|
Ruyi (scepter)
A ''ruyi'' () is a Chinese curved decorative object that serves as either a ceremonial scepter in Chinese Buddhism or a talisman symbolizing power and good fortune in Chinese folklore. The "ruyi" image frequently appears as a motif in Asian art. A traditional ''ruyi'' has a long S-shaped handle and a head fashioned like a fist, cloud, or lingzhi mushroom. ''Ruyi'' are constructed from diverse materials. For example, the Palace Museum in Beijing has nearly 3,000 ''ruyi'' variously made of gold, silver, iron, bamboo, wood, ivory, coral, rhinoceros horn, lacquer, crystal, jade, and precious gems. Word The Chinese term ''ruyi'' is a compound of ''ru'' 如 "as; like; such as; as if; for example; supposing; be like; be similar; accord with" and ''yi'' 意 "wish; will; desire; intention; suggestion; thought; idea; meaning; imagination". Standard Chinese uses ''ruyi'' either as a stative verb meaning "as desired; as one wishes, as one likes; according to one's wishes; following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia Museum Of Art
The Philadelphia Museum of Art (PMA) is an List of art museums#North America, art museum originally chartered in 1876 for the Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia. The main museum building was completed in 1928 on Fairmount, a hill located at the northwest end of the Benjamin Franklin Parkway at Eakins Oval. The museum administers collections containing over 240,000 objects including major holdings of European, American and Asian origin. The various classes of artwork include sculpture, paintings, prints, drawings, photographs, armor, and decorative arts. The Philadelphia Museum of Art administers several annexes including the Rodin Museum, also located on the Benjamin Franklin Parkway, and the Perelman Building, Ruth and Raymond G. Perelman Building, which is located across the street just north of the main building. The Perelman Building, which opened in 2007, houses more than 150,000 prints, drawings and photographs, 30,000 costume and textile pieces, and over 1,000 modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese Language
Vietnamese () is an Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic language Speech, spoken primarily in Vietnam where it is the official language. It belongs to the Vietic languages, Vietic subgroup of the Austroasiatic language family. Vietnamese is spoken natively by around 86 million people, and as a second language by 11 million people, several times as many as the rest of the Austroasiatic family combined. It is the native language of Vietnamese people, ethnic Vietnamese (Kinh), as well as the second language, second or First language, first language for List of ethnic groups in Vietnam, other ethnicities of Vietnam, and used by Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese diaspora in the world. Like many languages in Southeast Asia and East Asia, Vietnamese is highly analytic language, analytic and is tone (linguistics), tonal. It has head-initial directionality, with subject–verb–object order and modifiers following the words they modify. It also uses noun classifier (linguistics), classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthold Laufer
Berthold Laufer (October 11, 1874 – September 13, 1934) was a German anthropologist and historical geographer with an expertise in East Asian languages. The American Museum of Natural History calls him "one of the most distinguished sinologists of his generation". Life Laufer was born in Cologne in Germany to Max and Eugenie Laufer (née Schlesinger). His paternal grandparents Salomon and Johanna Laufer were adherents of the Jewish faith. Laufer had a brother Heinrich (died 10 July 1935) who worked as a physician in Cairo. Laufer attended the Friedrich Wilhelms Gymnasium from 1884 to 1893. He continued his studies in Berlin (1893–1895), and completed his doctorate in oriental languages at the University of Leipzig in 1897. The following year he emigrated to the United States where he remained until his death. He carried out ethnographic fieldwork on the Amur River and Sakhalin Island during 1898–1899 as part of the Jesup North Pacific Expedition. He was fluent in more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Yuan Of Han
Emperor Yuan of Han, personal name Liu Shi (劉奭; 75 BC – 8 July 33 BC), was an Emperor of China, emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty. He reigned from 48 BC to 33 BC. Emperor Yuan promoted Confucianism as the official creed of the Chinese government. He appointed adherents of Confucius to important government posts. However, at the same time that he was solidifying Confucianism's position as the official ideology, the empire's condition slowly deteriorated due to his indecisiveness, his inability to stop factional infighting between officials in his administration, and the trust he held in certain corrupt officials. He was succeeded by Emperor Cheng of Han, Emperor Cheng. Family background When Emperor Yuan was born Liu Shi in 75 BC, his parents Emperor Xuan of Han, Liu Bingyi and Xu Pingjun were commoners without titles. Bingyi was a great-grandson of Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu, and his grandfather Liu Ju was Emperor Wu's crown prince, until Emperor Wu's paranoia forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jing Fang
Jing Fang () (78–37 BC), born Li Fang (), courtesy name Junming (), was a Chinese music theorist, mathematician and astronomer born in present-day Puyang, Henan during the Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD). Although better known for his work in musical measurements, he also accurately described the basic mechanics of lunar and solar eclipses. Yijing The historian Ban Gu (32–92 AD) wrote that Jing Fang was an expert at making predictions from the hexagrams of the ancient ''Yijing''. A book on Yijing divination attributed to him describes the najia method of hexagram interpretation, which correlates their separate lines with elements of the Chinese calendar. Not only was he instrumental in the development of Yijing correlative cosmology, but he has also shed a new light on China's history, in particular Qin and Han. Music theory According to the 3rd-century historian Sima Biao, Jing Fang received an appointment as an official in the Music Bureau under Emperor Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fangshi
''Fangshi'' () were Chinese technical specialists who flourished from the third century BCE to the fifth century CE. English translations of include alchemist, astrologer, diviner, exorcist, geomancer, doctor, magician, monk, mystic, necromancer, occultist, omenologist, physician, physiognomist, technician, technologist, thaumaturge, and wizard. Etymology The Chinese word combines and . Many English-language texts transliterate this word as (older texts use ), but some literally translate it. *"gentlemen possessing magical recipes" *"recipe gentlemen" *"masters of recipes" *"'direction-scholar', that is, one versed in interpreting omens from their orientation" [from "wind angle" divination below] *"Esoteric Masters" *"gentleman who possess techniques, technician" *"masters of recipes and methods" *"masters of methods" *"masters of esoterica" The Chinese historian Yu Ying-shi concludes that "as a general term, may be translated 'religious Taoists' or 'popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanshu
The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), an Eastern Han court official, with the help of his sister Ban Zhao, continuing the work of their father, Ban Biao. They modelled their work on the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (), a cross-dynastic general history, but theirs was the first in this annals-biography form to cover a single dynasty. It is the best source, sometimes the only one, for many topics such as literature in this period. The ''Book of Han'' is also called the ''Book of the Former Han'' () to distinguish it from the '' Book of the Later Han'' () which covers the Eastern Han period (25–220 CE), and was composed in the fifth century by Fan Ye (398–445 CE). Contents This history developed from a continuation of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consort Qi (Han Dynasty)
Consort Qi (224? – 194 BC), also known as Lady Qi, was a consort of Emperor Gaozu, founder of the Han dynasty. Biography It is important to note that most of our information about Lady Qi comes from sources whose accuracy might be in question and authors known for hyperbole. Her rival, Empress Lü Zhi, was used to symbolize the supposed dangers of women in power; thus, Lady Qi and her alleged fate have been formed into a rhetorical tool. Qi was born in Dingtao, Shandong. She bore Emperor Gaozu a son Liu Ruyi, who was later installed as Prince of Zhao. Gaozu felt that the crown prince Liu Ying, the future Emperor Hui of Han (his second son) was an unsuitable heir to his throne. He tried several times, fruitlessly, to replace Liu Ying with Liu Ruyi, over the objections of Liu Ying's mother, Empress Lü Zhi. Because of this, Lü Zhi hated Qi deeply. Nevertheless, Gaozu ordered Liu Ruyi to proceed to his principality of Zhao (capital in present-day Handan, Hebei) on his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
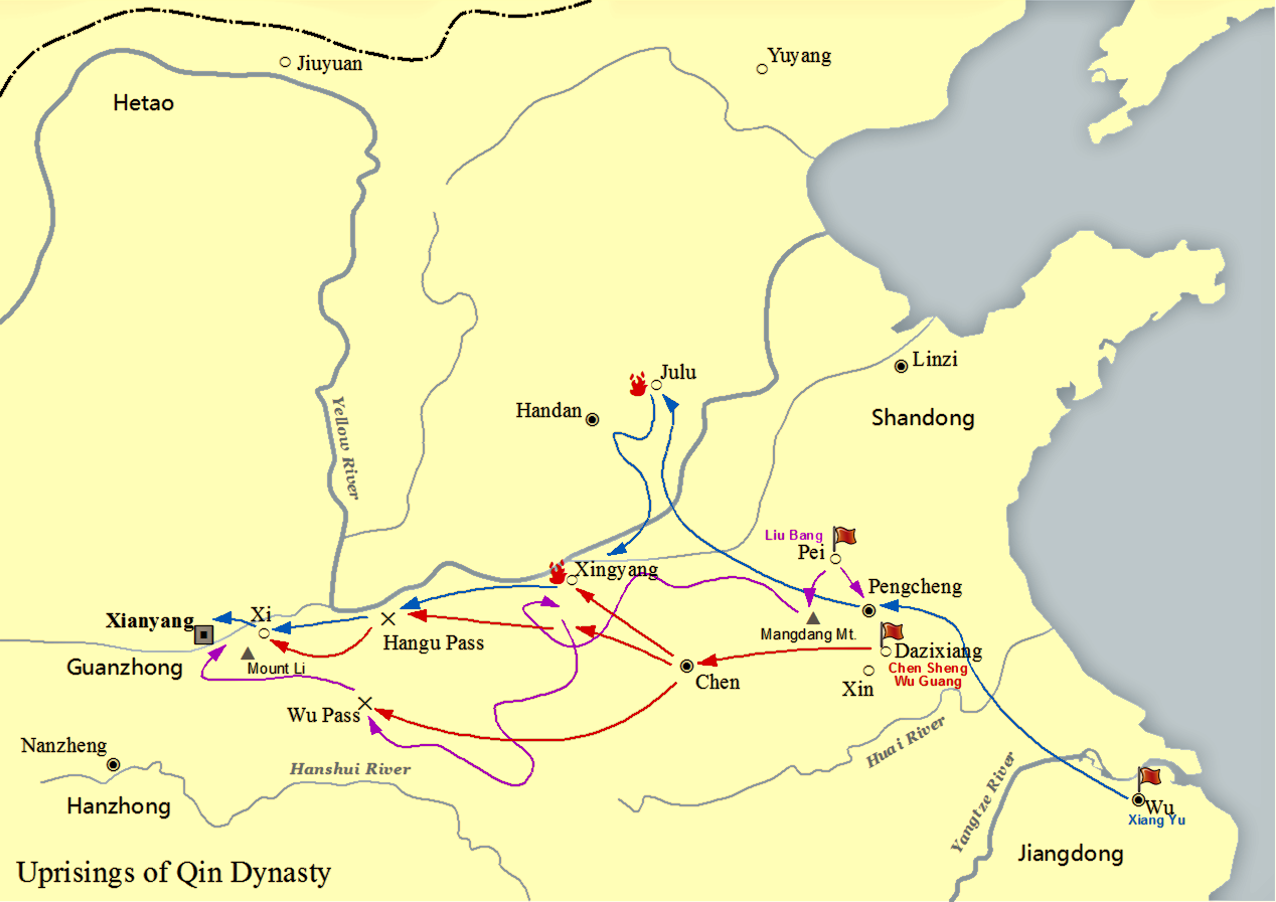
Emperor Gaozu Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (2561 June 195 BC), also known by his given name Liu Bang, was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 202 to 195 BC. He is considered by traditional Chinese historiography to be one of the greatest emperors in history, credited with establishing the first Pax Sinica, one of China's longest golden ages. Liu Bang was among the few dynastic founders to have been born in a peasant family. He initially entered the Qin dynasty bureaucracy as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town in Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. During the political chaos following the death of Qin Shi Huang, who had been the first emperor in Chinese history, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became a rebel leader, taking up arms against the Qin dynasty. He outmanoeuvred rival rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland and forced the surrender of the Qin ruler Ziying in 206 BC. After the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Ruyi
Liu Ruyi (208 – January 194BCAccording to volume 12 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'', Liu Ruyi was poisoned in the 12th month of the 1st year of Emperor Hui's reign. This corresponds to 31 Dec 195 BCE - 28 Jan 194 BCE in the proleptic Julian calendar.), posthumously known as the "Suffering King of Zhao" (趙隱王, ''Zhào Yǐnwáng''), was the only son of the first Han emperor Liu Bang's concubine Consort Qi. He was a favorite of the emperor and appointed king or prince of Dai and Zhao, but loathed by his stepmother, the Empress Lü Zhi, as consort Qi had attempted to persuade Liu Bang to have Liu Ruyi replace Liu Ying (Lü's son) as crown prince. Despite his half-brother Emperor Hui's protection, she finally succeeded in killing him in 194BC. Life Liu Ruyi was the third son of Liu Bang, the founder of China's Han dynasty who became posthumously known as Emperor Gaozu ("High Ancestor"). He was the only son of the concubine Consort Qi. As a boy, after his uncle Liu Zhong aban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiji
The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st centuries BC by the Han dynasty historian Sima Qian, building upon work begun by his father Sima Tan. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Shiji'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and Qin Shi Huang, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Shiji'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historiographical conventions, the ''Shiji'' does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |