|
Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.4a
The Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.4a was an experimental British single-engined scout aircraft of the First World War. Four S.E.4a aircraft were built, being used for research purposes and as home-defence fighters by the Royal Flying Corps. In spite of its type number it had little or no relationship to the earlier S.E.4 Development and design In 1915, Henry Folland of the Royal Aircraft Factory designed a new single-engined scout aircraft, the S.E.4a. While it had a similar designation to Folland's earlier Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.4 of 1914, which had been designed to be the fastest aircraft in the world, the S.E.4a was fundamentally a new aircraft, intended to investigate the relationship between stability and manoeuvrability, and for possible operational use. The resulting design was a single-engined, single bay biplane. The fuselage structure was of mixed construction, with a steel tube forward section and a wooden box-girder rear section. The first prototype's fuselage w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
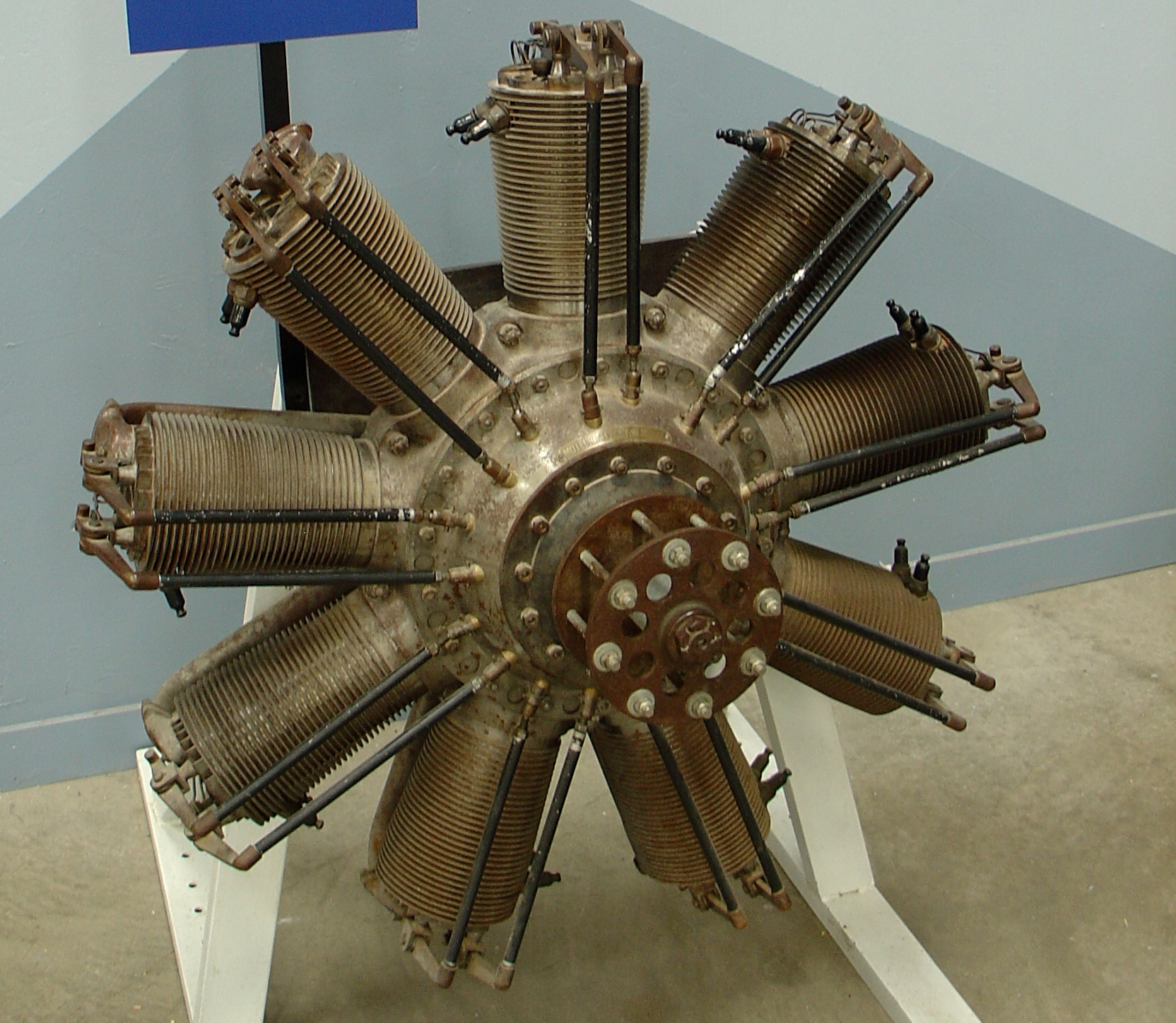
Rotary Engine
The rotary engine is an early type of internal combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration. The engine's crankshaft remained stationary in operation, while the entire crankcase and its attached cylinders rotated around it as a unit. Its main application was in aviation, although it also saw use in a few early motorcycles and automobiles. This type of engine was widely used as an alternative to conventional inline engines (straight or V) during World War I and the years immediately preceding that conflict. It has been described as "a very efficient solution to the problems of power output, weight, and reliability". By the early 1920s, the inherent limitations of this type of engine had rendered it obsolete. Description Distinction between "rotary" and "radial" engines A rotary engine is essentially a standard Otto cycle engine, with cylinders arranged radially around a central crankshaft just like a conventional radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biplanes
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage over a monoplane, it produces more drag (aerodynamics), drag than a monoplane wing. Improved structural techniques, better materials and higher speeds made the biplane configuration obsolete for most purposes by the late 1930s. Biplanes offer several advantages over conventional cantilever monoplane designs: they permit lighter wing structures, low wing loading and smaller span for a given wing area. However, interference between the airflow over each wing increases drag substantially, and biplanes generally need extensive bracing, which causes additional drag. Biplanes are distinguished from tandem wing arrangements, where the wings are placed forward and aft, instead of above and below. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Aircraft Factory Aircraft
Royal may refer to: People * Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * A member of a royal family or royalty Places United States * Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Royal, Illinois, a village * Royal, Iowa, a city * Royal, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Royal, Nebraska, a village * Royal, Franklin County, North Carolina, an unincorporated area * Royal, Utah, a ghost town * Royal, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Royal Gorge, on the Arkansas River in Colorado * Royal Township (other) Elsewhere * Mount Royal, a hill in Montreal, Canada * Royal Canal, Dublin, Ireland * Royal National Park, New South Wales, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Royal'' (Jesse Royal album), 2021 * Royal (Ayo album), 2020 * ''The Royal'', a British medical drama television series * ''The Royal Magazine'', a monthly British literary magazine published between 1898 and 1939 * ''The Raja Saab'', working title ''Royal'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910s British Fighter Aircraft
Year 191 ( CXCI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Bradua (or, less frequently, year 944 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 191 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Parthia * King Vologases IV of Parthia dies after a 44-year reign, and is succeeded by his son Vologases V. China * A coalition of Chinese warlords from the east of Hangu Pass launches a punitive campaign against the warlord Dong Zhuo, who seized control of the central government in 189, and held the figurehead Emperor Xian hostage. After suffering some defeats against the coalition forces, Dong Zhuo forcefully relocates the imperial capital from Luoyang to Chang'an. Before leaving, Dong Zhuo orders his troops to loot the tombs of the Han emperors, and then destroy Luoyang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
303 British
The .303 British (designated as the 303 British by the C.I.P. and SAAMI) or 7.7×56mmR, is a calibre Rim (firearms)#Rimmed, rimmed Tapering (firearms), tapered bottleneck centerfire rifle Cartridge (firearms), cartridge. The .303-inch bore diameter is measured between rifling Rifling, lands as is the common practice in Europe which follows the traditional black powder convention. It was first manufactured in United Kingdom, Britain as a stop-gap black powder round put into service in December 1888 for the Lee–Metford rifle. From 1891 the cartridge used smokeless powder which had been the intention from the outset, but the decision on which smokeless powder to adopt had been delayed. It was the standard British and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth military cartridge for rifles and machine guns from 1889 until it was replaced by the 7.62×51mm NATO in the 1950s. Cartridge specifications The .303 British has a 3.64 litre, mL (56 grain (measure), gr H2O) cartridge case capa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Joyce Green
Joyce Green, at Long Reach, near Dartford, was one of the first Royal Flying Corps (RFC) airfields. It was established in 1911 by Vickers Limited (the aircraft and weapons manufacturer) who used it as an airfield and testing ground. At the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the RFC followed and established a base. Subject to frequent flooding and a reputation as being unsuitable and too dangerous for training, it was eventually replaced by a more suitable site at RAF Biggin Hill. There were two parts to Joyce Green's military operations; the RFC, and the Wireless Experimental establishment. The latter were the first to move out in 1917 (after exhaustive searching south of London) when they found an ideal site on a farmer's field near the village of Biggin Hill; the RFC were soon to recognize the new site's suitability for flying and its strategic location, and soon followed, transferring there on 13 February 1917. The RFC took with them their Bristol Fighters, leaving Joyce Green w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hounslow Heath Aerodrome
Hounslow Heath Aerodrome was a grass airfield, operational 1914–1920. It was in the London borough of Hounslow, and hosted the British Empire's first scheduled daily international commercial flights, in 1919. The site today includes the main remaining part of Hounslow Heath. The last commercial flights took place in 1920, after which services moved to Croydon Airport. Hounslow Heath Aerodrome is not to be confused with Great West Aerodrome, which opened nearby in 1929, and which is now Heathrow Airport. Earlier use of the site A British army cavalry unit had been based since 1793 at Hounslow Barracks, centred 500 metres north of the site, regularly using most of Hounslow Heath for training exercises. Nine years before for the first precision mapmaking and surveying it saw General Roy's Baseline measured from one end of the heath to the other. The act marked a key stage in the Principal Triangulation of Great Britain and was repeated with greater precision on later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Rhône
Le Rhône was the name given to a series of Rotary engine, rotary aircraft engines built between 1910 and 1920. Le Rhône series engines were originally sold by the Gnome et Rhône#Le Rhône, Société des Moteurs Le Rhône and, following a 1914 corporate buyout, by its successor company, Gnome et Rhône. During World War I, more than 22,000 nine cylinder Le Rhône engines were built, with the type far outselling Gnome et Rhône's other main wartime engine series, the Gnome Monosoupape. Licenses for production of Le Rhône series engines were negotiated with companies in Great Britain, Austria, Italy, Russia, Sweden and Germany. Le Rhône-designed engines powered many of the most famous WW1 aircraft, including the Sopwith Pup, the Sopwith Camel, the Nieuport 11, Nieuport 11 "Bebe" and the Fokker Dr.I, Fokker Dr.1 "Triplane". Operation As with all rotary engines, the crankshaft of the Rhône remained stationary in operation, with the entire crankcase and its attached cylinders ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerget
Clerget-Blin (full name being ''Société Clerget-Blin et Cie'') was a French precision engineering company formed in 1913 by the engineer and inventor Pierre Clerget and industrialist Eugène Blin. In 1939, the company was absorbed into the ''Groupe d'étude des moteurs à huile lourde'' (GEHL; "Diesel Engine Study Group"), which was further merged into SNECMA in 1947. Products The Clerget-Blin company mainly produced aircraft engines. Their successful rotary engine designs were also built in Britain by companies such as Gwynnes Limited, Ruston Proctor, and Gordon Watney, to increase production during World War I.Lumsden 2003, p.133. See also *List of aircraft engine manufacturers This is a list of aircraft engine manufacturers both past and present. 0–9 * 2si – US * 3w (aero-engine manufacturer), 3WMiguel Vidal, Ricardo. ''El Motor de Aviación de la A a la Z. ''Aeroteca, 2012. A * Alliott Verdon Roe, A.V. Roe ... Notes Bibliography * Gunston, Bill. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |