|
Round Mountain (Antarctica)
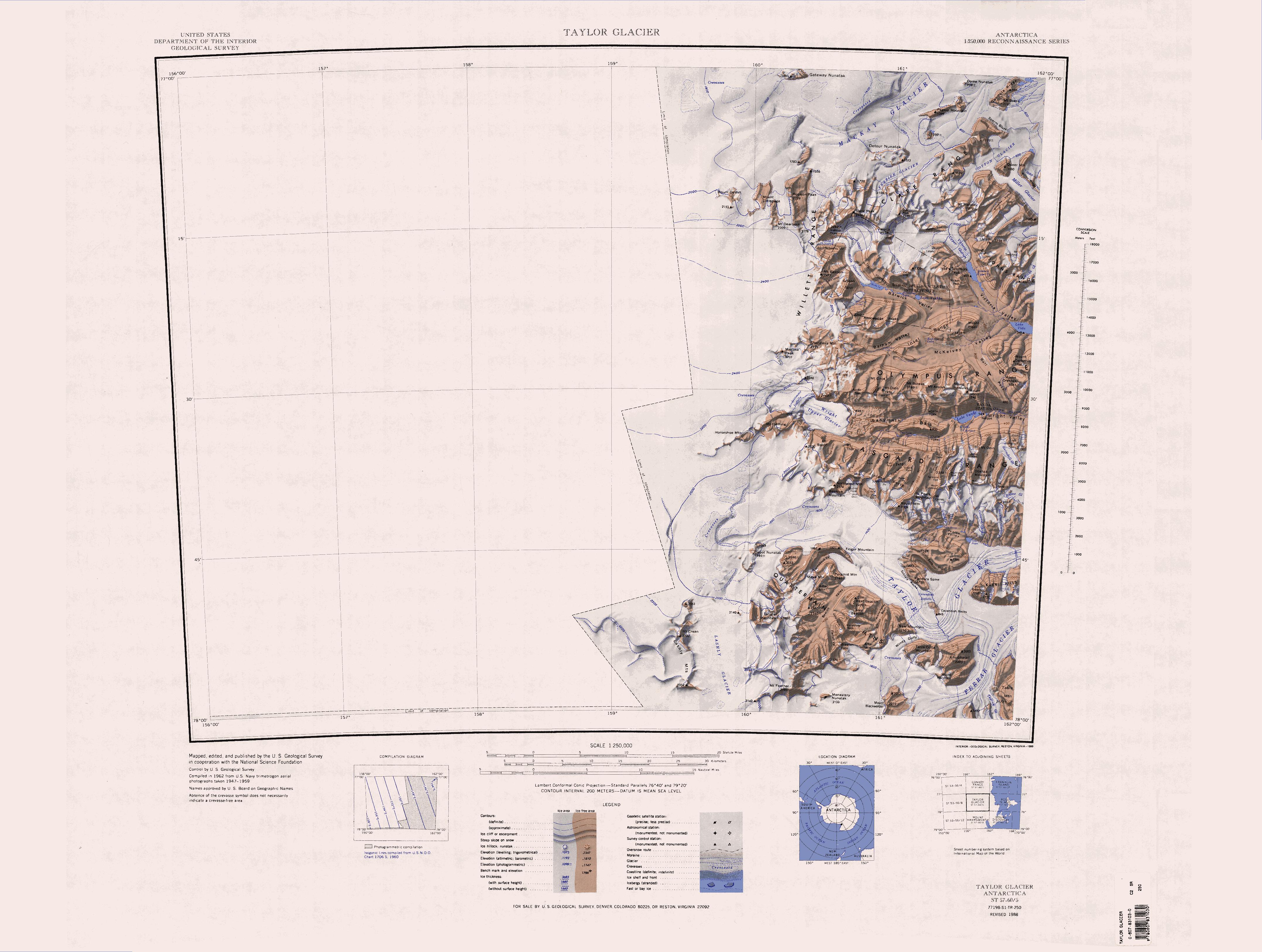
The Inland Forts () are a line of peaks extending between Northwest Mountain and Saint Pauls Mountain, in the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The peaks were discovered by Ervon r. Koenig and named by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04. Location The Inland Forts are to the south of the western end of the Asgard Range. They face the head of the Taylor Glacier to the southwest. A number of valley run north from the Inland Forts down to the lowlands between the Wright Upper Glacier and the Wright Valley. Features Named features, from west to east, include Beehive Mountain, Northwest Mountain, Hess Mesa, Mudrey Cirque, West Grain, Sutherland Peak, Mary Cirque, East Groin, Wolak Peak, Round Mountain and Saint Pauls Mountain. Beehive Mountain . A mountain north of Finger Mountain, standing at the north margin and near the head of Taylor Glacier. Named by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) (1901-04), possibly at the suggestion of Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Valley
The Wright Valley () is a large east–west trending valley, formerly occupied by a glacier but now ice free except for Wright Upper Glacier at its head and Wright Lower Glacier at its mouth, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the VUWAE (1958-59) for Sir Charles Wright, for whom the BrAE (1910-13) named the glacier at the mouth of this valley. The Wright Valley is the central one of the three large McMurdo Dry Valleys in the Transantarctic Mountains, located west of McMurdo Sound. Wright Valley contains the Onyx River, the longest river in Antarctica, Lake Brownworth, the origin of the Onyx River, and Lake Vanda, which is fed by the Onyx River. Its southwestern branch, ''South Fork'', is the location of Don Juan Pond. The upland area known as the Labyrinth is at the valley's west end. Exploration Although portions of the interconnected valley system were discovered in 1903 by the ''Discovery'' expedition led by Captain Robert Falcon Scott, the Wright Valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sykes Glacier
The Wright Valley () is a large east–west trending valley, formerly occupied by a glacier but now ice free except for Wright Upper Glacier at its head and Wright Lower Glacier at its mouth, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the VUWAE (1958-59) for Sir Charles Wright, for whom the BrAE (1910-13) named the glacier at the mouth of this valley. The Wright Valley is the central one of the three large McMurdo Dry Valleys in the Transantarctic Mountains, located west of McMurdo Sound. Wright Valley contains the Onyx River, the longest river in Antarctica, Lake Brownworth, the origin of the Onyx River, and Lake Vanda, which is fed by the Onyx River. Its southwestern branch, ''South Fork'', is the location of Don Juan Pond. The upland area known as the Labyrinth is at the valley's west end. Exploration Although portions of the interconnected valley system were discovered in 1903 by the ''Discovery'' expedition led by Captain Robert Falcon Scott, the Wright Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee
New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) is an adjudicating committee established to authorize the naming of features in the Ross Dependency on the Antarctic continent. It is composed of the members of the New Zealand Geographic Board plus selected specialists on Antarctica. This committee works in collaboration with similar place-naming authorities in Australia, Great Britain and the United States to reach concurrence on each decision. The NZ-APC committee was established in 1956. Names attributed by the committee * Alberich Glacier, named after Alberich, king of the elves and chief of the Nibelungen * Arena Saddle, named in conjunction with Arena Valley * Brawhm Pass, named after the six party members of the University of New South Wales expeditions of 1964–65 and 1966–67 * Caliper Cove, named for descriptive features * Canada Stream, named in conjunction with Canada Glacier * Cape Crossfire, named for descriptive features * Cuneiform Cliffs, named for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinth (Antarctica) lies to the east.
The The Labyrinth () is an extensive flat upland area which has been deeply eroded, at the west end of Wright Valley, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was so named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) because the eroded dolerite of which it is formed gives an appearance of a labyrinth. Location The Labyrinth lies in the western Wright Valley. The Asgard Range, Mount Thor and Linnaeus Terrace are to the south. The Olympus Range and Mount Dido are to the north. Minotaur Pass provides a route through the Olympus Range to McKelvey Valley. The Wright Upper Glacier fills the Wright Valley to the west, and the Dais A dais or daïs ( or , American English also but sometimes considered nonstandard)dais in the Random House Dictionary< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
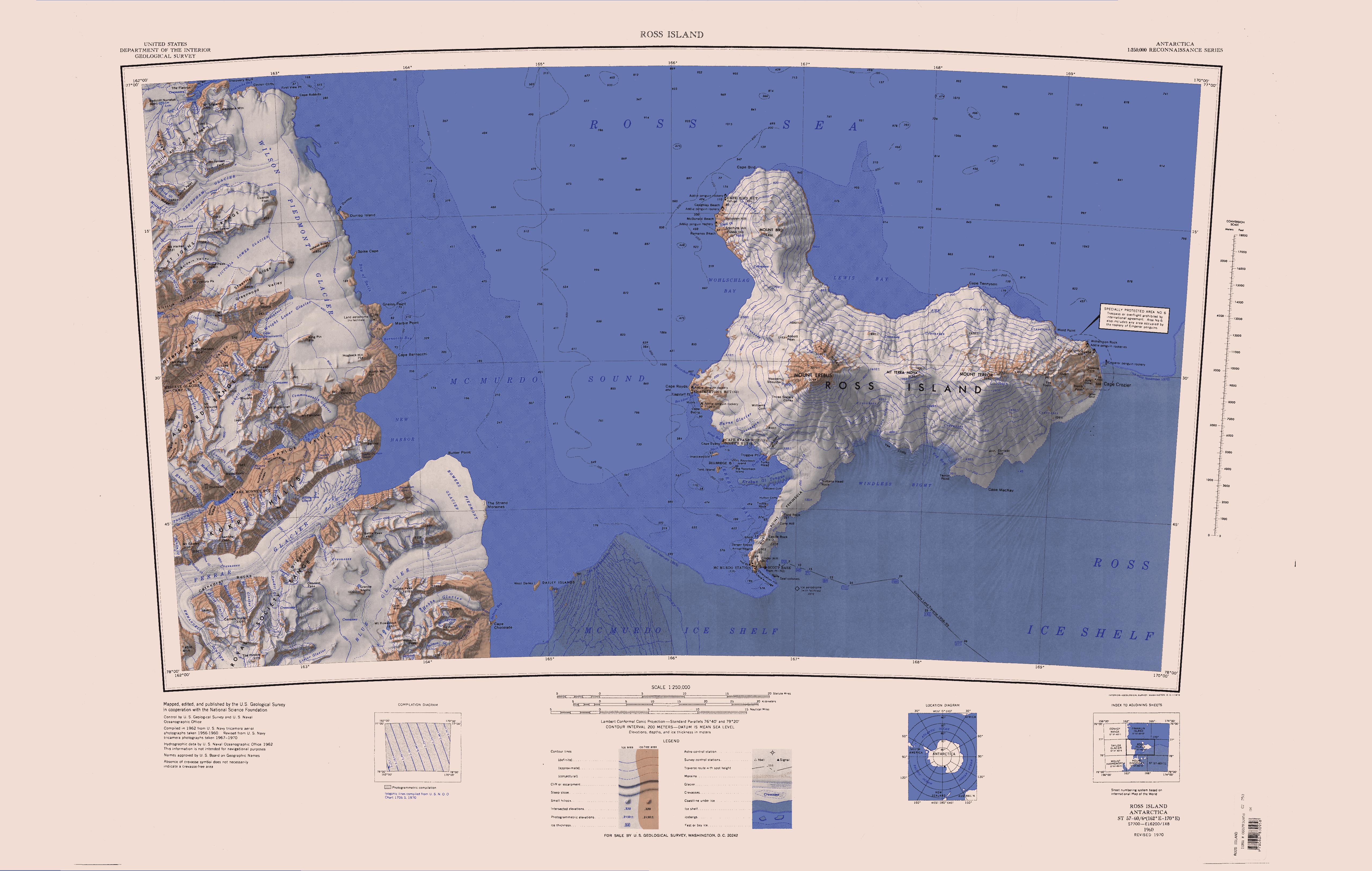
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,500 residents, though the population fluctuates seasonally; during the antarctic night, there are fewer than two hundred people. It serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. Personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station usually first pass through McMurdo, either by flight or by the McMurdo to South Pole Traverse; it is a hub for activities and science projects in Antarctica. McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott, and Palmer are the three non-seasonal United States stations on the continent, though by the Antarctic Treaty System the bases are not a legal claim (though the right is not forfeited); they are dedicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
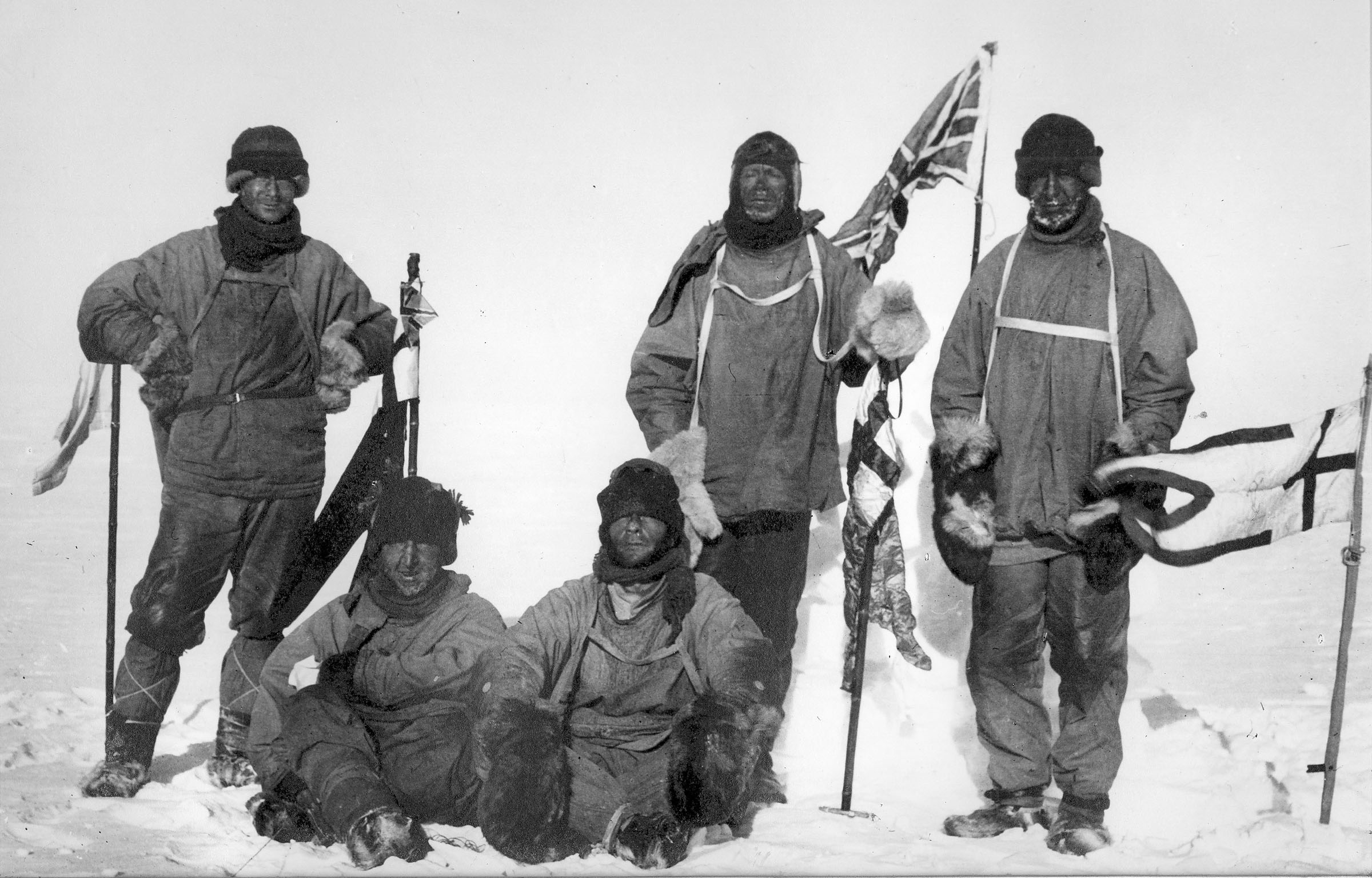
British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13
The ''Terra Nova'' Expedition, officially the British Antarctic Expedition, was an expedition to Antarctica which took place between 1910 and 1913. Led by Captain Robert Falcon Scott, the expedition had various scientific and geographical objectives. Scott wished to continue the scientific work that he had begun when leading the ''Discovery'' Expedition from 1901 to 1904, and wanted to be the first to reach the geographic South Pole. He and four companions attained the pole on 17 January 1912, where they found that a Norwegian team led by Roald Amundsen had preceded them by 34 days. Scott's party of five died on the return journey from the pole; some of their bodies, journals, and photographs were found by a search party eight months later. The expedition, named after its supply ship, was a private venture financed by public contributions and a government grant. It had further backing from the Admiralty, which released experienced seamen to the expedition, and from the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Mountain
The Inland Forts () are a line of peaks extending between Northwest Mountain and Saint Pauls Mountain, in the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The peaks were discovered by Ervon r. Koenig and named by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04. Location The Inland Forts are to the south of the western end of the Asgard Range. They face the head of the Taylor Glacier to the southwest. A number of valley run north from the Inland Forts down to the lowlands between the Wright Upper Glacier and the Wright Valley. Features Named features, from west to east, include Beehive Mountain, Northwest Mountain, Hess Mesa, Mudrey Cirque, West Grain, Sutherland Peak, Mary Cirque, East Groin, Wolak Peak, Round Mountain and Saint Pauls Mountain. Beehive Mountain . A mountain north of Finger Mountain, standing at the north margin and near the head of Taylor Glacier. Named by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) (1901-04), possibly at the suggestion of Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger Mountain
Finger Mountain is a topographical formation in interior Alaska. Not actually a mountain, it is a wide broad hill, with an altitude of around 2202 ft. It is named for Finger Rock, a distinctive granite protrusion on its surface. Finger Mountain Wayside is a partially maintained pullout along the Dalton Highway The James W. Dalton Highway, usually referred to as the Dalton Highway (and signed as Alaska Route 11), is a road in Alaska. It begins at the Elliott Highway, north of Fairbanks, and ends at Deadhorse (an unincorporated community within t ... at mile 97.5. It features informational signs and some facilities for travelers. References Hills of Alaska Landforms of Yukon–Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska {{YukonKoyukukAK-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |