|
Rumaila Oil Field
The Rumaila oil field is a super-giant oil field located in southern Iraq, approximately 50km to the south west of Basra City. Discovered in 1953 by the Basrah Petroleum Company (BPC), an associate company of the Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC), Page 471in: the field is estimated to contain 17 billion barrels, which accounts for 12% of Iraq's oil reserves, estimated at 143 billion barrels. Rumaila is said to be the largest oilfield ever discovered in Iraq and one of the three largest oilfields in the world. Under Abdul-Karim Qasim, the oilfield was nationalised by the Iraqi government by Public Law No. 80 on 11 December 1961. Since then, this massive oil field has remained under Iraqi control. The assets and rights of IPC were nationalized by Saddam Hussein in 1972, and those of BPC in 1975. The dispute between Iraq and Kuwait over alleged slant-drilling in the field was one of the reasons for Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990. After decades of under investment, due to san ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the Iraq–Kuwait border, southeast, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest, and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The country covers an area of and has Demographics of Iraq, a population of over 46 million, making it the List of countries by area, 58th largest country by area and the List of countries by population, 31st most populous in the world. Baghdad, home to over 8 million people, is the capital city and the List of largest cities of Iraq, largest in the country. Starting in the 6th millennium BC, the fertile plains between Iraq's Tigris and Euphrates rivers, referred to as Mesopotamia, fostered the rise of early cities, civilisations, and empires including Sumer, Akkadian Empire, Akkad, and Assyria. Known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserves-to-production Ratio
The reserves-to-production ratio (RPR or R/P) is the remaining amount of a non-renewable resource, expressed in time. While applicable to all natural resources, the RPR is most commonly applied to fossil fuels, particularly petroleum and natural gas. The ''reserve'' portion (numerator) of the ratio is the amount of a resource known to exist in an area and to be economically recoverable (proven reserves). The ''production'' portion (denominator) of the ratio is the amount of resource produced in one year at the current rate. ''RPR = (amount of known resource) / (amount used per year)'' This ratio is used by companies and government agencies in forecasting the future availability of a resource to determine project life, future income, employment, etc., and to determine whether more exploration must be undertaken to ensure continued supply of the resource. Annual production of a resource can usually be calculated to quite an accurate number. However, reserve quantities can only be es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majnoon Oil Field
The Majnoon Oil Field is a super-giant oil field located from Basra in southern Iraq. Majnoon is one of the richest oilfields in the world with an estimated 38 billion barrels of oil reserves. The field was named ''Majnoon'' which means ''crazy'' in Arabic in reference to excessive amount of oil in a dense area. History The field was discovered by Braspetro, a Brazilian company in 1975, under the leadership of Bolivar Montenegro Guerra in a shallow Upper Cretaceous formation. Development came to a halt in 1980 during the engineering phase of the project, due to Iran–Iraq War, particularly Operation Kheibar. At the time, Braspetro had finished drilling of 20 wells and pressed 14 drilling rigs into service. In the course of the war, Iran occupied and sabotaged the area. After the war, Southern Oil Company of Iraq restarted the production. In the1990's, Total S.A. of France negotiated a development contract with Saddam Hussein but was unable to sign the deal due to United Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghawar Field
Ghawar (Arabic: الغوار) is an oil field located in Al-Ahsa Governorate, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Measuring (some ), it is by far the largest conventional oil field in the world, and accounts for roughly a third of the cumulative oil production of Saudi Arabia as of 2018. Ghawar is entirely owned and operated by Saudi Aramco, the state-run Saudi oil company. In April 2019, the company first published its profit figures since its nationalization nearly 40 years ago in the context of issuing a bond to international markets. The bond prospectus revealed that Ghawar is able to pump a maximum of per day—well below the more than per day that had become conventional wisdom in the market. Geology Ghawar occupies an anticline above a basement fault block dating to Carboniferous time, about 320million years ago; Cretaceous tectonic activity, as the northeast margin of Africa began to impinge on southwest Asia, enhanced the structure. Reservoir rocks are Jurassic Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into the ocean or coastal waters, but spills may also occur on land. Oil spills can result from the release of crude oil from oil tanker, tankers, Oil platform, offshore platforms, drilling rigs, and Oil well, wells. They may also involve spills of Oil refinery, refined petroleum products, such as gasoline and diesel fuel, as well as their by-products. Additionally, heavier fuels used by large ships, such as bunker fuel, or spills of any oily refuse or waste oil, contribute to such incidents. These spills can have severe environmental and economic consequences. Oil spills penetrate into the structure of the plumage of birds and the fur of mammals, reducing its insulating ability, and making them more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations and muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconventional (oil And Gas) Reservoir
Unconventional (oil and gas) reservoirs, or unconventional resources (resource plays) are Petroleum geology, accumulations where oil and gas Phase (matter), phases are tightly bound to the rock fabric by strong capillary action, capillary forces, requiring specialized measures for evaluation and Petroleum extraction, extraction. Conventional reservoir Oil and gas are Petroleum#Transformation of kerogen into fossil fuels, generated naturally at depths of around 4 or 5 km below Earth’s Earth#Surface, surface. Being lighter than the water-Groundwater, saturated rocks below the water table, the oil and gas are driven by buoyancy up through aquifer pathways towards Earth's surface over time. Some of the oil and gas percolate all the way to the surface as natural Petroleum seep, seepages, either on land or on the sea floor. The rest remains trapped underground by Petroleum reservoir#seal rock, geological barriers in a variety of Petroleum reservoir#Geology#traps, trap geometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Flare
A gas flare, alternatively known as a flare stack, flare boom, ground flare, or flare pit, is a gas combustion device used in places such as petroleum refineries, chemical plants and natural gas processing plants, oil or gas extraction sites having oil wells, gas wells, offshore oil and gas rigs and landfills. In industrial plants, flare stacks are primarily used for burning off flammable gas released by safety valves during unplanned overpressuring of plant equipment. (See Chapter 11, ''Flare Stack Plume Rise''). During plant or partial plant startups and shutdowns, they are also often used for the planned combustion of gases over relatively short periods. At oil and gas extraction sites, gas flares are similarly used for a variety of startup, maintenance, testing, safety, and emergency purposes. In a practice known as production flaring, they may also be used to dispose of large amounts of unwanted associated petroleum gas, possibly throughout the life of an oil well. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Gas
Liquefied petroleum gas, also referred to as liquid petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas), is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, ''n''-butane and isobutane. It can also contain some propylene, butylene, and isobutylene/isobutene. LPG is used as a fuel gas in heating appliances, cooking equipment, and vehicles, and is used as an aerosol propellant and a refrigerant, replacing chlorofluorocarbons in an effort to reduce the damage it causes to the ozone layer. When specifically used as a vehicle fuel, it is often referred to as autogas or just as gas. Varieties of LPG that are bought and sold include mixes that are mostly propane (), mostly butane (), and, most commonly, mixes including both propane and butane. In the northern hemisphere winter, the mixes contain more propane, while in summer, they contain more butane. In the United States, mainly two grades of LPG are sold: commercial propane and HD-5. These specifications a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbons, Aromatic
Aromatic compounds or arenes are organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties: * Typically unreactive * Often non polar and hydrophobic * High carbon-hydrogen ratio * Burn with a strong sooty yellow flame, due to high C:H ratio * Undergo electrophilic substitution reactions and nucleophilic aromatic substitutions Arenes are typically split into two categories - benzoids, that contain a benzene derivative and follow the benzene ring model, and non-benzoids that contain other aromatic cyclic derivatives. Aromatic compounds are commonly used in organic synthesis and are involved in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
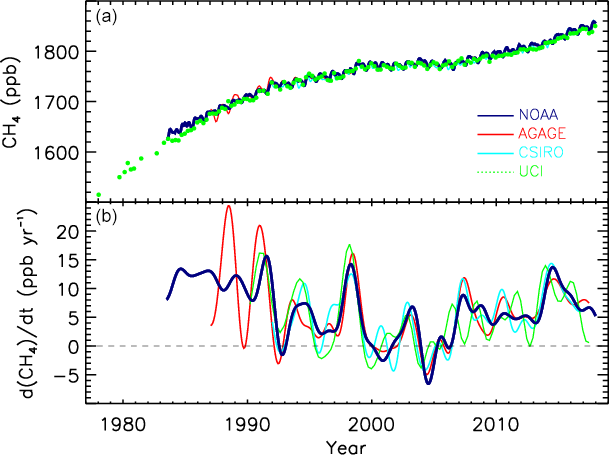
Methane Emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40% (230 million tons). Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits. Since the Industrial Revolution, concentrations of Atmospheric methane, methane in the atmosphere have more than doubled, and about 20 percent of the warming the planet has experienced can be attributed to the gas. About one-third (33%) of anthropogenic greenhouse gases, anthropogenic emissions are from gas release during the mining, extraction and delivery of fossil fuels; mostly due to gas venting and gas leaks from both active fossil fuel infrastructure and orphan wells. Russia is the world's top methane e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Health (Iraq)
The Ministry of Health is a central government ministry of Iraq tasked to provide health and medical services to every Iraqi citizen in normal times as well as times of emergency. Since 2022 the minister of health is Saleh Mehdi Al-Hasnawi. Vision The Ministry's mission is to respond to the needs of the public regarding healthcare services by developing organisational structures that facilitate sustainability and decentralisation. Additionally, the Ministry delivers and develops policies, strategies, regulations, laws and frameworks in order to improve and reform the healthcare system. Furthermore, the Ministry works to establish a healthy working environment that encourages continuous professional development. Finally, the Ministry seeks to improve scientific research output for the purpose of promoting the healthcare services in Iraq. Organizational structure *First Deputy **Blood Transfusion Center **Health Education Dept. **Finance & Auditing Dept. * Second Deputy **Liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-National Force – Iraq
The Multi-National Force – Iraq (MNF–I), often referred to as the Coalition forces, was a U.S.-led military command during the Iraq War from 2004 to 2009. The vast majority of MNF-I was made up of United States Army forces. However it also supervised British, Australian, Polish, Spanish, and other countries' forces. It replaced the previous force, Combined Joint Task Force 7, on 15 May 2004. It was significantly reinforced during the Iraq War troop surge of 2007. MNF-I was reorganized into its successor, United States Forces – Iraq, on 1 January 2010. The United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq, which does humanitarian work and has a number of guards and military observers, has also operated in Iraq since 2003. The U.N. Assistance Mission in Iraq was not a part of the MNF-I, but a separate entity. The NATO Training Mission – Iraq, was in Iraq from 2004 to December 2011, where it trained the Iraqi Army and the Iraqi Police. History The MNF-I's objectives, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |