|
S12 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn)
Line S12 is a S-Bahn line of the S-Bahn Köln network in Germany. It is operated by DB Regio using DBAG Class 423, class 423 electric multiple units. The S12 runs from Horrem station, Horrem via Köln Hauptbahnhof, Cologne to Au (Sieg) station, Au (Sieg). It shares this route for most of its run with the S 19. With over , it is the second longest S-Bahn line in North Rhine-Westphalia, after S9 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn), S9. The S12 operates every 20 minutes Monday to Saturday between Köln Ehrenfeld and Hennef (Sieg), with every third train continuing to Au (Sieg). The S19 also operates hourly between Au (Sieg) and Hennef, so there is a service every 30 minutes. One S12 services an hour is extended to Horrem, so with the S19, four trains operate hourly in each direction between Hennef (Sieg), Cologne and Horrem. On Sundays and public holidays, the S12 operates every 30 minutes between Horrem and Au (Sieg). The route runs on the Cologne–Aachen high-speed railway, Cologne–Aachen line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-Bahn
The S-Bahn ( , ), , is a hybrid urban rail, urban–suburban rail system serving a metropolitan region predominantly in German language, German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit systems, while smaller ones often resemble Commuter rail, commuter or even regional rail systems. The name ''S-Bahn'' derives from (), (, not to be confused with the present-day ''Stadtbahn'') or (). Similar systems in Austria and German-speaking Switzerland are known as S-Bahn as well. In Belgium, it is known as S-Trein (Flemish dialects, Flemish) or Train S (French language, French). In Denmark, they are known as S-tog , and in the Czech Republic as Esko or S-lines. In Milan, they are known as Milan S Lines, Linee S. S-Bahn is also a treated as a Train categories in Europe, train category in several European countries. Characteristics There is no complete definition of an S-Bahn system. S-Bahn are, where they exist, the most local typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
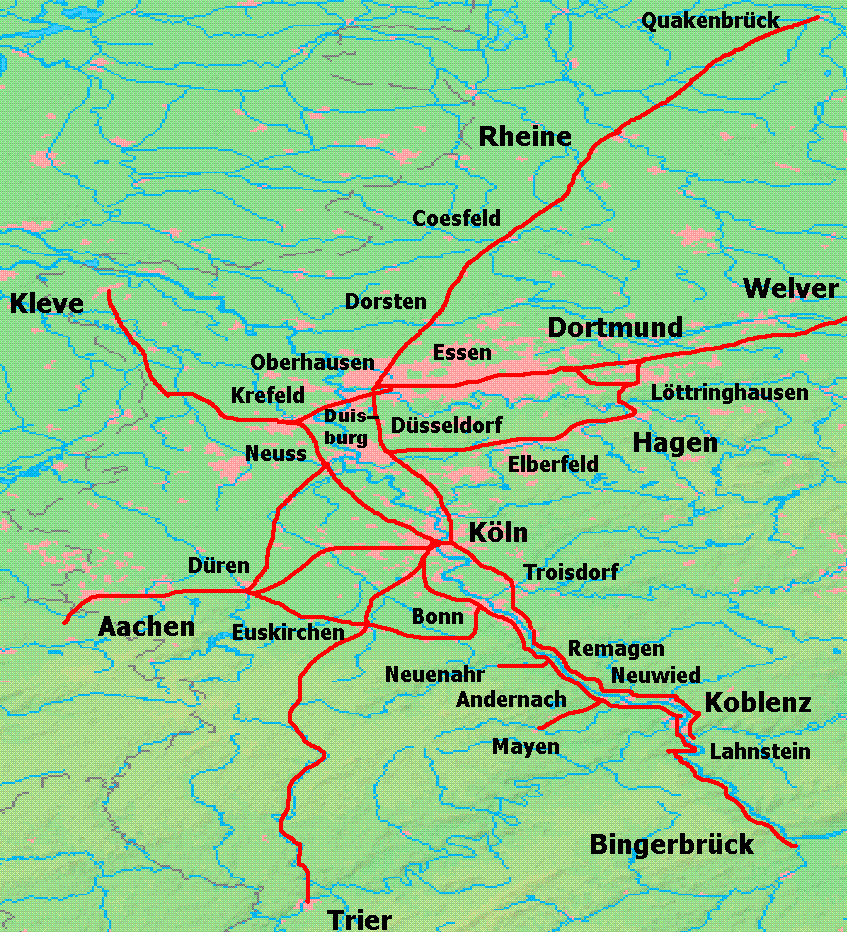
Troisdorf–Mülheim-Speldorf Railway
The Troisdorf–Mülheim-Speldorf railway is the main axis for freight between Cologne and the Ruhr area in Germany and the Netherlands. It connects the marshalling yards of Duisburg-Wedau (formerly important, now closed and demolished) and Gremberg (in Cologne). History The track was opened on 18 November 1874 by the Rhenish Railway Company () to connect its Ruhr line with the Right Rhine line. It runs parallel, but a few kilometres to the east of the Cologne–Duisburg trunk line opened by the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (''Cöln-Mindener Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'') thirty years earlier, from which it hoped to draw traffic. Since the line bypasses the centre of the towns, soon after the nationalisation of both companies in 1879/1880 passenger operations were closed on parts of it. Except on a few short sections the line is now used exclusively for freight. Passengers After the Second World War passenger services ran only on the section from Mülheim-Speldorf to Düsseldor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Rhine Railway
The East Rhine Railway (German: ''Rechte Rheinstrecke'', literally 'right (of the) Rhine railway') is a major, double-track, electrified railway line, running along the right bank of the Rhine from Cologne to Wiesbaden. The -long line forms two Deutsche Bahn routes. Route 465 extends from Cologne to Koblenz, via Troisdorf, Bonn-Beuel, Unkel, and Neuwied. From Koblenz, Route 466 extends to Wiesbaden, via Rüdesheim am Rhein. Together with the Taunus railway (Route 645.1), the line is used by Stadt-Express line SE-10 of the Rhine-Main Transport Association, which runs from Frankfurt to Koblenz and Neuwied. With the Cologne-Frankfurt high-speed railway and the Sieg Railway, the East Rhine Railway forms a six-track line between Cologne-Porz and Troisdorf. It includes two tunnels between Rüdesheim and Niederlahnstein, including the well-known Loreley Tunnel near Sankt Goarshausen. History Soon after the opening of the first railways in the region, a line on the right ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenish Railway Company
The Rhenish Railway Company (German language, German: ''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE) was along with the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) and the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (BME) one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Foundation The industrialists of the Rhineland and the Bergisches Land, then part of Prussia, sought to avoid paying the high tolls for using the Rhine imposed by the Netherlands and very early in its development, saw the possibility of the new means of transport, the railway. As early as the 1830s committees were established by the cities of the Rhineland to promote proposals for building railways. Some of the members of the Cologne committee under David Hansemann (1790–1864)—a merchant and banker from Aachen—and the Aachen Committee favoured a railway line through Belgium to the seaport of Antwerp via Liege. Belgium, which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne–Aachen High-speed Railway
The Cologne–Aachen high-speed line is the Germany, German part of the Trans-European transport networks project ''high-speed line Paris–Brussels–Cologne''. It is not a newly built railway line, but a project to upgrade the existing railway line which was opened in 1841 by the Rhenish Railway Company. When it was continued into Belgium in 1843, it became the world's first international railway line. The line inside Germany has a length of about . The first from Cologne to Düren have been rebuilt. Since 2002 the line allows for speeds up to . Separate tracks have been built parallel to the high-speed tracks for local Rhein-Ruhr S-Bahn, S-Bahn traffic. The remaining line from Düren to Aachen allows speeds up to with some slower sections. Upgrades of Düren–Aachen are planned for the near future. In Belgium, the high-speed line is continued as HSL 3. Regional-Express services on the line are RE 1 (''NRW-Express'') and RE 9 (''Rhein-Sieg-Express'') with push-pull trains wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB 423 256
DB, dB or db may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * ''Daily Bugle'' or ''DB'', a fictional New York City newspaper in Marvel Comics * ''Doing Business Report'', by the World Bank Group * Dragon Ball, a Japanese media franchise Music * D♭ (musical note) * DB Records, Atlanta, Georgia, US * The dB's, an American band in the 1980s * DJ DB, a New York–based British DJ Brands and enterprises * DB (car), a French automobile maker * Brit Air (IATA airline code) * DB Breweries, a New Zealand company * DB Networks, an American information security firm * Deutsche Bahn, a German railway company since 1994 * Deutsche Bank (NYSE symbol), a multinational investment bank headquartered in Frankfurt, Germany * Deutsche Bundesbahn, national railway company of the Federal Republic of Germany, 1949–1994 * Dolderbahn, a rack railway in Zürich, Switzerland Places * Dâmbovița County (ISO 3166-2:RO code), Romania * DB Draw, a bridge over the Passaic River, US * Discovery Bay, a resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S9 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn)
Line S 9 is an S-Bahn line on the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn, Rhine-Ruhr network, operated by DB Regio. It runs from Recklinghausen Hbf / Haltern am See station, Haltern am See in the north through Gladbeck West station, Gladbeck West - Essen Hauptbahnhof, Essen Hbf to Hagen Hauptbahnhof, Hagen (Westphalia) Main Station in the south. During the day two services per hour run between Wuppertal and Gladbeck West station, Gladbeck West, one service per hour between Gladbeck and Recklinghausen Hbf and Gladbeck and Haltern am See and one service per hour between Wuppertal and Hagen, using Stadler FLIRT, FLIRT 3XL electric multiple units. Line S 9 runs over lines built by various railway companies: *Line branch 1 from Wanne-Eickel-Hamburg railway, Recklinghausen Hbf (Wanne-Eickel-Hamburg railway) - to Oberhausen-Osterfeld Süd-Hamm railway, Abzwg Blumenthal (Oberhausen-Osterfeld Süd-Hamm railway), opened by Prussian state railways on 1 May 1905, direction Gladbeck West station, Gladbeck West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Au (Sieg) Station
Au (Sieg) station is a railway junction in the town of Au in the municipality of Windeck, which is in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It lies on the Sieg Railway to Siegen station, Siegen, where the Engers–Au railway branches off to Altenkirchen, where it connects with the Upper Westerwald Railway (''Oberwesterwaldbahn''). Despite the town’s small population, the junction station is important for commuters from the districts of Altenkirchen (district), Altenkirchen, Neuwied (district), Neuwied and Westerwaldkreis for its connections towards Siegen, Cologne, Bonn, Düsseldorf and Aachen. History Au station was opened in August 1860 as part of the Deutz–Gießen railway by the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (''Cöln-Mindener Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft''). The Engers–Au railway (''Oberwesterwaldbahn'', Upper Westerwald Railway) to Altenkirchen (Westerw) station, Altenkirchen was opened in May 1887, connecting to Engers station, Engers. Thus, it became a railway juncti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köln Hauptbahnhof
Köln Hauptbahnhof () is the central station, central railway station of Cologne, Germany. The station is an important local, national and international transport hub, with many Intercity-Express, ICE, Eurostar and Intercity (Deutsche Bahn), Intercity trains calling there, as well as regional Regional-Express, RegionalBahn and local Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn, S-Bahn trains. EuroNight and Nightjet night services also call at the station. It has frequent connections to Frankfurt by way of the Cologne–Frankfurt high-speed rail line, which starts in southern Cologne. On an average day, about 280,000 travellers frequent the station, making it the List of busiest railway stations in Germany, fifth busiest station in Germany. The station is situated next to Cologne Cathedral. There is another important station in Cologne, the Köln Messe/Deutz station across the river Rhine, just about 400 metres away from Köln Hauptbahnhof. The stations are linked by the Hohenzollern Bridge, a six-track rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horrem Station
Horrem station is a station in the Kerpen district of Horrem in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is a railway junction of the Cologne–Aachen high-speed railway and the Erft Railway (Horrem–Bedburg, connecting with Neuss Central Station, Neuss). The triangular station of Horrem is served by regional services and by S-Bahn trains of the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn. Long-distance trains run through on the high-speed line without stopping. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a German railway station categories, category 3 station. History The station was opened on 6 September 1841 along with the Köln-Lövenich station, Lövenich–Aachen Central Station, Aachen section of the Cologne–Aachen railway. The station building was demolished in 2012 and completely rebuilt in 2013. The new station building was built as part of a pilot project of Deutsche Bahn’s ''StationGreen XL-Modul'' program, strictly according to ecological principles and equipped with eco-friendly technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBAG Class 423
The Deutsche Bahn Class 423 EMU is a light-weight articulated electric railcar for S-Bahn commuter networks in Germany. The train has similar dimensions to its predecessor, the Class 420 EMU, but is significantly lighter and has one large passenger compartment, while that of the 420 is divided into three parts. The 423 additionally has six doors in each carriage (three on each side), which is down from eight on the 420 (four on each side). They are numbered from 423 001 to 423 462. Both Munich and Frankfurt ordered Class 423s for their S-Bahn systems; they were delivered between 1999 and 2004. The 423 has spawned a family of slightly modified designs ordered for S-Bahns across Germany: the Class 422, Class 424, Class 425/426 and Class 430. Description A Class 423 unit consists of four cars that share three jacobs bogies and can only be separated at maintenance facilities. The inner two cars are designated as Class 433. A 423 unit typically consists of the following cars, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |