|
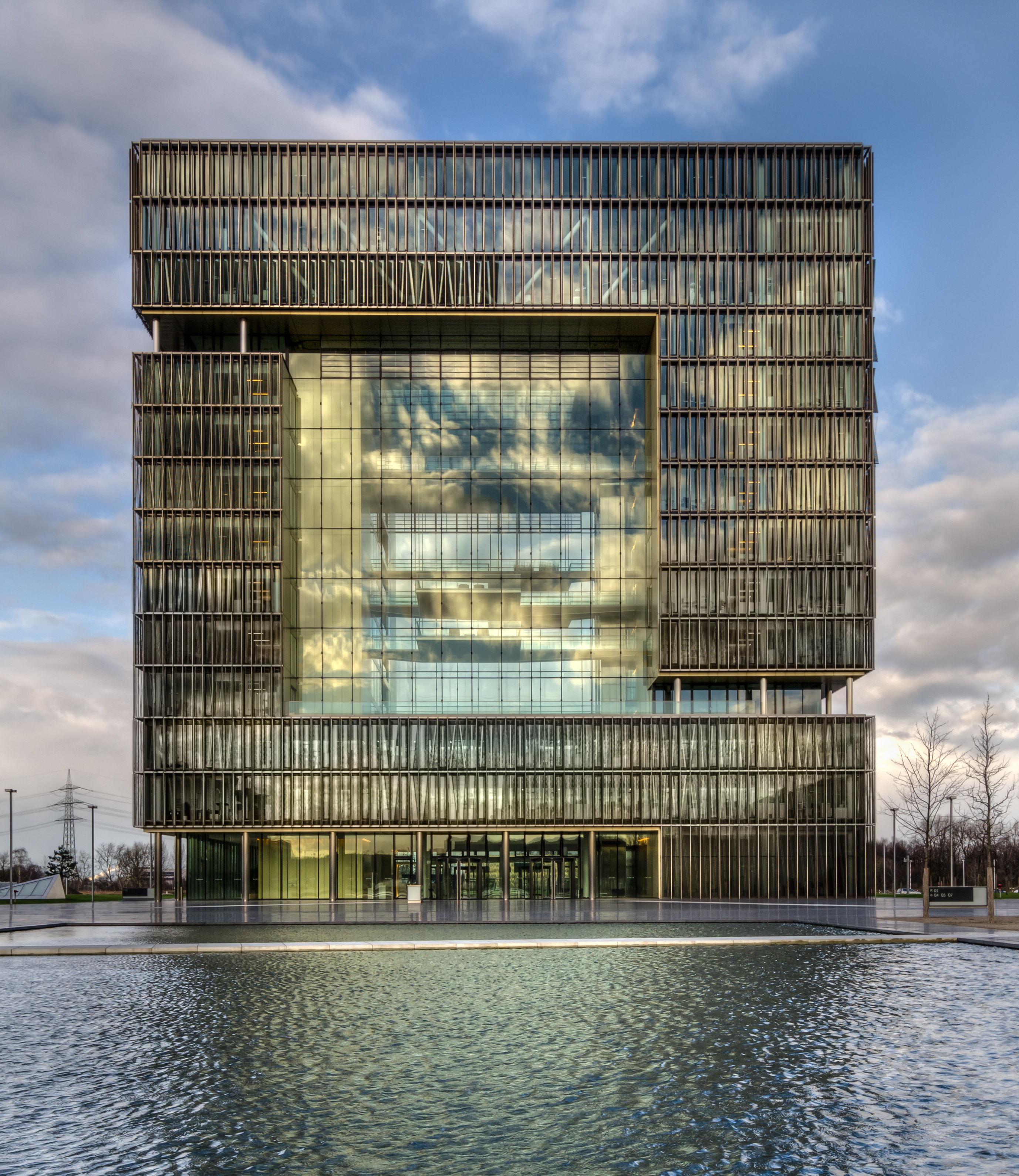
Rourkela Steel Plant
Rourkela Steel Plant (RSP), is a public sector, integrated steel plant in Rourkela, Odisha state, India. It was established on 3 February 1959 with the help of West German industrial corporations on approximately 19,000 acres of land acquired from tribal inhabitants. The plant is operated by the Steel Authority of India (SAIL), a Central PSU. After the 2010-12 expansion, RSP currently has a production capacity of 4.5 MTPA (Million Tonne per Annum) of Hot Metal, 4.2 MTPA of Crude Steel and 3.9 MTPA of Saleable Steel, employs 19,134 employees as of February 2011 and produces a mix of products. The RSP reported an annual revenue of ₹26,830.57 crores (US$ 3.54 billion) and profit before taxes (PBT) of ₹6347.65 crores (US$ 837.53 million) for the financial year 2021–22. History A temple to modernization The Rourkela Steel Plant Project was first announced by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1953. The steel plant at Rourkela was proposed in India's Second Five-Year Plan, drafted in 1954 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel Authority Of India
Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) is an Indian public sector steel manufacturing corporation based in New Delhi. It is the largest government-owned steel producer, with an annual production of 18.29 million metric tons. Incorporated on 24 January 1973, SAIL has 54,431 employees and is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Steel. SAIL operates and owns five integrated steel plants at Bhilai, Rourkela, Durgapur, Bokaro and Burnpur ( Asansol) and three special steel plants at Salem, Durgapur and Bhadravathi. It also owns a Ferro Alloy plant at Chandrapur. It also has an R&D Centre for Iron & Steel (RDCIS) and a Centre for Engineering in Ranchi, Jharkhand. The company has a total of 692 patents globally, out of which 343 have been granted. More than 64% of the 692 patents are active. SAIL has filed the maximum number of patents in India, followed by Egypt and Germany. History 1959–1973 SAIL traces its origin to the Hindustan Steel Limited (HSL) which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundergarh District
Sundargarh District is a district in the northwestern part of Odisha state in eastern India. Sundargarh district is bounded by Raigarh district of Chhattisgarh in the west, Jashpur district of Chhattisgarh in the North-West, Simdega district of Jharkhand in the North, West Singhbhum district of Jharkhand and Keonjhar district of Odisha in the east and Jharsuguda, Sambalpur, Deogarh and Angul districts of Odisha in the South. The town of Sundargarh is the district headquarters. Rourkela is the largest city in the entire district. Geography The Sundargarh district forms the northwestern part of the Odisha state and is the second largest district in the state accounting for 6.23% of the total area. The geographical area of the district is . The district spreads from 21°36′N to 22°32′N and from 83°32′E to 85°22′E. Demographics According to the 2011 census Sundargarh district has a population of 2,093,437, roughly equal to the nation of North Macedonia or the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the position of global market leader in industrial automation and industrial software. The origins of the conglomerate can be traced back to 1847 to the ''Telegraphen Bau-Anstalt von Siemens & Halske'' established in Berlin by Werner von Siemens and Johann Georg Halske. In 1966, the present-day corporation emerged from the merger of three companies: Siemens & Halske, Siemens-Schuckert, and Siemens-Reiniger-Werke. Today headquartered in Munich and Berlin, Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 320,000 people worldwide and reported a global revenue of around €78 billion in 2023. The company is a component of the DAX and Euro Stoxx 50 stock market indices. As of December 2023, Siemens is the second largest German company by market ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEG (German Company)
; AEG) was a German producer of electrical equipment. It was established in 1883 by Emil Rathenau as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität'' in Berlin. The company's initial focus was driven by electrical lighting, as in 1881, Rathenau had acquired the rights to the electric light bulb at the International Exposition of Electricity in Paris. Using small power stations, his company introduced electrical lighting to cafés, restaurants, and theaters, despite the high costs and limitations. By the end of the 19th century, AEG had constructed 248 power stations, providing a total of 210,000 hp of electricity for lighting, tramways, and household devices. During the World War II, Second World War, AEG worked with the Nazi Party and benefited from forced labour from concentration camps. After the war, its headquarters moved to Frankfurt am Main. In 1967, AEG joined with its subsidiary Telefunken, Telefunken AG, creating ''Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannesmann
Mannesmann was a German industrial conglomerate. It was originally established as a manufacturer of steel pipes in 1890 under the name "Deutsch-Österreichische Mannesmannröhren-Werke AG" (lit. "German-Austrian Mannesmann pipe-works joint-stock company"). In the twentieth century, Mannesmann's product range grew and the company expanded into numerous sectors; starting from various steel products and trading to mechanical and electrical engineering, automotive and telecommunications. From 1955, the conglomerate's management holding with headquarters in Düsseldorf was named Mannesmann AG. The particular success of the corporate activities in the area of telecommunications that started in 1990 was the predominant reason for the takeover of Mannesmann by the British telecommunications company Vodafone in 2000, still one of the largest-ever company takeovers worldwide. Back then, the Mannesmann Group had 130,860 employees worldwide and revenues of €23.27 billion. The name M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAN SE
MAN SE (abbreviation of ''Maschinenfabrik Augsburg- Nürnberg'', ) was a manufacturing and engineering company based in Munich, Germany. Its primary output was commercial vehicles and diesel engines through its MAN Truck & Bus and MAN Latin America divisions, and participation in the manufacturer Sinotruk. MAN SE was majority-owned by Traton, the heavy commercial vehicle subsidiary of automaker Volkswagen AG, until August 2021 when Traton completed a squeeze-out of all remaining shareholders and formally merged MAN SE into Traton SE, meaning the former subsidiaries of MAN SE were now directly owned by Traton, and MAN SE ceased to exist. History Foundation MAN traces its origins back to 1758, when the "St. Antony" ironworks commenced operation in Oberhausen, as the first heavy-industry enterprise in the Ruhr region. In 1808, the three ironworks "St. Antony", "Gute Hoffnung" (English: "Good Hope"), and "Neue Essen" (English: "New Forges") merged, to form the Hütte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demag
Demag (In German ''Deutsche Maschinenbau-Aktiengesellschaft'') was a German heavy equipment industrial group whose individual companies are now scattered. The Demag name can be today found for example as the Demag Cranes and Components and Sumitomo (SHI) Demag. The roots of Demag date back prior to its formation, but became Märkische Maschinenbau-Anstalt, Ludwig A.-G in 1906 as the biggest crane building company in Germany employing 250-300 people. The company was a manufacturer of industrial cranes that included types like, bridge cranes, hoist (device), overhead cranes, Gantry crane to name a few. In 1910 came the hour of the Deutsche Maschinenfabrik in Duisburg – known worldwide by its telegram abbreviation Demag (now ''Demag Cranes & Components GmbH''). In 1973 The Mannesmann group assumed ownership of Demag. Founding The Demag company was formed finally 1910 in Duisburg through the union of the ''Märkische Maschinenbau-Anstalt L. Stuckenholz AG'', the ''Duisburg Mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ThyssenKrupp
ThyssenKrupp AG (, ; stylized as thyssenkrupp) is a German industrial engineering and steel production multinational conglomerate. It resulted from the 1999 merger of Thyssen AG and Krupp and has its operational headquarters in Duisburg and Essen. The company says that it is one of the largest steel producers in the world, and it was ranked tenth-largest worldwide by revenue in 2015."The world's largest steel companies in 2015, based on revenue" ''Statista'' It is divided into 670 subsidiaries worldwide. The largest shareholders are the Alfried Krupp von Bohlen un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Ministry For Economic Affairs And Climate Action
The Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (, ; abbreviated BMWE, formerly BMWi) is a Cabinet of Germany, cabinet-level ministry of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was previously known as the "Ministry of Economy". It was recreated in 2005 as "Ministry of Economics and Technology" after it had previously been merged with other ministries to form the Federal Ministry for Economics and Labour between 2002 and 2005. The ministry is advised by the Council of Advisors on Digital Economy. History The historical predecessor of the current Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action was the ''Reichswirtschaftsamt'' (Reich Economic Office), founded in 1917. In 1919, this became the ''Reichswirtschaftsministerium'' (Reich Ministry of Economy), which existed until 1945. In postwar occupied Germany, its functions were exercised by the Administrative Office of Economy () between 1946 and 1949. After the founding of the Federal Republic of Germany, the Federal Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and other allies represented the "First World", while the Soviet Union, China, Cuba, North Korea, Vietnam, and their allies represented the "Second World". This terminology provided a way of broadly categorizing the nations of the Earth into three groups based on political divisions. Due to the complex history of evolving meanings and contexts, there is no clear or agreed-upon definition of the Third World. Strictly speaking, "Third World" was a political, rather than economic, grouping. Since most Third World countries were economically poor and non-industrialized, it became a stereotype to refer to developing countries as "third-world countries". In political discourse, the term Third World was often associated with being underdeveloped. China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |