|
Ruspina
Ruspina was a Phoenician, Carthaginian and Roman town located in Monastir, Tunisia, situated in Roman times in '' Africa propria'', and mentioned by Pliny the Elder and Ptolemy. Name The Phoenician and Punic name () or () seems to mean "Angle Cape". It was used for the cape and hills at the south end of the Bay of Hammamet and for the main settlement near the cape. The Punic name was variously hellenized as ''Rhouspînon'' (),Strabo, ''Geogr.'', Book XVII, Ch. iii, §12. ''Rhouspino'', (), ''Rhouspína'' (), or ''Rhoúspina'' () but consistently latinized as Ruspina. Geography The exact location of the city is uncertain. Nathan Davis believes it was located at modern day Monastir. Multiple tombs and ruins have been discovered in this city that may have been part of Ruspina. History The Carthaginian town came under Roman hegemony after the Punic Wars. In 46BC, the town was the first in Africa to ally itself with Julius Caesar during his civil war. Jul. Caes., '' Bell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ruspina
The Battle of Ruspina was fought on 4 January 46 BC in the Roman province of Africa, between the Republican forces of the Optimates and forces loyal to Julius Caesar. The Republican army was commanded by Titus Labienus, Caesar's former lieutenant during the Gallic Wars who had defected to the Republican side at the beginning of the civil war. Prelude Julius Caesar entered Lilybaeum in Sicily on 17 December 47 BC and assembled an army there to defeat the Optimates in Africa. He set sail on 25 December, but his limited intelligence about a proper landing site and winds scattered his fleet. He had six legions and 2,000 cavalry but only the bare necessity of supplies due to a lack of shipping. Caesar landed near Hadrumentum with 3,500 legionaries and 150 cavalry. The city's garrison refused to surrender and Caesar set up camp at Ruspina. On 1 January 46 BC, he arrived at Leptis where he was reinforced by some of his scattered troops (elements of fifth and the tenth legions). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
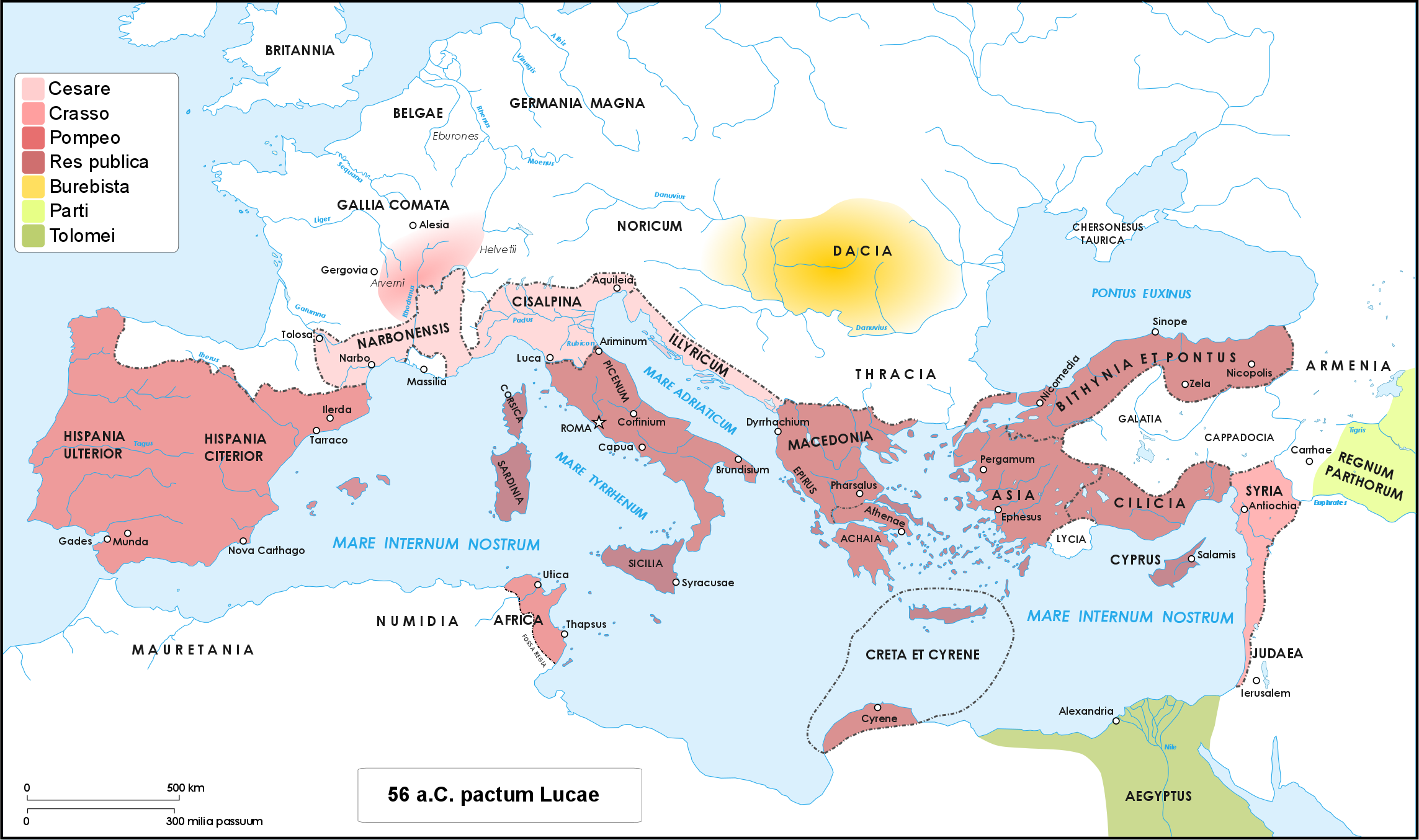
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastir, Tunisia
Monastir, also called Mestir ( ', from the Greek "hermit's cell, monastery"), is a city on the central coast of Tunisia, in the Sahel area, some south of Sousse and south of Tunis. Traditionally a fishing port, Monastir is now a major tourist resort. Its population is about 93,306. It is the capital of Monastir Governorate. Geography Location Monastir is a peninsula surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea on three sides and forming, to the south, the Gulf of Monastir of the same name, which extends to Cap of Ras Dimass. It offers diverse landscapes, in particular its sandy and rocky beaches as well as a cliff stretching over nearly six kilometers. History Monastir was founded on the ruins of the Punic– Roman city of Ruspina. The city features a well-preserved Ribat of Monastir that was used to scan the sea for hostile ships and as a defence against the attacks of the Byzantine fleet. Several ulema came to stay in the ''ribat'' of this peaceful city for contemplation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Labienus
Titus Labienus (17 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul and mentioned frequently in the accounts of his military campaigns, Labienus chose to oppose him during the Civil War and was killed at Munda. He was the father of Quintus Labienus. Biography Early career As his praetorship was in 60 or 59 BC, Titus Labienus most likely was born around 100 BC.Tyrrell (3) Many sources suggest that he came from the town of Cingulum in Picenum. His family was of equestrian status. He most likely had early ties with Pompey during his time as a patron for Picenum and his desire to rise in military rank. His early service was c. 78–75 BC in Cilicia under Publius Servilius Vatia Isauricus fighting pirates and the Isaurian hill tribes. Tribune of the Plebs, Trial of Gaius Rabirius In 63 BC, Titus Labienus was a tribune of the Ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthaginian Empire
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest ''metropoleis'' in the world.George Modelski, ''World Cities: –3000 to 2000'', Washington DC: FAROS 2000, 2003. . Figures in main tables are preferentially cited. Part of former estimates can be read at Evolutionary World Politics Homepage Archived 2008-12-28 at the Wayback Machine It was the centre of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power led by the Punic people who dominated the ancient western and central Mediterranean Sea. Following the Punic Wars, Carthage was Siege of Carthage (Third Punic War), destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC, who later rebuilt Roman Carthage, the city lavishly. Carthage Phoenician settlement of No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civilization which expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel. The Phoenicians extended their cultural influence through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula, evidenced by thousands of Phoenician inscriptions. The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions after the decline of most major Mediterranean basin cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. They called themselves Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, but the territory they occupied was notably smaller than that of Bronze Age Canaan. The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy's Geography
The ''Geography'' (, , "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, compiling the geographical knowledge of the 2nd-century Roman Empire. Originally written by Claudius Ptolemy in Greek at Alexandria around 150 AD, the work was a revision of a now-lost atlas by Marinus of Tyre using additional Roman and Persian gazetteers and new principles. Its translation – Kitab Surat al-Ard – into Arabic by Al-Khwarismi in the 9th century was highly influential on the geographical knowledge and cartographic traditions of the Islamic world. Alongside the works of Islamic scholars – and the commentary containing revised and more accurate data by Alfraganus – Ptolemy's work was subsequently highly influential on Medieval and Renaissance Europe. Manuscripts Versions of Ptolemy's work in antiquity were probably proper atlases with attached maps, although some scholars believe that the refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Colonies In Tunisia
Phoenician may refer to: * Phoenicia, an ancient civilization * Phoenician alphabet **Phoenician (Unicode block) * Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism * Phoenician language * List of Phoenician cities See also * Phoenix (mythology) The phoenix is a Legendary creature, legendary immortal bird that cyclically regenerates or is otherwise born again. Originating in Greek mythology, it has analogs in many cultures, such as Egyptian mythology, Egyptian and Persian mythology. Ass ... * Phoenix (other) * Phoenicia (other) * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. As a young man, he was a partisan and protégé of the dictator Sulla, after whose death he achieved much military and political success himself. He was an ally and a rival of Julius Caesar, and died in civil war with him. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first consulship without following the traditional '' cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated three triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bello Africo
''De Bello Africo'' (also ''Bellum Africum''; ''On the African War'') is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's accounts of his campaigns, '' De Bello Gallico'' and '' De Bello Civili'', and its sequel by an unknown author '' De Bello Alexandrino''. It details Caesar's campaigns against his Republican enemies in the province of Africa. Authorship ''De Bello Africo'' is preceded by '' De Bello Alexandrino'' and followed by '' De Bello Hispaniensi''. These three works end the Caesarean corpus relating Caesar's Civil War. The historical narratives, though attributed to Caesar, are assumed to have been written by three different anonymous authors around 40 BC. Though normally collected and bound with Caesar's authentic writings, their authorship has been debated since antiquity. One very plausible theory favors Aulus Hirtius as the author of '' De Bello Alexandrino'' (see there for details). But due to considerable differences in style, scholarly consensus has agreed that neither ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region, and a four-year-long Mercenary War, revolt against Carthage. The First Punic War broke out on the Mediterranean island of Sicily in 264BC as a result of Rome's expansionary attitude combined with Carthage's proprietary approach to the island. At the start of the war Carthage was the dominant power of the western Mediterranean, with an extensive maritime empire (a thalassocracy), while Rome was a rapidly expanding power in Roman Italy, Italy, with a strong Roman army of the mid-Republic, army but no navy. The fighting took place primarily on Sicily and its surrounding waters, as well as in North Africa, Corsica and Sardinia. It lasted twenty-three years, until 241BC, when the Carthaginians were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |