|
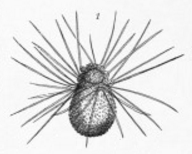
Rotorboides
''Rotorboides'' is a genus of recent (Holocene) bottom dwelling (benthic) forams from the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans, related to '' Rosalina''. The test is trochospiral and planoconvex, with a broadly rounded periphery and about six to nine chambers in the final whorl. Sutures on the spiral side are crescentic and strongly oblique. Chambers on the umbilical side are subtriangular, each with a triangular folium, or flap, that extends into the umbilical area, folia of successive chambers fuse to form an umbilical plate that is solid or has only rare perforations. Sutures on the umbilical side are radial and deeply incised. The test wall is calcareous, coarsely perforate on the spiral side, but imperforate adjacent to the sutures. The umbilical side is imperforate and smooth. The aperture is an interiomarginal arch, outside the umbilicus, extending nearly to the periphery. References * Alfred R. Loeblich Jr and Helen Tappan, 1988. Forminiferal Genera and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosalina (foraminifera)
''Rosalina'' is a genus of foraminifera included in the rotaliid family Rosalinidae. ''Rosalina'' has a smooth plano-convex to concavo-convex trochospiral test in which the chambers are rapidly enlarging and all visible on the convex spiral side and subtriangular and strongly overlapping on the umbilical side, the final chamber taking up about one-third of the circumference. Sutures on the spiral side are depressed and oblique, curving back at the periphery. The umbilicus is open, partly covered by triangular umbilical flaps extending from each chamber of the final whorl. Chamber interiors are simple and undivided with subacute peripheries. Walls are calcareous, with an organic inner lining, and are distinctly perforate. The aperture is a low interiomarginal arch near the periphery on the umbilical side, with narrow bordering lip. ''Rosalina'' has a stratigraphic range from the Eocene to recent and a cosmopolitan distribution. Related genera include '' Neoconorbina'', ''Roto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
SAR is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon (under the Sar name), including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade. Harosa is sometimes used synonymously with TSAR. Etymology The name SAR is an acronym derived from the first letters of its three constituent clades; it has been alternatively spelled RAS. The term Harosa (at the subkingdom level) has also been used, with Stramenopiles replaced by its synonym Heterokonta in this variant of the acronym. History of discovery Before the discovery of the SAR supergroup, stramenopiles and alveolates were classified in the supergroup Chromalveolata alongside haptophytes and cryptomonads, being believed to have acquired plastids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera and Radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters ( synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeletons ( thecae or loricas), which are in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retaria
Retaria is a clade within the supergroup Rhizaria containing the Foraminifera and the Radiolaria. In 2019, the Retaria were recognized as a basal Rhizaria group, as sister of the Cercozoa Cercozoa (now synonymised with Filosa) is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by phylogeny, molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or Ubiqu .... References External links Taxa named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith Rhizaria phyla Rhizaria taxa {{Retaria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "Test (biology), test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and ''Textularia'' in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthos, benthic, with different sized species playing a role within the macrobenthos, meiobenthos, and Benthos, microbenthos), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotaliida
The Rotaliida are an order of Foraminifera, characterized by multilocular tests (shells) composed of bilamellar perforate hyaline lamellar calcite that may be optically radial or granular. In form, rotaliid tests are typically enrolled, but may be reduced to biserial or uniserial, or may be encrusting with proliferated chambers. Chambers may be simple or subdivided by secondary partitions; the surface is smooth, papillate, costate, striate, or cancellate; the aperture is simple or with an internal toothplate, entosolenian tube, or hemicylindrical structure; it may have an internal canal or stolen systems. Rotaliids are primarily oceanic benthos, although some are common in shallower estuarine waters. They also include many important fossils, such as the nummulitids. Taxonomy The Rotaliida are now divided into the following superfamilies: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discorbacea
Discorbacea, Discorboidea in recent taxonomies, is a superfamily of foraminifera, Loeblich and Tappan,1988Forminiferal Genera and their Classification (testate protists), with a range extending from the Middle Triassic to the present, characterized by chambers arranged in a low trochospiral; an umbilical or interiomarginal aperture, with or without supplementary apertures; and a wall structure that is optically radial.Loeblick and Tappan,1964. Sarcodina Chiefly "Thecamoebians" and Foraminiferida; Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology The ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology,'' published from 1953–2007 by the Geological Society of America and the University of Kansas, then 2009–present by the University of Kansas Paleontological Institute, is a definitive multi-authore ..., part C Protista 2Sen Gupta, 2002. Modern Foraminifer Pub Springer Eight families are currently recognized, further characterized here in. * Discorbidae – Discorbacea in which each chamber is part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred R
Alfred may refer to: Arts and entertainment *'' Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series * ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne * ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák *"Alfred (Interlude)" and "Alfred (Outro)", songs by Eminem from the 2020 album '' Music to Be Murdered By'' Business and organisations * Alfred, a radio station in Shaftesbury, England * Alfred Music, an American music publisher * Alfred University, New York, U.S. * The Alfred Hospital, a hospital in Melbourne, Australia People * Alfred (name) includes a list of people and fictional characters called Alfred * Alfred the Great (848/49 – 899), or Alfred I, a king of the West Saxons and of the Anglo-Saxons Places Antarctica * Mount Alfred (Antarctica) Australia * Alfredtown, New South Wales * County of Alfred, South Australia Canada * Alfred and Plantagenet, Ontario ** Alfred, Ontario, a community in Alfred and Plantagenet * Alfred Island, Nunavu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich
Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich (October 12, 1917 – August 18, 2004) was an American micropaleontologist who was a professor of geology at the University of California, Los Angeles, a United States Geological Survey (USGS) biostratigrapher, and a scientific illustrator whose micropaleontology specialty was research on Cretaceous foraminifera. She received a Guggenheim Fellowship award in 1953 and travelled to Europe to focus on her studies of foraminifera with her husband. She would also be awarded with multiple other titles and was recognized as the first woman professor in Tulane University. Early life Helen Nina Tappan Leoblich was born on October 12, 1917, in Norman, Oklahoma on Columbus Day, which is why her middle name is Nina. Her mother Mary Pearl Jenks Tappan was a math teacher at Cornell, and her father, Frank Girard Tappan, was a Dean of Electrical Engineering at the University of Oklahoma.In Memoriam: Dr. Helen Nina Tappan Loeblich. Journal of Foraminifera R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |