|
Rostromedial Tegmental Nucleus
The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. This region was discovered by the researchers, M. Barrot, J.Kaufling and T. Jhou. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and possesses robust functional and structural links to the dopamine pathways. Notably, both acute and chronic exposure to psychostimulants have been shown to induce FosB and ΔFosB expression in the RMTg; no other drug type has been shown to induce these proteins in the RMTg. Inputs The RMTg receives incoming projections from the following structures: *Medial prefrontal cortex *Cingulate cortex *Preoptic area *Lateral hypothalamus * Lateral habenula *Superior colliculus *Periaqueductal gray * Dorsal raphe *Laterodorsal tegmental nucleus *Substantia nigra *Nucleus accumbens *Pontine tegmentum *Ventral pallidum Outputs GABA projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A substance is GABAergic if it produces its effects via interactions with the GABA system, such as by stimulating or blocking neurotransmission. A GABAergic or GABAnergic agent is any chemical that modifies the effects of GABA in the body or brain. Some different classes of GABAergic drugs include agonists, antagonists, modulators, reuptake inhibitors and enzymes. See also * Adenosinergic * Adrenergic * Cannabinoidergic * Cholinergic * Dopaminergic Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain. Dopaminergic pathways, Dopaminergic brain pathways facil ... * Glutamat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for ' nucleus adjacent to the septum') is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region ( D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can alter brain function in synapses similar to natural rewards like food or falling in love in ways that perpetuate craving and weakens self-control for people with pre-existing vulnerabilities. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological factors that are implicated in the development of addiction. While mice given cocaine showed the compulsive and involuntary nature of addiction, for humans this is more complex, related to behavior or personality traits. Classic signs of addiction include compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, ''preoccupation'' with substances or behavior, and continued use des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
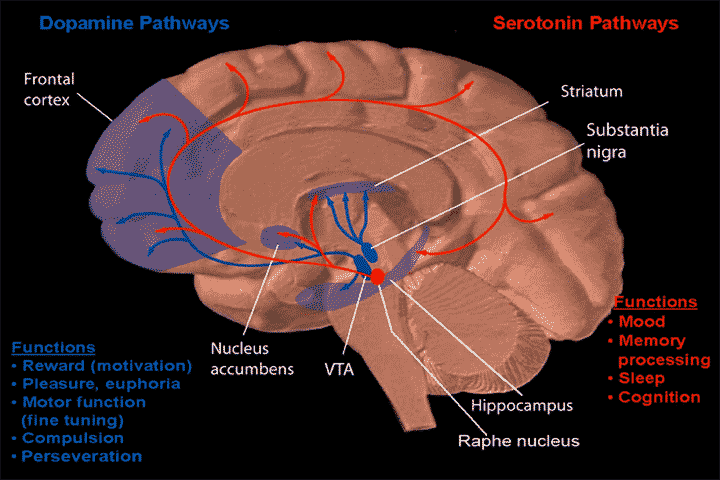
Dopamine Pathway
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including motion, movement, cognition, executive functions, Reward system, reward, motivation, and Neuroendocrine cell, neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neuron, projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons. There are more than 10 dopaminergic cell groups and pathways. The four major dopaminergic pathways are the mesolimbic pathway, the mesocortical pathway, the nigrostriatal pathway, and the tuberoinfundibular pathway. The mesolimbic pathway and the mesocortical pathway form the mesocorticolimbic system. Two other dopaminergic pathways to be considered are the hypothalamospinal tract and the incertohypothalamic pathway. Parkinson's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), substance use disorders (addiction), and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can be attributed to dysfuncti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Heroin is used medically in several countries to Pain reliever, relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy. Medical-grade diamorphine is used as a pure Hydrochloride, hydrochloride salt. Various white and brown powders sold illegally around the world as ''heroin'' are routinely diluted with cutting agents. Black tar heroin is a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation during clandestine production of street heroin. Heroin is typically Drug injection, injected, usually into a vein, but it can also be snorted, smoked, or inhaled. In a clinical context, the route of administration is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are multiple methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual administration, sublingual; via inhalation; intramuscular, injection into a muscle, Subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin, or injection into the spinal cord area; transdermal; or via rectal administration, rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during Childbirth, labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
μ-opioid Receptor
The μ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ(''mu'')-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical μ-opioid receptor agonist is morphine, the primary psychoactive alkaloid in opium and for which the receptor was named, with Mu (letter), mu being the first letter of Morpheus, the compound's namesake in the original Greek. It is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that activates the Gi alpha subunit, Gi alpha subunit, inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity, lowering Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP levels. Structure The structure of the inactive μ-opioid receptor has been determined with the antagonists Beta-Funaltrexamine, β-FNA and alvimopan. Many structures of the active state are also available, with agonists including DAMGO, Β-Endorphin, β-endorphin, fentanyl and morphine. The structure with the agonist BU72 has the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substantia Nigra Pars Compacta
The pars compacta (SNpc, SNc) is one of two subdivisions of the ''substantia nigra'' of the midbrain (the other being the pars reticulata); it is situated medial to the ''pars reticulata''. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons. It projects to the striatum and portions of the cerebral cortex. It is functionally involved in fine motor control. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons in this region. Anatomy In humans, the nerve cell bodies of the ''pars compacta'' are coloured black by the pigment neuromelanin. The degree of pigmentation increases with age. This pigmentation is visible as a distinctive black stripe in brain sections and is the origin of the name given to this volume of the brain. Microanatomy The neurons have particularly long and thick dendrites. The ventral dendrites, particularly, go down deeply in the pars reticulata. Other similar neurons are more sparsely distributed in the midbrain and constitute "groups" with no well-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opiate
An opiate is an alkaloid substance derived from opium (or poppy straw). It differs from the similar term ''opioid'' in that the latter is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonists). Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant ''Papaver somniferum''. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions, with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Most opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America. In 2014, between 13 and 20 million people used opioids recreationally, representing 0.3% to 0.4% of the global population between the ages of 15 and 65. According to the CDC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Peptides
Opioid peptides or opiate peptides are peptides that bind to opioid receptors in the brain; opiates and opioids mimic the effect of these peptides. Such peptides may be produced by the body itself, for example endorphins. The effects of these peptides vary, but they all resemble those of opiates. Brain opioid peptide systems are known to play an important role in motivation, emotion, attachment theory, attachment behaviour, the response to Stress (biology), stress and pain, Hunger (motivational state), control of food intake, and the rewarding effects of alcohol (drug), alcohol and nicotine. Opioid-like peptides may also be absorbed from partially digestion, digested food (casomorphins, Gluten exorphin, exorphins, and rubiscolins). opioid food peptides, Opioid peptides from food typically have lengths between 4–8 amino acids. Endogenous opioids are generally much longer. Opioid peptides are released by post-translational proteolytic cleavage of Protein precursor, precursor pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphe Nuclei
The raphe nuclei (, "seam") are a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem. They have 5-HT1 receptors which are coupled with Gi/Go-protein-inhibiting adenyl cyclase. They function as autoreceptors in the brain and decrease the release of serotonin. The anxiolytic drug Buspirone acts as partial agonist against these receptors. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act in these nuclei, as well as at their targets. Anatomy The raphe nuclei are traditionally considered to be the medial portion of the reticular formation, and appear as a ridge of cells in the center and most medial portion of the brain stem. In order from caudal to rostral, the raphe nuclei are known as the '' nucleus raphe obscurus'', the '' nucleus raphe pallidus'', the '' nucleus raphe magnus'', the '' nucleus raphe pontis'', the '' median raphe nucleus'', ''dorsal raphe nucleus'', ''caudal linear nucleus''. In the first systematic examination of the raph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |