|
Roxburghshire
Roxburghshire or the County of Roxburgh () is a historic county and registration county in the Southern Uplands of Scotland. It borders Dumfriesshire to the west, Selkirkshire and Midlothian to the northwest, and Berwickshire to the north. To the southwest it borders Cumberland and to the southeast Northumberland, both in England. It was named after the Royal Burgh of Roxburgh, a town which declined markedly in the 15th century and is no longer in existence. Latterly, the county town of Roxburghshire was Jedburgh. The county has much the same area as Teviotdale, the basin drained by the River Teviot and tributaries, together with the adjacent stretch of the Tweed into which it flows. The term is often treated as synonymous with Roxburghshire, but may omit Liddesdale as Liddel Water drains to the west coast.Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland, by, Francis Groome, publ. 2nd edition 1896. Article on Roxburghshire History The county appears to have originated in the 12th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selkirkshire
Selkirkshire or the County of Selkirk is a Counties of Scotland, historic county and registration county of Scotland. It borders Peeblesshire to the west, Midlothian to the north, Roxburghshire to the east, and Dumfriesshire to the south. It derives its name from its county town, the royal burgh of Selkirk, Scottish Borders, Selkirk. The county was historically also known as Ettrick Forest. Unlike many historic counties, Selkirkshire does not have its own lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area, but forms part of the Roxburgh, Ettrick and Lauderdale lieutenancy area. History In the 1st Century Anno Domini, AD Selkirk formed part of the lands of the native people who hunted it rather than settled there. Neither the Roman Empire, Romans, Angles (tribe), Angles, or the Saxons cleared much of the forestry there and for centuries Selkirk was known for its forest coverage. Indeed, an alternative name for the county was Ettrick Forest. Under the Scottish kings the forest was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
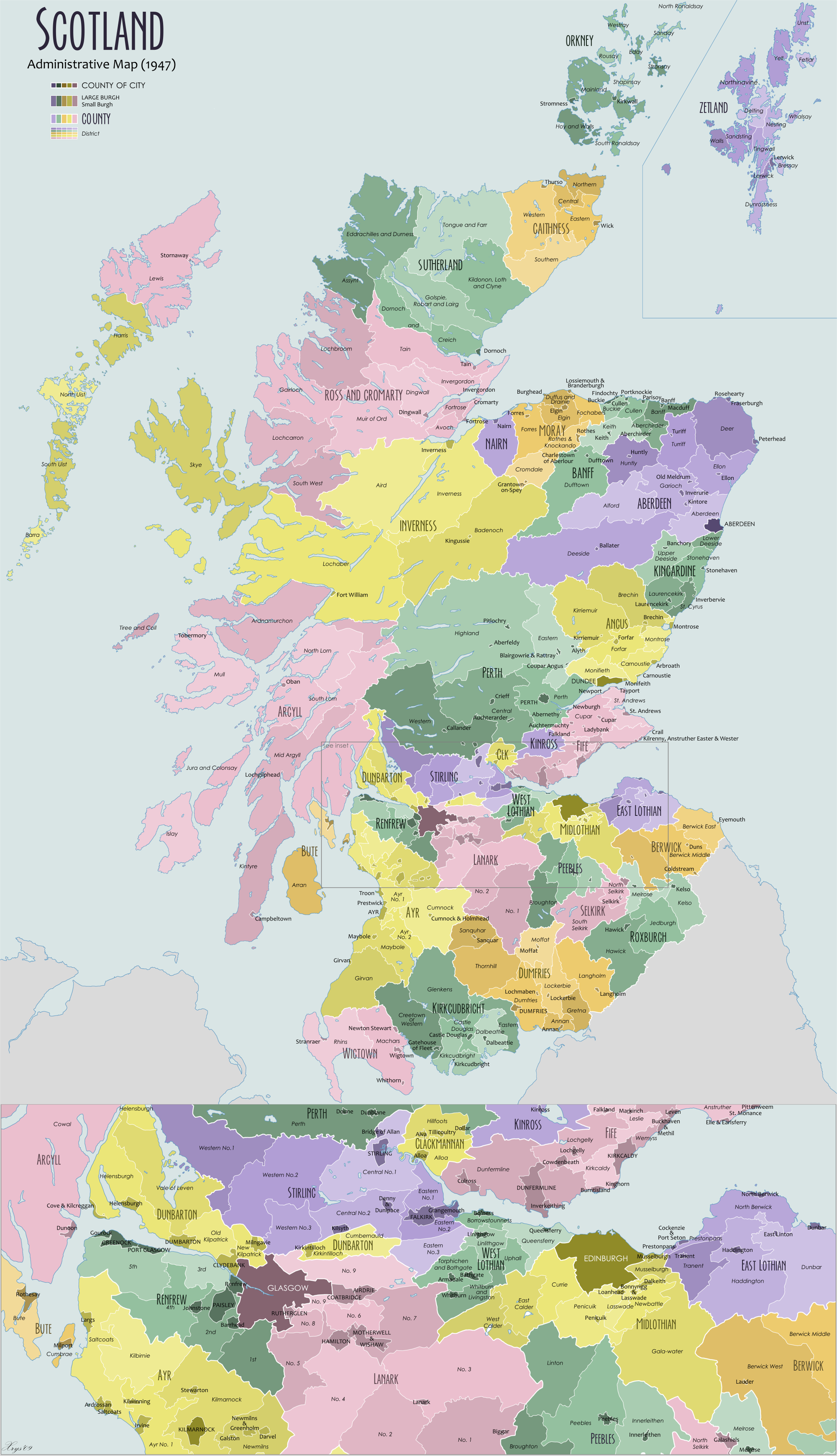
Shires Of Scotland
The counties or shires of Scotland () were historic subdivisions of Scotland. The shires were originally established in the Middle Ages for judicial purposes, being territories over which a Sheriff principal, sheriff had jurisdiction. They were distinct from the various older mormaerdoms, earldoms and other territories into which Scotland was also divided, which are collectively termed the provinces of Scotland by modern historians. The provinces gradually lost their functions, whereas the shires gradually gained functions. From the 16th century, the shires served as county constituency, constituencies, electing shire commissioners to the Parliament of Scotland. From 1667 each shire had Commissioners of Supply, commissioners of supply responsible for collecting local taxes; the commissioners of supply were subsequently given various local government functions as well. From 1797, the shires also served as areas for organising the militia, which was the responsibility of a lord-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roxburgh
Roxburgh () is a civil parish and formerly a royal burgh, in the historic county of Roxburghshire in the Scottish Borders, Scotland. It was an important trading burgh in High Medieval to early modern Scotland. In the Middle Ages it had at least as much importance as Edinburgh, Stirling, Perth, or Berwick-upon-Tweed, for a time acting as ''de facto'' capital (as royal residence of David I). History Its significance lay in its position in the centre of some of Lowland Scotland's most agriculturally fertile areas, and its position upon the River Tweed, which allowed river transport of goods via the main seaport of Berwick-upon-Tweed. Its position also acted as a barrier to English invasion. Standing on a defensible peninsula between the rivers Tweed and Teviot, with Roxburgh Castle guarding the narrow neck of the peninsula, it was a settlement of some importance during the reign of David I who conferred Royal Burgh status upon the town. At its zenith, between the reigns of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedburgh
Jedburgh ( ; ; or ) is a town and former royal burgh in the Scottish Borders and the traditional county town of the Shires of Scotland, historic county of Roxburghshire. History Jedburgh began as ''Jedworð'', the "worth" or enclosed settlement on the Jed. Later the more familiar word "burgh" was substituted for this, though the original name survives as Jeddart/Jethart. Bishop Ecgred of Lindisfarne founded a church at Jedburgh in the 9th century, and King David I of Scotland made it a priory between 1118 and 1138, housing Augustinians, Augustinian monks from Beauvais in France. The abbey was founded in 1147, but border wars with England in the 16th century left it a ruin. The deeply religious Scottish king Malcolm IV of Scotland, Malcolm IV died at Jedburgh in 1165, aged 24. His death is thought to have been caused by Paget's disease of bone. David I built a Jedburgh Castle, castle at Jedburgh, and in 1174 it was one of five fortresses ceded to England. It was an occasiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries () is a Counties of Scotland, historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county. In terms of historic counties it borders Kirkcudbrightshire to the west, Ayrshire to the north-west, Lanarkshire, Peeblesshire and Selkirkshire to the north, and Roxburghshire to the east. To the south is the coast of the Solway Firth, and on the other side of the border between Scotland and England the England, English county of Cumberland. Dumfriesshire has three traditional subdivisions, based on the three main valleys in the county: Annandale, Dumfries and Galloway, Annandale, Eskdale, Scotland, Eskdale and Nithsdale. These had been independent provinces of Scotland, provinces in medieval times but were gradually superseded as administrative areas by the area controlled by the sheriff principal, sheriff of Dumfries, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedburgh Sheriff Court
Jedburgh Sheriff Court, formerly County Buildings, is a judicial building in the Market Square in Jedburgh in Scotland. The building, which continues to be used as a courthouse, is a Category B listed building. History The first building on the southwest side of the Market Square was a town house, which dated back to 1664. A gatehouse to Jedburgh Abbey, with tower and spire, was erected to the south of the building and initially deployed as a prison, in 1755. It was in the old town house that Sir Walter Scott worked as a young advocate in 1793. By the early 19th century, old town house was dilapidated and the Commissioners of Supply decided to commission a new courthouse for the area. The new building was designed in the neoclassical style, built in ashlar stone and was completed in 1812. The original design featured a symmetrical main frontage of nine bays facing onto Castle Gate. The central section of three bays, which was slightly projected forward, featured a three-bay arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospatric (sheriff Of Roxburgh)
Gospatric is the first known sheriff of Roxburgh, a burgh in Teviotdale. His father is thought to have been Uhtred son of Ulfkill. A ''Cospatricio vicecomite'' ("Gospatric the Sheriff") is mentioned in the foundation charter of Selkirk Abbey. The charter was issued by Earl David (later King David I) and probably dates to between either 1120 and 1121, or 1123 and 1124, though it could be as early as 1114. A ''Gospatricus Vicecomes'' ("Gospatric the Sheriff") witnessed a grant by David, now king of Scotland, to Durham Cathedral Priory, sometime between April 1126 and March 1127. He witnessed a grant of land in Roxburgh to the church of St John of the castle of Roxburgh sometime between 1124 and 1133. Although Sir Archibald Campbell Lawrie was uncertain what sheriffdom Gospatric held, G. W. S. Barrow and Norman Reid believed it to be Roxburghshire because of this charter. Gospatric came to know Aelred of Rievaulx Aelred of Rievaulx (), also known as also Ailred, Ælred, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish counties of Dumfriesshire and Roxburghshire to the north. The area includes the city of Carlisle, part of the Lake District and North Pennines, and the Solway Firth coastline. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974, when it was subsumed into Cumbria with Westmorland as well as parts of Yorkshire and Lancashire. It gives its name to the unitary authority area of Cumberland, which has similar boundaries but excludes Penrith. Early history In the Early Middle Ages, Cumbria was part of the Kingdom of Strathclyde in the Hen Ogledd, or "Old North", and its people spoke a Brittonic language now called Cumbric. The first record of the term 'Cumberland' appears in AD 945, when the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liddesdale
Liddesdale is a district in the Roxburghshire, County of Roxburgh, southern Scotland. It includes the area of the valley of the Liddel Water that extends in a south-westerly direction from the vicinity of Peel Fell to the River Esk, Dumfries and Galloway, River Esk, a distance of . History Liddesdale is sometimes considered to form the northern end of the Maiden Way Roman Britain, Roman Roman roads in Britain, road. At one time the points of vantage on the river and its affluents were occupied by freebooters' peel towers, but many of them have disappeared and the remainder are in decay. Larriston Tower belonged to the Clan Elliot, Elliots, Mangerton Tower, Mangerton, now little more than a site, to the Clan Armstrong, Armstrongs and Park to "Little Jock Elliot", the outlaw who nearly killed James Hepburn, 4th Earl of Bothwell, Bothwell in an encounter in 1566. Gilnockie Tower, Hollows Tower, Johnnie Armstrong's peel, is in good condition; it is on the A7 road (Great Britain), A7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapman Code
Chapman codes are a set of 3-letter codes used in genealogy to identify the administrative divisions in the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Use They were created by the historian Colin R Chapman in the late 1970s, intended to provide a widely used shorthand in genealogy which follows the common practice of describing areas in terms of the counties existing in the 19th and 20th centuries. Other uses Chapman codes have no mapping, postal or administrative use. They can however be useful for disambiguation by postal services where a full county name or traditional abbreviation is not supplied after a place name which has more than one occurrence, a particular problem where these are post towns such as Richmond. Country codes *CHI Channel Islands *ENG England *IOM Isle of Man *IRL Ireland *NIR Northern Ireland *SCT Scotland *WLS Wales *ALL All countries Channel Islands *ALD Alderney *GSY Guernsey *JSY Jersey *SRK Sark England Historic countie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in England in 1889, the headquarters of the new councils were usually established in the county town of each county; however, the concept of a county town pre-dates these councils. The concept of a county town is ill-defined and unofficial. Some counties in Great Britain have their administrative bodies housed elsewhere. For example, Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster is the county town of Lancashire, but the county council is in Preston, Lancashire, Preston. Owing to the creation of Unitary authorities of England, unitary authorities, some county towns in Great Britain are administratively separate from the county. For example, Nottingham is separated from the rest of Nottinghamshire, and Brighton and Hove is separate from East Sussex. On a ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |