|
S. Toraighyrov Pavlodar Regional Universal Scientific Library
The S. Toraighyrov Pavlodar Regional Universal Scientific Library is a library located in Pavlodar, Kazakhstan. It was established as a district library in 1896, evolving from a city library established a few years prior, growing in status through various political changes in Kazakhstan. With the formation of the Pavlodar Region in 1938, the library was granted the status of a regional library. In 1959, the library was named after Soviet writer Nikolay Ostrovsky. In 1996, as the library celebrated its centenary, it was renamed after the Kazakh writer Sultanmahmut Toraygirov, and consolidated its collections in multiple separate buildings into a single building at a new location. History In 1892, the Pavlodar municipal council established a city library and reading room, initially in a private home. Donations from merchant Artemy Ivanovich Derov and other patrons of the city raised funds for the library's maintenance. By 1896, it had become a ''Uyezd'' () Library, which is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to the China–Kazakhstan border, east, Kyrgyzstan to the Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, southeast, Uzbekistan to the Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, south, and Turkmenistan to the Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, while the largest city and leading cultural and commercial hub is Almaty. Kazakhstan is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, ninth-largest country by land area and the largest landlocked country. Steppe, Hilly plateaus and plains account for nearly half its vast territory, with Upland and lowland, lowlands composing another third; its southern and eastern frontiers are composed of low mountainous regions. Kazakhstan has a population of 20 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlodar
Pavlodar (; ; ) is a city in northeastern Kazakhstan and the capital of Pavlodar Region. It is located northeast of the national capital Astana and southeast of the Russian city of Omsk along the Irtysh River. In 2010, the city had a population of 331,710. The population of Pavlodar is composed predominantly of ethnic Kazakhs and Russians, with significant Ukrainian, German, Tatar and North Caucasian minorities. The city is served by Pavlodar Airport. History One of the oldest cities in northern Kazakhstan, Pavlodar was founded in the 9th century as the settlements of Khakan-Kimak and Imakia, the capitals of the Kimek–Kipchak confederation. Koryakovsky fort was founded in 1720 as an Imperial Russian outpost. The settlement was created to establish control over the region's salt lakes, an important source of valuable salt. In 1861 the settlement was renamed Pavlodar and incorporated as a town. Pavlodar's significance was due in large measure to the substantial agricul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
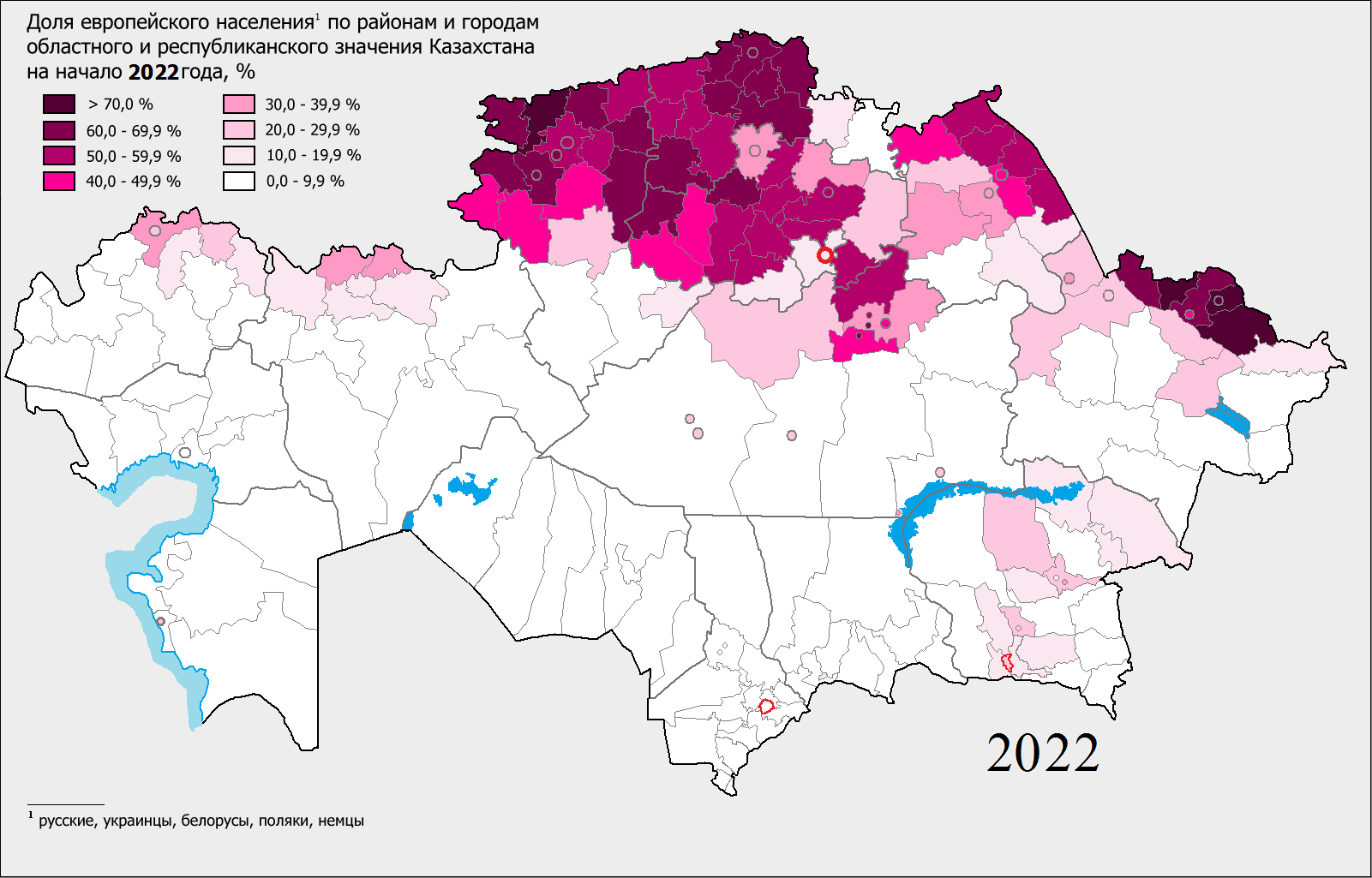
Pavlodar Region
Pavlodar Region (; ) is a region of Kazakhstan. The population of the region was and The latest official estimate (as at the start of 2022) was 756,511. Its capital is the city of Pavlodar, which had a population of 360,014 at the start of 2018. Many people, especially Ukrainians, migrated to Pavlodar in Nikita Khrushchev's Virgin Lands Campaign. The Bayanaul National Park, a protected area of the Kazakh Uplands, is located in the Bayanaul Range, within 100 km of Ekibastuz. Geography Pavlodar borders Russia ( Altai Krai, Omsk Oblast and Novosibirsk Oblast) to the north, and also borders the following Kazakh regions: Akmola (to the west), East Kazakhstan (to the south-east), North Kazakhstan (to the north-west), and Karaganda (to the south). The southern part of the district is in the Kazakh Uplands, while the northern part falls within the Baraba Plain and Kulunda Plain. The highest point of the region is Akbet, a high summit located in the Bayanaul Range. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolay Ostrovsky
Nikolai Alekseyevich Ostrovsky (; ; 29 September 1904 – 22 December 1936) was a Soviet socialist realist writer. He is best known for his novel '' How the Steel Was Tempered''. Life Ostrovsky was born in the village of ''Viliya'' (today a village in Rivne Raion (until 2020 it was situated in Ostroh Raion), Rivne Oblast) in the Volhynian Governorate (Volhynia), then part of the Russian Empire, into a Ukrainian working-class family. He attended a parochial school until he was nine and was an honor student. In 1914, his family moved to the railroad town of Shepetivka (today in Khmelnytskyi Oblast) where Ostrovsky started working in the kitchens at the railroad station, a timber yard, then becoming a stoker's mate and then an electrician at the local power station. In 1917, at the age of thirteen he became a Bolshevik party activist. At the same period he developed ankylosing spondylitis, which would later blind and paralyze him. According to the official biography, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanmahmut Toraygirov
Sultanmakhmut Toraygirov (, ''Sūltanmahmūt Toraiğyrov''; 29 October 1893 – 21 May 1920) was a prominent Kazakh writer and poet. He was born in Kyzyltu (near the city of Kokshetau) but moved to Bayanaul in the province of Pavlodar at the age of four. Toraygirov wrote his first poems when only 13 years old. From 1913 on, he was the sub-editor for the first Kazakh journal ''Aikap''. In 1914 and 1915 he worked as a teacher in Bayanaul. In 1916 Toraygirov moved to Tomsk in Russia, but the next year the February Revolution made him return to Semey, in Kazakhstan. During this time he developed his style and wrote prolifically. Toraygirov released several poem collections and his novel ''Beauty Kamar'', released posthumously in 1933, was one of the first Kazakh language novels. He was very active politically, advocating both Kazakh national interests and the new Soviet ideals. Toraygirov died in 1920 at the age of 26. The state university in Pavlodar Pavlodar (; ; ) is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the laboring and exploited people, article I. was a socialist state from 1917 to 1922, and afterwards the largest and most populous Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republic of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1922 to 1991, until becoming a Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Russian SFSR, sovereign part of the Soviet Union with priority of Russian laws over Union-level legislation in 1990 and 1991, the last two years of the existence of the USSR.The Free Dictionary Russian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian State Library
The Russian State Library () is one of the three national libraries of Russia, located in Moscow. It is the largest library in the country, second largest in Europe and one of the largest in the world. Its holdings crossed over 47 million units in 2017. It is a federal library overseen by the Ministry of Culture, including being under its fiscal jurisdiction. Its foundation lay in the opening of the Moscow Public Museum and Rumyantsev Museum in Moscow in 1862. This museum evolved from a number of collections, most notably Count Nikolay Rumyantsev's library and historical collection. It was renamed after Lenin in 1924, popularly known as the Lenin Library or Leninka, and its current name was adopted in 1992. See: The library has several buildings of varying architectural styles. In 2012 the library had over 275 km of shelves, including over 17 million books and serial volumes, 13 million magazines, 370 thousand music scores and sound records, 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Kazakhstan, the Kazakh SSR, KSSR, or simply Kazakhstan, was one of the transcontinental country, transcontinental Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1936 to 1991. Located in northern Central Asia, it was created on 5 December 1936 from the Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic, Kazakh ASSR, an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics of the Soviet Union, autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. At in area, it was the second-largest republic in the USSR, after the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Its capital was Almaty, Alma-Ata (today known as Almaty). During its existence as a Soviet Socialist Republic, it was ruled by the Communist Party of Kazakhstan (Soviet Union), Communist Party of the Kazakh SSR (QKP). On 25 October 1990, the Supreme Soviet of the Kazakh SSR declared its sovereignty on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akim
An ''akim'' (, , әкімдер / ''äkimder''; ; , ) is the head of a local government in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. ''Akim'' is derived from the Arabic word '' hakim'', which means "ruler" or "governor". Definitions Kazakhstan In Kazakhstan, an ''äkim'' is the head of an ''äkimdik'', a municipal, district, or provincial government (''äkimdik''), and serves as the Presidential representative. ''Äkims'' of regions and cities are appointed to the post by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. Meanwhile, the ''äkims'' of other administrative and territorial units are appointed or selected to the post in an order defined by the President. He may also dismiss äkims from their posts. Powers of ''äkims'' ends with the introduction into the post of new-elected president of the republic. Thus, the ''äkim'' continues to fulfill the duties before appointment of corresponding äkim by the President of Kazakhstan. Kyrgyzstan In Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan, offici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libraries In Kazakhstan
A library is a collection of books, and possibly other materials and media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location, a virtual space, or both. A library's collection normally includes printed materials which may be borrowed, and usually also includes a reference section of publications which may only be utilized inside the premises. Resources such as commercial releases of films, television programmes, other video recordings, radio, music and audio recordings may be available in many formats. These include DVDs, Blu-rays, CDs, cassettes, or other applicable formats such as microform. They may also provide access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. In addition, some libraries offer creation stations for makers which offer access to a 3D printing station with a 3D scanner. Libraries can vary widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |