|
Rudraprayag
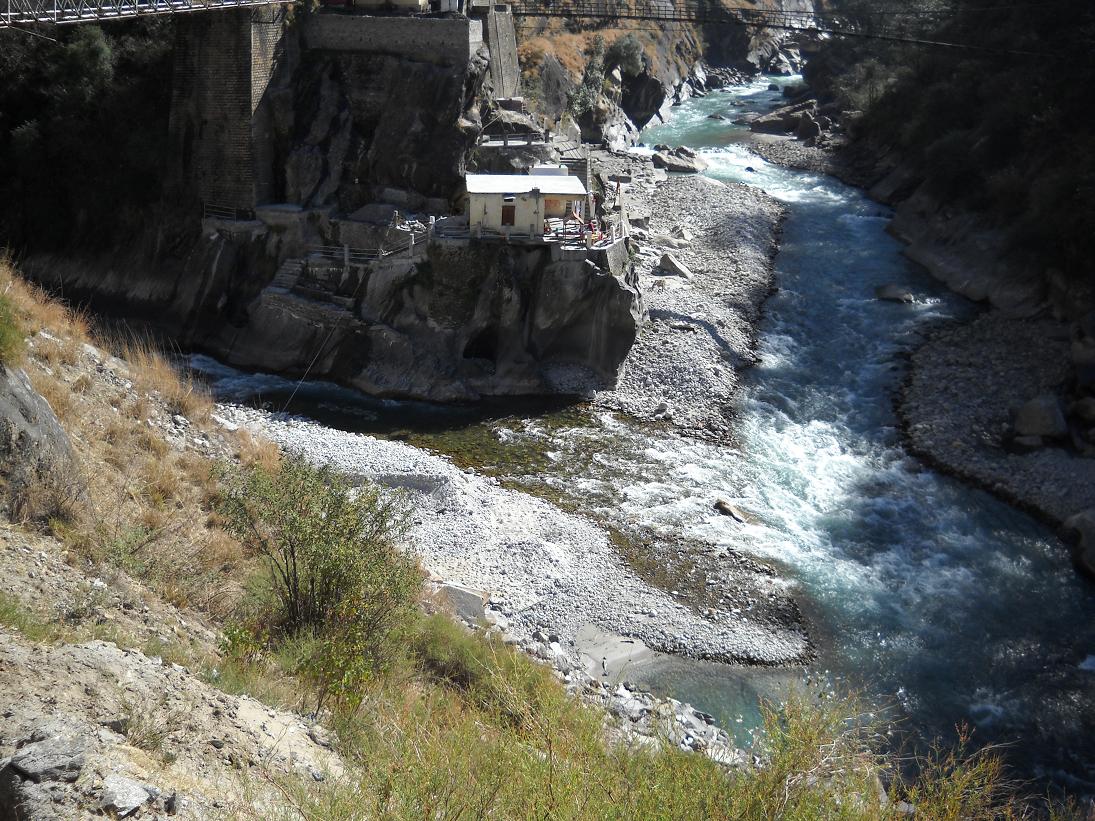
Rudraprayag is a city and a municipality in Rudraprayag district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Rudraprayag is one of the Panch Prayag (five confluences) of Alaknanda River, the point of confluence of rivers Alaknanda and Mandakini. Kedarnath, a Hindu holy city, is located 86 km from Rudraprayag. The man-eating leopard of Rudraprayag hunted and written about by Jim Corbett lived here. Geography Rudraprayag district is located at . It has an average elevation of 895 metres (2,936 feet). Many of the newer buildings and particularly the S''angam'' (confluence) area was severely damaged in the 2013 Uttarakhand floods. A footbridge over the Mandakini river and a road bridge 6 km downstream at Raitoli was washed away. The layout of the Sangam has altered significantly. The road along the Mandakini valley, leading to Kedarnath, was damaged at many points. Demographics According to the 2011 census, the population of Rudraprayag is 9,313, of which 5,2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudraprayag District
Rudraprayag is a district of the state of Uttarakhand of northern India. The district occupies an area of 1984 km2. The town of Rudraprayag is the administrative headquarters of the district. The district is bounded by Uttarkashi District on the north, Chamoli District on the east, Pauri Garhwal District on the south, and Tehri Garhwal District on the west. Overview Rudraprayag District was established on 16 September 1997. It was carved out from the following areas of three adjoining districts: * The whole of Augustmuni and Ukhimath block and part of Pokhri and Karnprayag block from Chamoli District * Part of Jakholi and Kirtinagar block from Tehri District * Part of Khirsu block from Pauri District The internationally known Kedarnath Temple is at the north, Madmaheshwar at east, Nagrasu at southern east and Srinagar at extreme south. The Mandakini River is the main river of the district. As of 2011 it is the least populous district of Uttarakhand (out of 13). Demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopard Of Rudraprayag
The Leopard of Rudraprayag was a male man-eating leopard that measured to about 228.6 cm (7 ft 6 in) long, reputed to have killed over 125 people. It was eventually killed by hunter and author Jim Corbett. Attacks The first victim of the leopard was from Benji Village, and was killed in 1918. For the next eight years, people were afraid to venture alone at night on the road to the Hindu holy shrines of Kedarnath and Badrinath, for it passed through the leopard's territory, and few villagers left their houses after dark. The leopard, preferring human flesh, would break down doors, leap through windows, claw through the mud or thatch walls of huts and drag the occupants out before devouring them. According to official records, the leopard killed over 125 people. However, Corbett notes that the number of deaths was probably higher as a result of unreported kills and deaths due to injuries sustained in attacks. Hunt for the leopard Units of Gurkha soldiers and British soldiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaknanda
The Alaknanda is a Himalayan river in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and one of the two headstreams of the Ganges, the major river of Northern India and a river considered holy in Hinduism. In hydrology, the Alaknanda is considered the headstream, source stream of the Ganges on account of its greater length and discharge; while, in Hindu tradition and culture, the other headstream, the Bhagirathi River, Bhagirathi, is considered the source stream. Course The Alaknanda rises at the confluence and foot of the Satopanth Glacier, Satopanth and Bhagirath Kharak glaciers in Uttarakhand. From its origin, it travels to the village of Mana, India, Mana, meets with the Saraswati River (Uttarakhand), Saraswati River, a right bank tributary, and continues downstream through narrow valleys. It reaches the Badrinath valley, arrives at Hanumanchatti, and meets with the Ghrit Ganga, a right bank tributary. From Hanumanchatti, the river goes to Pandukeshwar and flows through wide valleys and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaknanda River
The Alaknanda is a Himalayan river in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and one of the two headstreams of the Ganges, the major river of Northern India and a river considered holy in Hinduism. In hydrology, the Alaknanda is considered the source stream of the Ganges on account of its greater length and discharge; while, in Hindu tradition and culture, the other headstream, the Bhagirathi, is considered the source stream. Course The Alaknanda rises at the confluence and foot of the Satopanth and Bhagirath Kharak glaciers in Uttarakhand. From its origin, it travels to the village of Mana, meets with the Saraswati River, a right bank tributary, and continues downstream through narrow valleys. It reaches the Badrinath valley, arrives at Hanumanchatti, and meets with the Ghrit Ganga, a right bank tributary. From Hanumanchatti, the river goes to Pandukeshwar and flows through wide valleys and steep terrains. At Vishnuprayag it meets Dhauliganga, a left bank tributary, and travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Corbett
Edward James Corbett (25 July 1875 – 19 April 1955) was an Anglo-Indian hunter and author. He gained fame through hunting and killing several man-eating tigers and leopards in Northern India, as detailed in his bestselling 1944 memoir '' Man-Eaters of Kumaon''. In his later years, he became an outspoken advocate of the nascent conservation movement. Born in Naini Tal, Corbett explored and hunted in the jungles of India in childhood. He shot his first man-eater in 1907 and continued to hunt and kill such animals over the next four decades. Animals such as the Champawat Tiger, the Leopard of Rudraprayag, and the Panar Leopard had taken hundreds of victims in the divisions of Kumaon and Garwhal, before their deaths at Corbett's hands. ''Man-Eaters of Kumaon'', which detailed several such hunts, became an international bestseller; it was followed by several other books and was adapted into a 1948 Hollywood film. Corbett increasingly disdained what he saw as the rapacious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedarnath
Kedarnath is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand, India, known primarily for the Kedarnath Temple. It is approximately 86.5 kilometres from Rudraprayag, the district headquarters. Kedarnath is the most remote of the four Chota Char Dham pilgrimage sites. It is located in the Himalayas, about above sea level near the Chorabari Glacier, which is the source of the Mandakini River. The town is flanked by snow-capped peaks, most prominently the Kedarnath Mountain. The nearest road head is at Gaurikund about 16 km away. The town suffered extensive destruction during June 2013 from the flash floods caused by torrential rains in Uttarakhand. Etymology The name "Kedarnath" means "the Lord of the Field". It is derived from the Sanskrit words ''kedara'' ("field") and ''natha'' ("lord"). The text ''Kashi Kedara Mahatmya'' states that it is so-called because "the crop of liberation" grows here. History Kedarnath is a pilgrimage site or '' tirt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panch Prayag
Panch Prayag (Pañcha prayāga) is an expression in Hindu religious ethos, specifically used to connote the five sacred river confluences in the Garhwal Himalayas in the state of Uttarakhand, India. The five ''prayag''s - ''prayaga'' meaning "place of confluence of rivers" in Sanskrit - also termed as "Prayag pentad" are Vishnuprayag, Nandaprayag, Karnaprayag, Rudraprayag and Devprayag, in the descending flow sequence of their occurrence. Alaknanda + Dhauliganga = Vishnu Prayag Alaknanda + Nandakini = Nand Prayag Alaknanda + Pindarganga = Karna Prayag Alaknanda + Mandakini = Rudra Prayag Alaknanda + Bhagirathi = Dev Prayag Path The three most holy rivers, Ganga, Yamuna and Sarasvati, originate in this area. According to the holy texts the river Sarasvati too was a tributary of Ganga and used to join it at the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj along with Yamuna. But, the Mahabharat mentions that it later dried. Today Sarasvati joins Alaknanda at Keshav Prayag in Mana village before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandakini River
The Mandakini River is a tributary of the Alaknanda River in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. The river runs for approximately between the Rudraprayag and Sonprayag areas and emerges from the Chorabari Glacier. The Mandakini merges with river Songanga at Sonprayag and flows past the Hindu temple Madhyamaheshwar at Ukhimath. At the end of its course it drains into the Alaknanda, which flows into the Ganges. The Mandakini is considered by Hindus a sacred river within Uttarakhand as it runs past the Kedarnath and Madhyamaheshwar temples. For this reason, the Mandakini has been the site of pilgrimages and religious tourism, with treks passing significant sites of spirituality such as Tungnath and Deoria Tal. The Mandakini area also attracts millions of tourists annually for whitewater rafting, hiking, and religious tours around the winter Chardham being offered. In 2011, more than 25 million tourists visited the river (for comparison, the State of Uttarakhand has a popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand (, ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2007), is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the northwest, Tibet to the north, Nepal to the east, Uttar Pradesh to the south and southeast, with a small part touching Haryana in the west. Uttarakhand has a total area of , equal to 1.6% of the total area of India. Dehradun serves as the state capital, with Nainital being the judicial capital. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal division, Garhwal and Kumaon division, Kumaon, with a total of List of districts of Uttarakhand, 13 districts. The forest cover in the state is 45.4% of the state's geographical area. The cultivable area is 16% of the total geographical area. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, originate from the Gangotri and Yamunotri glaciers respectively. Ranked 6th among the Top 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwali Language
Garhwali (, , in native pronunciation) is an Indo-Aryan language of the Central Pahari subgroup. It is primarily spoken by over million Garhwali people in the Garhwal region of the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand in the Indian Himalayas. Garhwali has a number of regional dialects. It is not an endangered language (''Ethnologue'' lists it as "vigorous"), it is nonetheless designated as "vulnerable" in UNESCO's ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'', which indicates that the language requires consistent conservation efforts. Names ''Ethnologue'' has catalogued alternate names by which Garhwali is known such as ''Gadhavali, Gadhawala, Gadwahi, Gashwali, Girwali, Godauli, Gorwali, Gurvali,'' and ''Pahari Garhwali''. These alternate names of the language may have come from the speakers having more than one name for their language, or variant Romanisations of what is essentially the same name. Gadwallis schollar Gadwall's Kukareithi use Gadwallis or Gaddish for al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts Of India
A district (''Zila (country subdivision), zila''), also known as revenue district, is an Administrative divisions of India, administrative division of an States and union territories of India, Indian state or territory. In some cases, districts are further subdivided into Revenue division, sub-divisions, and in others directly into tehsil, ''tehsils'' or ''talukas''. , there are a total of 780 districts in India. This count includes Mahe and Yanam which are Census districts and not Administrative districts and also includes the temporary Maha Kumbh Mela district but excludes Itanagar Capital Complex which has a Deputy Commissioner but is not an official district. District Administration ;The District officials include: *District Judge (India), District & Sessions Judge (Principal & additional), an officer belonging to the Judiciary of India, Indian Judicial Service (state), responsible for justice and passing orders of imprisonment, including the Capital punishment, death pena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |