|
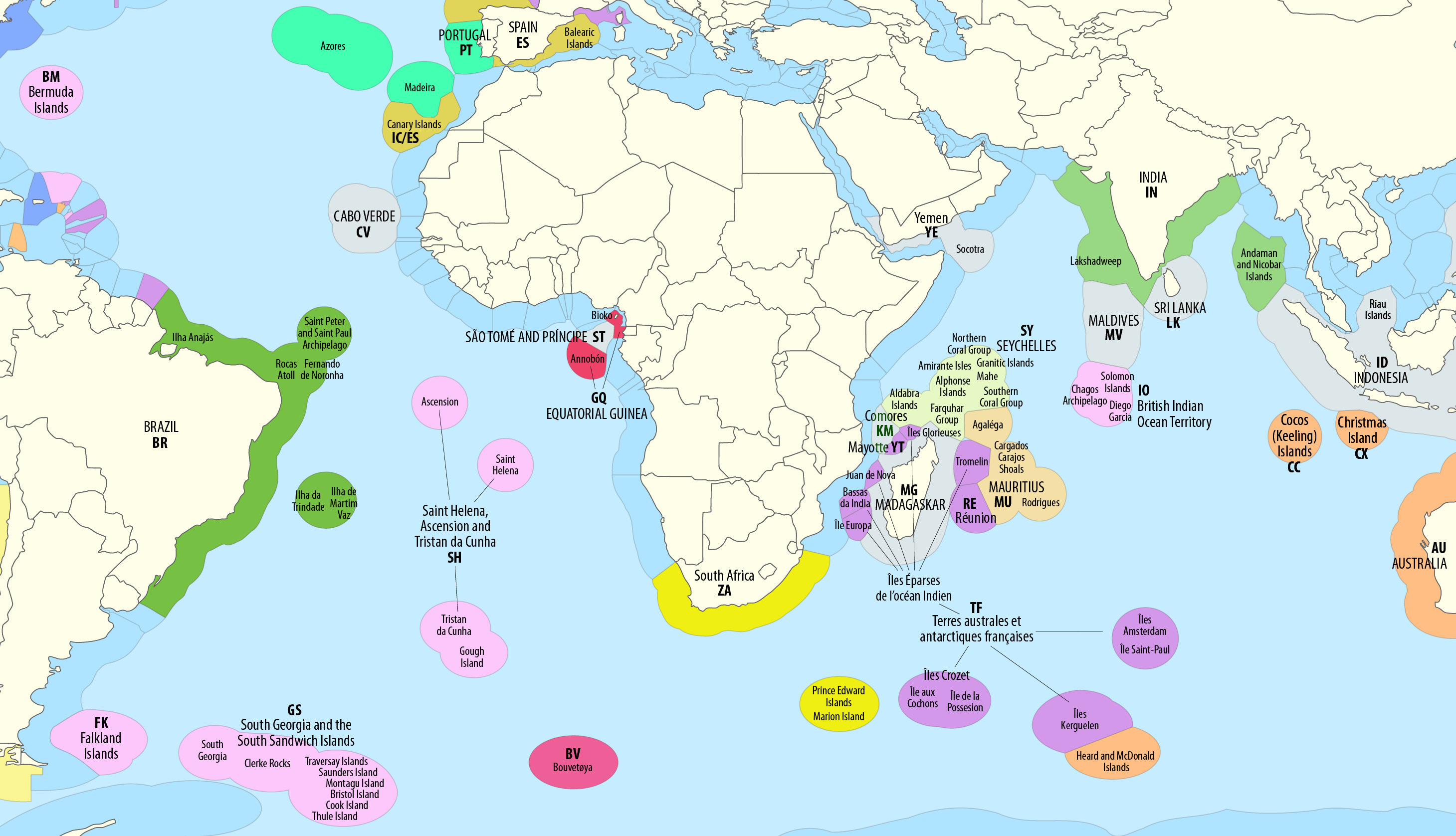
Rondo Island
Rondo Island (; ) is Indonesia's northernmost territory,2007Atoll Research Bulletin Issue 544, Page 48] located in the Andaman Sea, with a 0.650 km2 area 35m above sea level. The island is one of the outlying islands of Indonesia in the Aceh province of the Sumatra region. It is administratively part of the in Sabang City, whose administration center is on Weh Island, south of Rondo. Rondo is 50 km offshore from Indonesia's Sumatra mainland. This otherwise uninhabited island, accessible only by boat, has an Indonesian military outpost with a heliport and blue-roofed barracks, an adjacent lighthouse complex with a red-roofed lighthouse keeper's house and a white skeletal lighthouse topped with a viewing gallery and lantern. India's southernmost territory (Indira Point) on Great Nicobar Island of the Nicobar Islands is approximately 84 miles or 135 km to the north from the Indonesia's northernmost territory on Rondo Island.James Horsburgh, 1852The India Director ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Indonesia
This is a list of some of the regions of Indonesia. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the central government. At different times of Indonesia's history, the nation has been designated as having regions that do not necessarily correlate to the current administrative or physical geography of the territory of the nation. Geographical units According to ISO 3166-2:ID, Indonesia is divided into seven geographical units, with each unit consisting of major islands or an island group. These geographical units are as follows: Eastern Indonesia and Western Indonesia During the last stages of the Dutch colonial era, the area east of Java and Kalimantan was known as the Great East and later known as Eastern Indonesia. On 24 December 1946, the State of East Indonesia was formed covering the same area (excluding Western New Guinea). It was a component of the United States of Indonesia, and was dissolved into the unitary Republic of Indonesia in 17 August 1950. Currently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups. Coral belongs to the class Anthozoa in the animal phylum Cnidaria, which includes sea anemones and jellyfish. Unlike sea anemones, corals secrete hard carbonate exoskeletons that support and protect the coral. Most reefs grow best in warm, shallow, clear, sunny and agitated water. Coral reefs first appeared 485 million years ago, at the dawn of the Early Ordovician, displacing the microbial and sponge reefs of the Cambrian. Sometimes called ''rainforests of the sea'', shallow coral reefs form some of Earth's most diverse ecosystems. They occupy less than 0.1% of the world's ocean area, about half the area of France, yet they provide a home for at least 25% of all marine species, including fish, mollusks, worms, crustaceans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family, collectively called the Southern Ming, survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fei Xin
Fei Xin (; - after 1436) was a member of the military personnel of the fleet of the Ming dynasty admiral Zheng He, known as the author of a book about the countries visited by Chinese ships. Biography Little is known about Fei Xin's life. His family originated from Kunshan, in today's Jiangsu Province. Based on other dates mentioned by him, it is likely that he was born in the 17th year of the Hongwu era (1385), although some authors' calculation give 1388 as the date of his birth. He taught himself the Arabic language. According to what Fei Xin says in the preface to his book, his family was poor. His older brother was called up to serve at the nearby Taicang garrison, but soon died, and young Fei Xin took his place, in or after 1398. J.J.L. Duyvendak speculated that the Fei brothers had been conscripted as a punishment for some political or other offense of their father or grandfather; there is no actual proof of that, but Fei Xin's later biographer, Roderich Ptak, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy In The Strait Of Malacca
Piracy in the Strait of Malacca has long been a threat to ship owners and the mariners who ply the 900 km-long (550 miles) sea lane. In recent years, coordinated patrols by Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore along with increased security on vessels have sparked a sharp downturn in piracy. The Strait of Malacca's geography makes the region very susceptible to piracy. It was and still is an important passageway between China and India, used heavily for commercial trade. The strait is on the route between Europe, the Suez Canal, the oil-exporting countries of the Persian Gulf, and the busy ports of East Asia. It is narrow, contains thousands of islets, and is an outlet for many rivers, making it ideal for pirates to evade capture. History Piracy in the Strait of Malacca was not only a lucrative way of life but also an important political tool. Rulers relied on the region's pirates to maintain control. For example, it was through the loyalty of Orang Laut pirate c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Economic Times
''The Economic Times'' is an Indian English-language business-focused daily newspaper. Owned by The Times Group, ''The Economic Times'' began publication in 1961 and it is sold in all major cities in India. As of 2012, it is the world's second-most widely read English-language business newspaper, after ''The Wall Street Journal'', with a daily readership of over 800,000. According to the Audit Bureau of Circulations (India), Audit Bureau of Circulations, the newspaper's Print circulation, circulation averaged 269,882 copies during the latter half of 2022. It is published simultaneously from 14 cities: Mumbai, Bangalore, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Ahmedabad, Nagpur, Chandigarh, Pune, Indore, and Bhopal. Its main content is based on the Economy of India, Indian economy, international finance, share prices, prices of commodities as well as other matters related to finance. This newspaper is Publishing, published by Bennett Coleman & Co. Ltd, Bennett, Cole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Malacca
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, long and from wide, between the Malay Peninsula to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean). As the main shipping channel between the Indian and Pacific oceans, it is one of the most important shipping lanes in the world. Etymology The name "Malacca" is traditionally associated with the Malacca tree ('' Phyllanthus emblica''), also known as the Indian gooseberry tree, and is believed to derive from the local Malay word "Melaka". According to historical traditions, Parameswara, a Sumatran prince and the founder of the Malacca Sultanate, selected the site for his new kingdom where the city of Malacca now stands. It is said that he named the location "Melaka" after the Malacca tree under which he had rested. Over time, the name "Malacca" came to refer not only to the city but also to the strategically significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea. Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelf, continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Silk Route
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula, eastern Africa, and Europe. It began by the 2nd century BCE and flourished until the 15th century CE. The Maritime Silk Road was primarily established and operated by Austronesian sailors in Southeast Asia who sailed large long-distance ocean-going sewn-plank and lashed-lug trade ships. The route was also utilized by the dhows of the Persian and Arab traders in the Arabian Sea and beyond, and the Tamil merchants in South Asia. China also started building their own trade ships ('' chuán'') and followed the routes in the later period, from the 10th to the 15th centuries CE. The network followed the footsteps of older Austronesian jade maritime networks in Southeast Asia, as well as the maritime spice networks between Southeast Asia and South Asia, and the West Asian maritime networks in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclusive Economic Zone Of Thailand
Thailand has the world's 64th largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ), with an area of . It claims an EEZ of from its shores, which has long coastlines with the Andaman Sea and Strait of Malacca to the west and the Gulf of Thailand to the east, although all of its EEZ is limited by maritime boundaries with neighbouring countries. Thailand's western sea territory stretches from the west coast of southern Thailand in the Andaman Sea and the Strait of Malacca. It shares treaty-defined maritime boundaries with Myanmar, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India, Indonesia and Malaysia. Disputes Thailand has not established agreements with Cambodia and Vietnam, who also have maritime territory in the Gulf of Thailand, leading to conflicts. It also has not established a treaty with Malaysia on their gulf waters; however, the Malaysia–Thailand joint development area was established for both countries to jointly exploit the resources in the area of their overlapping claims. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclusive Economic Zone Of India
India has the 18th-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ) with a total size of . It includes the Lakshadweep island group in the Laccadive Sea off the southwestern coast of India and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. India's EEZ is bordered to the west by Pakistan, to the south by the Maldives and Sri Lanka and to the east by Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia. Based on new scientific data, India has petitioned United Nations to extend its EEZ from 200 Nautical miles to 350 nautical miles. Legal framework India legally defined the concept of EEZ in the ''"Territorial Waters, Continental Shelf, Exclusive Economic Zone and Other Maritime Zones Act, 1976"''. In June 1997, India also ratified UNCLOS. India also enacted the ''"Maritime Zones of India (Regulation of fishing by foreign vessels) Act, 1981"'' prohibiting fishing by foreign vessel within Indian EEZ without a license. Additionally, India has also enacted laws reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |