|
Run On The Pound
Sterling crisis may refer to: * 1931 sterling crisis, emergency measures during the Great Depression * 1949 sterling crisis, devaluation * 1967 sterling crisis, devaluation * 1976 sterling crisis, IMF loan * 1992 sterling crisis ("Black Wednesday"), depreciation See also * Currency crisis A currency crisis is a type of financial crisis, and is often associated with a real economic crisis. A currency crisis raises the probability of a banking crisis or a default crisis. During a currency crisis the value of foreign denominated deb ... {{disambiguation Balance of payments Financial crises Economic history of the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1931 Sterling Crisis
Events January * January 2 – South Dakota native Ernest Lawrence invents the cyclotron, used to accelerate particles to study nuclear physics. * January 4 – German pilot Elly Beinhorn begins her flight to Africa. * January 22 – Sir Isaac Isaacs is sworn in as the first Australian-born Governor-General of Australia. * January 25 – Mohandas Gandhi is again released from imprisonment in India. * January 27 – Pierre Laval forms a government in France. * January 30 – Charlie Chaplin comedy drama film ''City Lights'' receives its public premiere at the Los Angeles Theater with Albert Einstein as guest of honor. Contrary to the current trend in cinema, it is a silent film, but with a score by Chaplin. Critically and commercially successful from the start, it will place consistently in lists of films considered the best of all time. February * February 4 – Soviet leader Joseph Stalin gives a speech calling for rapid industrialization, arguing that only strong indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1949 Sterling Devaluation
The devaluation of sterling in 1949 (or 1949 sterling crisis) was a major currency crisis in the United Kingdom that led to a 30.5% devaluation of sterling from $4.04 per pound to $2.80 on 18 September 1949. Although the devaluation was made in the United Kingdom, over 19 countries had currencies pegged to sterling and also devalued. Historical context The devaluation, unlike the competitive 1931 sterling devaluation, was done in cooperation between all European nations. There was a general understanding among European nations that sterling was overvalued and would need to be devalued. The IMF was in favour of a devaluation and wanted it to happen to allow other European currencies to also devalue. The timing of the devaluation remained unsure. This led to progressive pressure on the currency, up to a breaking point forcing the British government to devalue. The fundamental cause of the devaluation was a structural trade deficit of the United Kingdom with the United States. Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1967 Sterling Devaluation
The 1967 sterling devaluation (or 1967 sterling crisis) was a devaluation of pound sterling, sterling from $2.80 to $2.40 per pound sterling, pound on 18 November 1967. It ended a long currency crisis, sterling crisis that had started in 1964 with the election of Labour Party (UK), Labour in the 1964 United Kingdom general election, 1964 general election, but originated in the balance of payments crises of the preceding Conservative government. Historical background As soon as Harold Wilson's newly elected Labour government took power after winning the 1964 United Kingdom general election, 1964 general election, vowing to end the Conservatives' "stop-go" economic policies, sterling came under pressure because the market feared that Labour would devalue the currency so as to be able to implement a looser monetary policy, favouring growth. Upon coming to power, the government was informed that they had inherited an exceptionally large deficit of £800 million on Britain's external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
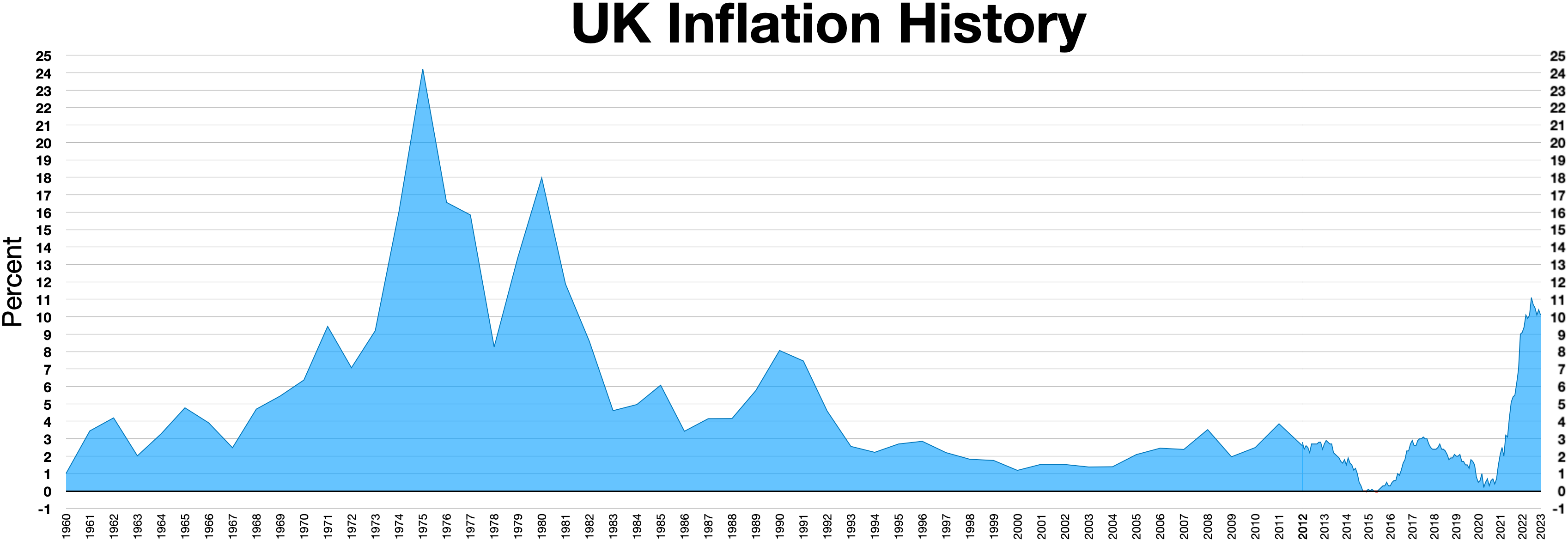
1976 Sterling Crisis
The 1976 sterling crisis was a currency crisis in the United Kingdom. Inflation (at close to 25% in 1975, causing high bond yields and borrowing costs), a balance-of-payments deficit, a public-spending deficit, and the 1973 oil crisis were contributors. The origins of the crisis have been attributed to the 1972 Conservative "spend for growth" budget initiating the inflation cycle. James Callaghan's Labour government had to borrow $3.9 billion from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), with the intention of maintaining the value of sterling. At the time this was the largest loan ever to have been requested from the IMF. History Initiation of the inflationary cycle is traced to Anthony Barber's 1972 budget which was designed to return the Conservatives to power in an election expected in 1974 or 1975. This budget led to a brief period of growth known as "The Barber Boom," followed by a wage-price spiral, high inflation and currency depreciation, culminating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Wednesday
Black Wednesday, or the 1992 sterling crisis, was a financial crisis that occurred on 16 September 1992 when the UK Government was forced to withdraw sterling from the (first) European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERMI), following a failed attempt to keep its exchange rate above the lower limit required for ERM participation. At that time, the United Kingdom held the Presidency of the Council of the European Union. The crisis damaged the credibility of the second Major ministry in handling of economic matters. The ruling Conservative Party suffered a landslide defeat five years later at the 1997 general election and did not return to power until 2010. The rebounding of the UK economy in the years following Black Wednesday has been attributed to the depreciation of sterling and the replacement of its currency tracking policy with an inflation targeting monetary stability policy. Prelude When the ERM was set up in 1979, the United Kingdom declined to join. This was a contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency Crisis
A currency crisis is a type of financial crisis, and is often associated with a real economic crisis. A currency crisis raises the probability of a banking crisis or a default crisis. During a currency crisis the value of foreign denominated debt will rise drastically relative to the declining value of the home currency. Generally doubt exists as to whether a country's central bank has sufficient foreign exchange reserves to maintain the country's fixed exchange rate, if it has any. The crisis is often accompanied by a speculative attack in the foreign exchange market. A currency crisis results from chronic balance of payments deficits, and thus is also called a balance of payments crisis. Often such a crisis culminates in a devaluation of the currency. Financial institutions and the government will struggle to meet debt obligations and economic crisis may ensue. Causation also runs the other way. The probability of a currency crisis rises when a country is experiencing a banki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Of Payments
In international economics, the balance of payments (also known as balance of international payments and abbreviated BOP or BoP) of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time (e.g., a quarter or a year) and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. In other words, it is economic transactions between countries during a period of time. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services. The balance of payments consists of three primary components: the current account, the financial account, and the capital account. The current account reflects a country's net income, while the financial account reflects the net change in ownership of national assets. The capital account reflects a part that has little effect on the total, and represents the sum of unilateral capital account transfers, and the acquisitions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Crises
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with Bank run#Systemic banking crises, banking panics, and many recessions coincided with these panics. Other situations that are often called financial crises include stock market crashes and the bursting of other financial Economic bubble, bubbles, currency crisis, currency crises, and sovereign defaults. Financial crises directly result in a loss of paper wealth but do not necessarily result in significant changes in the real economy (for example, the crisis resulting from the famous tulip mania bubble in the 17th century). Many economists have offered theories about how financial crises develop and how they could be prevented. There is little consensus and financial crises continue to occur from time to time. It is apparent however that a consistent feature of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |