|
Royal Greenland Trade Department
The Royal Greenland Trading Department (, KGH) was a Danish state enterprise charged with administering the realm's settlements and trade in Greenland. The company managed the government of Greenland from 1774 to 1908 through its Board of Managers in Copenhagen and a series of Royal Inspectors and Governors in Godthaab and Godhavn on Greenland. The company was headquartered at Grønlandske Handels Plads at Christianshavn. Following the introduction of home rule in Greenland in 1979, the company was reformed into several successors, including the KNI conglomerate, the Royal Greenland fishing company, and the Royal Arctic shipping company. History The Royal Greenland Trading Department was founded in 1774 as a successor to the failed General Trade Company (') which had previously managed the Dano-Norwegian whaling stations and Lutheran and Moravian missions in Greenland. At first, it possessed a monopoly on trade near the Danish trading stations and missions but, in 1776, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grønlandske Handels Plads (1810)
(Kongelige) Grønlandske Handels Plads (English language, English: "(Royal) Greenland Dock") is a waterfront area at the end of Strandgade in the northwestern corner of the Christianshavn neighbourhood of Copenhagen, Denmark. The area is bounded by the Trangraven canal to the north, Christianshavns Kanal, Christianshavn Canal to the east, Krøyers Plads to the south and the main harbor to the west. The waterfront is also known as Nordatlantens Brygge (English: North Atlantic Quay). It is named for the Royal Greenland Trading Department and was for more than 200 years a hub for Danish trade on Greenland, Iceland and the Faroe Islands. The most notable building is North Atlantic House, an 18th-century warehouse now used as a cultural centre for the North Atlantic area. The threeway Trangravsbroen bridge connects Grønlandske Handelsplads to Holmen, Copenhagen, Holmen on the other side of Trangraven and Bodenhoffs Plads (Islands Plads) on the other side of Christianshavn Canal while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Missions In Greenland
The Moravian missions in Greenland (; ; ) were established by the Moravian Church or United Brethren and operated between 1733 and 1900. They were operated under the auspices of the Royal Danish College of Missions until its dissolution in 1859 and were finally surrendered to the Lutheran Church of Denmark in 1900. Missionaries were allocated to the region and sometimes even sent wives who had been chosen for them and approved by the drawing of lots, a form of Cleromancy. List of missions * Neu-Herrnhut (settled by Matthäus Stach, Christian Stach, and Christian David in 1733 and formally established in 1747 at modern Nuuk) * Lichtenfels (founded by Matthaeus Stach, Jens Haven, and Peter Haven in 1748, Lüdecke, Cornelia.East Meets West: Meteorological observations of the Moravians in Greenland and Labrador since the 18th century". ''History of Meteorology'' 2, 2005. 1754,Cranz, David & al. The History of Greenland: including an account of the mission carried on by the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
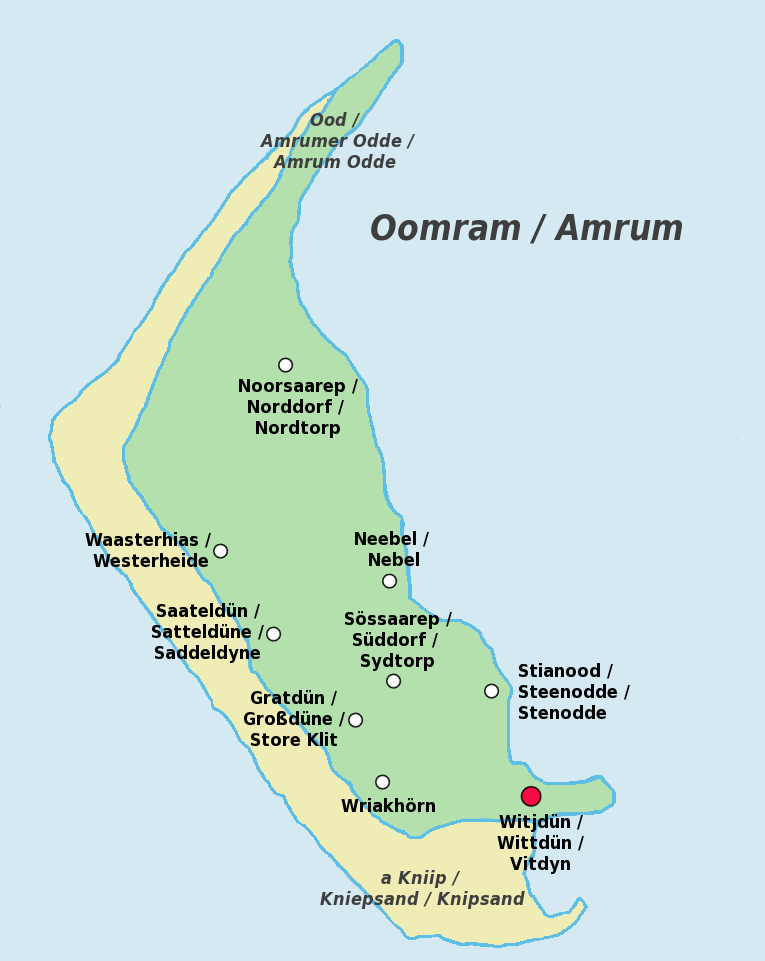
Amrum
Amrum (; Öömrang, ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the Germany, German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants. The island is made up of a sandy core of geestland and features an extended beach all along its west coast, facing the open North Sea. The east coast borders to mudflats of the Wadden Sea. Sand dunes are a characteristic part of Amrum's landscape, resulting in a vegetation that is largely made up of heath and shrubs. The island's only forest was planted in 1948. Amrum is a refuge for many species of birds and a number of marine mammals including the grey seal and harbour porpoise. Settlements on Amrum have been traced back to the Neolithic period when the area was still a part of the mainland of the Jutland peninsula. During the Middle Ages, Frisians, Frisian settlers arrived at Amrum and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Ministry Of The Interior
The Ministry of the Interior and Health () is a former Danish ministry that has existed twice in the 21st century by combination of existing ministries. The Ministry of Interior and Health was first created in 2001 under the first government of Anders Fogh Rasmussen, by combining the Ministry of the Interior (''Indenrigsministeriet'') and the Ministry of Health (''Sundhedsministeriet''). The minister was Lars Løkke Rasmussen and the permanent secretary Ib Valsborg, succeeded in 2005 by Christian Schønau. The ministry carried out a far-reaching . After the 2007 Folketing elections, the ministry was disbanded, and its areas of responsibility divided between two newly created ministries, the Ministry of Welfare and the Ministry of Health and Prevention. The ministry was recreated in February 2010 under Rasmussen's first government as Prime Minister, with the minister being Bertel Haarder and the permanent secretary . In October 2011 the Rasmussen government was succeeded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriolit Mine Og Handels Selskabet
Ivittuut (formerly, Ivigtût) ( Kalaallisut: "Grassy Place") is an abandoned mining town near Cape Desolation in southwestern Greenland, in the modern Sermersooq municipality on the ruins of the former Norse Middle Settlement. Ivittuut is one of the few places in the world so far discovered to have naturally occurring cryolite (Na3AlF6, sodium aluminum fluoride), an important agent in modern aluminum extraction. History The area was settled by about twenty farms of Norsemen, a district called the "Middle Settlement" by modern archaeologists from its placement between the larger Western and Eastern Settlements. It is the smallest and least well known of the three, and no written records of its residents survive, for which reasons it is believed to have been established last (and abandoned first) of the three. Investigations show a presence after 985 and with occupation continuing up to at least the 14th century. The town's cryolite deposit was discovered in 1799, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryolite
Cryolite ( Na3 Al F6, sodium hexafluoroaluminate) is a rare mineral identified with the once-large deposit at Ivittuut on the west coast of Greenland, mined commercially until 1987. It is used in the reduction ("smelting") of aluminium, in pest control, and as a dye. History Cryolite was first described in 1798 by Danish veterinarian and physician (1740–1801), from rock samples obtained from local Inuit who used the mineral for washing their hides; the actual source of the ore was later discovered in 1806 by the explorer Karl Ludwig Giesecke. who found the deposit at Ivigtut (old spelling) and nearby Arsuk Fjord, Southwest Greenland, where it was extracted by Øresund Chemical Industries. The name is derived from the Greek words (), and (). The Pennsylvania Salt Manufacturing Company used large amounts of cryolite to make caustic soda and fluorine compounds, including hydrofluoric acid at its Natrona, Pennsylvania, works, and at its integrated chemical plant in Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsissaet
The ''parsissaet'', (sometimes translated as local councils or guardian councils) were a form of local council in Greenland Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ... between 1857 and 1911. They were created by the Royal Greenland Trading Department (KGH). 1840 Commission In 1840, a government commission investigating the Greenland trade issued a report proposing that the KGH be operated on a non-profit basis, reïnvesting any surplus towards benefiting the Kalaallit, native Greenlanders; this was accepted, although the company reserved the right to interest on the government's investment into Greenland.Sørensen, Axel Kjaer. "Denmark-Greenland in the Twentieth Century". ''Meddelelser om Grønland'' [''Monographs on Greenland'']: ''Man and Society'', No. 34. The Commission f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinrich Rink
Dr. Hinrich Johannes Rink (first name sometimes as Henrik) (26 August 1819 – 15 December 1893) was a Danish geologist, one of the pioneers of glaciology, and the first accurate describer of the inland ice of Greenland. Rink, who first came to Greenland in 1848, spent 16 winters and 22 summers in the Arctic region, and became notable for Greenland's development. Becoming a Greenlandic scholar and administrator, he served as Royal Inspector of South Greenland and went on to become Director of the Royal Greenland Trading Department. With "Forstanderskaber", Rink introduced the first steps towards Greelandic home rule. Rink carried out and printed in four volumes the first systematic collection of Greenlandic oral tradition stories. He was the founder of '' Atuagagdliutit'', the first Kalaallisut language newspaper. Early years Rink was born in Copenhagen to Holstein parents. His father was Johannes Rink (1783–1865), a Kiel, Germany merchant, and his mother was Agnese Marga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Augustus Inglefield Two European Men Greenland 1854
Edward is an English male name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet The House of Plantagenet ( /plænˈtædʒənət/ ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by modern historians to identify four distinct royal houses: the Angev ... dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III of England, Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I of England, Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian Peninsula#Modern Iberia, Iberian peninsula since the 15th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Greenland
The Southern Inspectorate of Greenland (), also known as South Greenland, was a Danish inspectorate on Greenland consisting of the trading centers and missionary stations along the southwest coast of the island. History West Greenland was divided into the Southern Inspectorate and the Northern Inspectorate (North Greenland) from 1782. The boundary between the two ran at around 68°N latitude. Bell, James (1831). ''A System of Geography, Popular and Scientific''. Vol. 5p. 281 The Southern Inspectorate's northernmost town was Holstensborg, now Sisimiut, south of Egedesminde, now Aasiaat, which was the southernmost town of North Greenland. The Southern Inspectorate extended southwards to 59°30'N, or to the southernmost point of Greenland. The capital was at Godthaab (modern Nuuk). In 1911, as the administration of the colony was removed from the Royal Greenland Trading Department and folded into the Danish Ministry of the Interior The Ministry of the Interior and Health () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Greenland
The Northern Inspectorate of Greenland (), also known as North Greenland, was a Danish inspectorate on Greenland consisting of the trading centers and missionary stations along the northwest coast of the island. History West Greenland was divided into the Northern Inspectorate and the Southern Inspectorate ( South Greenland) from 1782. The boundary between the two ran at around 68°N latitude. The Northern Inspectorate's southernmost town was Egedesminde, now Aasiaat, north of Holstensborg, now Sisimiut, which was the northernmost town of South Greenland. The Northern Inspectorate extended northwards up to and including Upernavik, or, according to Bell (1831), to 78°N Bell, James (1831). ''A System of Geography, Popular and Scientific''. Vol. 5p. 281 to enclose Thule. The capital was at Godhavn (modern Qeqertarsuaq). In 1911, as the administration of the colony was removed from the Royal Greenland Trading Department The Royal Greenland Trading Department (, KGH) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |