone to extinction. Although individual populations have finite life-span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Landscape Connectivity
In landscape ecology, landscape connectivity is, broadly, "the degree to which the landscape facilitates or impedes movement among resource patches". Alternatively, connectivity may be a continuous property of the landscape and independent of patches and paths.Fischer, J. and D.B. Lindenmayer. 2006. Beyond fragmentation: the continuum model for fauna research and conservation in human-modified landscapes. Oikos, 112: 473–480. Connectivity includes both structural connectivity (the physical arrangements of disturbance and/or patches) and functional connectivity (the movement of individuals across contours of disturbance and/or among patches). Functional connectivity includes actual connectivity (requires observations of individual movements) and potential connectivity in which movement paths are estimated using the life-history data. A similar but different concept proposed by Jacques Baudry, landscape connectedness, refers to structural links between elements of spatial structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Michael E
SS ''Michael E'' was a cargo ship that was built in 1941. She was the first British catapult aircraft merchant ship (CAM ship): a merchant ship fitted with a rocket catapult to launch a single Hawker Hurricane fighter aircraft to defend a convoy against long-range German bombers. She was sunk on her maiden voyage by a German submarine. Description ''Michael E'' was built by William Hamilton & Co Ltd, Port Glasgow. Launched in 1941, she was completed in May of that year. She was the United Kingdom's first CAM ship, armed with an aircraft catapult on her bow to launch a Hawker Sea Hurricane. The ship was long between perpendiculars ( overall), with a beam of . She had a depth of and a draught of . She was measured at and . She had six corrugated furnaces feeding two single-ended boilers with a combined heating surface of . The boilers fed a 443 nominal horsepower triple-expansion steam engine that had cylinders of , and diameter by stroke. The engine was buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Richard Bierregaard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Thomas Lovejoy
Thomas Eugene Lovejoy III (August 22, 1941December 25, 2021) was an American ecologist who was President of the Amazon Biodiversity Center, a Senior Fellow at the United Nations Foundation and a university professor in the Environmental Science and Policy department at George Mason University. Lovejoy was the World Bank's chief biodiversity advisor and the lead specialist for environment for Latin America and the Caribbean as well as senior advisor to the president of the United Nations Foundation. In 2008, he also was the first Biodiversity Chair of the The H. John Heinz III Center For Science, Economics And The Environment, H. John Heinz III Center for Science, Economics and the Environment to 2013. Previously he served as president of the Heinz Center since May 2002. Lovejoy introduced the term ''biological diversity'' to the scientific community in 1980. He was a past chair of the Scientific Technical Advisory Panel (STAP) for the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the multibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh-largest by population, with over 212 million people. The country is a federation composed of 26 Federative units of Brazil, states and a Federal District (Brazil), Federal District, which hosts the capital, Brasília. List of cities in Brazil by population, Its most populous city is São Paulo, followed by Rio de Janeiro. Brazil has the most Portuguese-speaking countries, Portuguese speakers in the world and is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an Portuguese-speaking world, official language. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazil, coastline of . Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it Borders of Brazil, borders all other countries and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |