|
Rosemary Bank
Rosemary Bank is a seamount approximately west of Scotland, located in the Rockall Trough, in the northeast Atlantic. It was discovered in 1930 by the survey vessel HMS ''Rosemary'', from which it takes its name. It is one of only three seamounts known in Scottish waters. Rosemary Bank hosts a range of important habitats including deep sea sponge aggregations and cold water coral. Many species of fish, including orange roughy, blue ling, leafscale gulper shark and Portuguese dogfish are also found here. In 2014 the bank was declared a Nature Conservation Marine Protected Area (NCMPA) in order to protect the sponge aggregations, and the cenozoic marine geomorphology of the seabed. The designation was withdrawn in 2020, when it was replaced by the West of Scotland Marine Protected Area The West of Scotland Marine Protected Area covers a large area of the North Atlantic to the west of the Outer Hebrides. The Marine Protected Area (MPA) was designated by the Scottish Gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form.IHO, 2008. Standardization of Undersea Feature Names: Guidelines Proposal form Terminology, 4th ed. International Hydrographic Organization and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Monaco. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockall Trough
The Rockall Trough ( gd, Clais Sgeir Rocail) is a deep-water bathymetric feature to the northwest of Scotland and Ireland, running roughly from southwest to northeast, flanked on the north by the Rockall Plateau and to the south by the Porcupine Seabight. At the northern end, the channel is bounded by the Wyville-Thomson Ridge, named after Charles Wyville Thomson, professor of zoology at the University of Edinburgh and driving force behind the Challenger Expedition. At the southern end, the trough opens into the Porcupine abyssal plain. The Rockall Basin (also known as the Hatton Rockall Basin) is a large (c. 800 km by 150 km) sedimentary basin that lies beneath the trough. Both are named after Rockall, a rocky islet lying 301.4 km west of St Kilda. Features of the Rockall Plateau have been officially named after features of Middle-earth in the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, e.g. Eriador Seamount, Rohan Seamount, Gondor Seamount, Fangorn Bank, Edoras Bank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of Earth, the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North America, North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8th paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Rosemary
HMS ''Rosemary'' was an ''Arabis''-class minesweeping sloop of the British Royal Navy. Built by the Teesside shipbuilder Richardson, Duck and Company from 1915–1916, ''Rosemary'' carried out minesweeping and anti submarine operations during the First World War. She was used for fishery protection duties during the 1930s, and served through the Second World War, finally being sold for scrap in 1947. Design and construction The ''Arabis'' class was a slightly enlarged and improved derivative of the previous and sloops. They were designed at the start of the First World War as relatively fast minesweepers that could also carry out various miscellaneous duties in support of the fleet such as acting as dispatch vessels or carrying out towing operations, but as the war continued and the threat from German submarines grew, became increasingly involved in anti-submarine duties. ''Rosemary'' was long overall and between perpendiculars, with a beam of and a draught of . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep-water Coral
The habitat of deep-water corals, also known as cold-water corals, extends to deeper, darker parts of the oceans than tropical corals, ranging from near the surface to the abyss, beyond where water temperatures may be as cold as . Deep-water corals belong to the Phylum Cnidaria and are most often stony corals, but also include black and thorny corals and soft corals including the Gorgonians (sea fans). Like tropical corals, they provide habitat to other species, but deep-water corals do not require zooxanthellae to survive. While there are nearly as many species of deep-water corals as shallow-water species, only a few deep-water species develop traditional reefs. Instead, they form aggregations called patches, banks, bioherms, massifs, thickets or groves. These aggregations are often referred to as "reefs," but differ structurally and functionally. Deep sea reefs are sometimes referred to as "mounds," which more accurately describes the large calcium carbonate skeleton that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Roughy
The orange roughy (''Hoplostethus atlanticus''), also known as the red roughy, slimehead and deep sea perch, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family (Trachichthyidae). The UK Marine Conservation Society has categorized orange roughy as "vulnerable to exploitation". It is found in , deep (bathypelagic, ) waters of the Western Pacific Ocean, eastern Atlantic Ocean (from Iceland to Morocco; and from Walvis Bay, Namibia, to off Durban, South Africa), Indo-Pacific (off New Zealand and Australia), and in the eastern Pacific off Chile. The orange roughy is notable for its extraordinary lifespan, attaining over 200 years. It is important to commercial deep-trawl fisheries. The fish is a bright, brick-red color, fading to a yellowish-orange after death. Like other slimeheads, orange roughy is slow-growing and late to mature, resulting in a very low resilience, making them extremely susceptible to overfishing. Many stocks (especially those off New Zealand an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Ling
The blue ling (''Molva dypterygia'') is a member of the cod family from the North Atlantic. It is usually 70 to 110 cm long, but the maximum length is 155 cm. Blue ling feed on fish (flatfishes, gobies, rocklings) and crustaceans and benthic invertebrates Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate .... The fish reaches sexual maturity at the age of six to 12 years. References Blue ling (Icelandic Fisheries)Blålange (Institute of Marine Research, Norway)Blue ling at Fishbase.org {{Taxonbar, from=Q882968 blue ling Fauna of Atlantic Canada Fish of the North Atlantic Fish of Europe blue ling Taxa named by Thomas Pennant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leafscale Gulper Shark
The leafscale gulper shark (''Centrophorus squamosus'') is a dogfish of the family Centrophoridae. ''C. squamosus'' is reported to have a lifespan of approximately 70 years, based on otolith ring counts. It was the first described species in the genus Centrophorus, which now contains 13 species. Physical characteristics The leafscale gulper shark has no anal fin, two dorsal fins with spines, the first dorsal being relatively low and long, large eyes, and rough leaf-like denticles. Its maximum length is . Distribution Eastern Atlantic around continental slopes from Iceland south to the Cape of Good Hope, western Indian Ocean around Aldabra Islands, and western Pacific around Honshu, Japan, the Philippines, south-east Australia, and New Zealand. Habits and habitat The leafscale gulper shark lives near the bottom between , but usually below . Also occurs pelagically in much deeper water. It probably feeds on fish and cephalopods. It is ovoviviparous with a maximum of five y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Dogfish
The Portuguese dogfish (''Centroscymnus coelolepis'') or Portuguese shark, is a species of sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae. This globally distributed species has been reported down to a depth of , making it the deepest-living shark known. It inhabits lower continental slopes and abyssal plains, usually staying near the bottom. Stocky and dark brown in color, the Portuguese dogfish can be distinguished from similar-looking species (such as the kitefin shark, ''Dalatias licha'') by the small spines in front of its dorsal fins. Its dermal denticles are also unusual, resembling the scales of a bony fish. This species typically reaches in length; sharks in the Mediterranean Sea are much smaller and have distinct depth and food preferences. Relatively common, the Portuguese dogfish is an active hunter capable of tackling fast, large prey. It feeds mainly on cephalopods and fishes, though it also consumes invertebrates and cetacean carrion. This shark has acute vision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
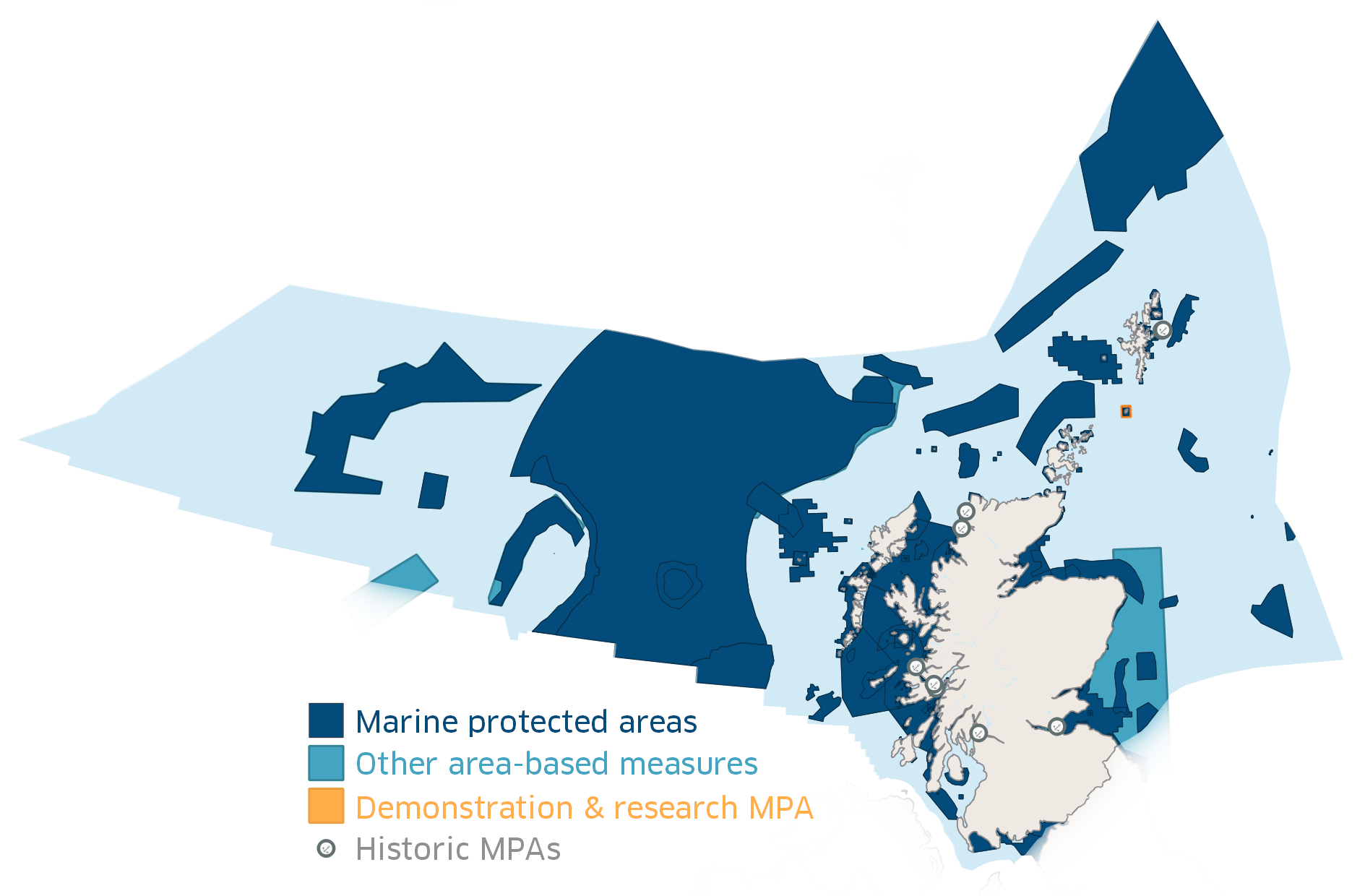
Marine Protected Areas In Scotland
In Scotland, Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are areas of sea defined so as to protect to habitats, wildlife, geology, undersea landforms, historic shipwrecks, and to demonstrate sustainable management of the sea. As of December 2020, approximately 37% of Scotland's seas are covered by the Scottish MPA network, which comprises 244 sites in total. Designation As of December 2020 Scotland's MPA network comprises 244 sites protected by a variety of different conservation designations, many of which are the same as those used on land, such as Special Protection Areas (SPA) and Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI).Scottish MPA network - Parliamentary Report. p. 11.Scottish MPA network - Parliamentary Report. p. 32. This figure includes four sites designated in December 2020: North-east Lewis; Shiant East Bank; Sea of the Hebrides; and the Southern Trench. The legal framework for designating MPAs depends on the designation: for example SSSIs are designated under the Nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.gif)