|
Ron Ross
Ronald S. Ross is an American computer scientist, retired United States Army lieutenant colonel, and senior cybersecurity advisor best known for leading the development of federal information security standards at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). He was a principal author of widely used NIST frameworks, including SP 800-53, SP 800-37, and SP 800-160, and has received multiple national honors for his contributions to cybersecurity policy and systems security engineering. Early life and education Ross graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and earned a master’s and doctorate in computer science from the Naval Postgraduate School, with a focus on artificial intelligence and robotics. He also completed studies at the Defense Systems Management College. Military service Ross served 20 years in the United States Army, where he was commissioned as a Second Lieutenant and served as a Mechanized Infantry and United States Army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789).See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 It operates under the authority, direction, and control of the United States Secretary of Defense, United States secretary of defense. It is one of the six armed forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Army is the most senior branch in order of precedence amongst the armed services. It has its roots in the Continental Army, formed on 14 June 1775 to fight against the British for independence during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal News Network
WFED (1500 AM) is a 50,000-watt Class A radio station in Washington, D.C. The station owned by Hubbard Broadcasting, and branded "Federal News Network", broadcasts a news/talk format focused on issues and news pertaining to members and staff of the United States government. WFED's studios are located at Hubbard's broadcast complex in northwest Washington, while its transmitter site is located at a three-tower array in Wheaton, Maryland. The station transmits full-time with a power of 50,000 watts. A single transmitter tower, with a non-directional signal, is used during the day. At night, all three towers are used for a directional pattern, with a null toward the west to protect KSTP in St. Paul, Minnesota. WFED's signal can be heard across most of the Eastern Seaboard at night. WFED became a Primary Entry Point station for the Emergency Alert System in 2014. Programming WFED's weekday programming consists primarily of original news and talk content for federal governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a set of voluntary guidelines designed to help organizations assess and improve their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cybersecurity risks. Developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the framework was initially published in 2014 for critical infrastructure sectors but has since been widely adopted across various industries, including government and private enterprises globally. The framework integrates existing standards, guidelines, and best practices to provide a structured approach to cybersecurity risk management. The CSF is composed of three primary components: the Core, Implementation Tiers, and Profiles. The Core outlines five key cybersecurity functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—each of which is further divided into specific categories and subcategories. These functions offer a high-level, outcome-driven approach to managing cybersecurity risks. The Implementati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
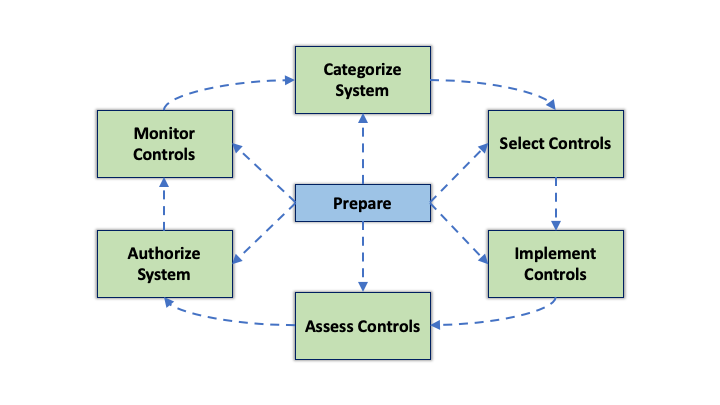
Risk Management Framework (NIST)
The Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a United States federal government guideline, standard, and process for managing risk to help secure information systems (computers and networks). The RMF was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and provides a structured process that integrates information security, privacy, and risk management activities into the system development life cycle. The RMF is an important aspect of a systems attainment of its Authority to Operate (ATO). Overview The primary document outlining the RMF is NIST Special Publication 800-37. The RMF steps link to several other NIST standards and guidelines, including NIST Special Publication 800-53. The RMF process includes the following steps: * ''Prepare'' to execute the RMF by establishing a context and setting priorities for managing security and privacy risk at both organizational and system levels. * ''Categorize'' the information system and the data it processes, stores, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Infrastructure Protection
In the U.S., critical infrastructure protection (CIP) is a concept that relates to the preparedness and response to serious incidents that involve the critical infrastructure of a region or the nation. The American Presidential directive PDD-63 of May 1998 set up a national program of "Critical Infrastructure Protection". In 2014 the NIST Cybersecurity Framework was published after further presidential directives. History The U.S. CIP is a national program to ensure the security of vulnerable and interconnected infrastructures of the United States. In May 1998, President Bill Clinton issued presidential directive PDD-63 on the subject of critical infrastructure protection. This recognized certain parts of the national infrastructure as critical to the national and economic security of the United States and the well-being of its citizenry, and required steps to be taken to protect it. This was updated on December 17, 2003, by President George W. Bush through Homeland Security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Defense
National security, or national defence (national defense in American English), is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military attack, national security is widely understood to include also non-military dimensions, such as the security from terrorism, minimization of crime, economic security, energy security, environmental security, food security, and cyber-security. Similarly, national security risks include, in addition to the actions of other states, action by violent non-state actors, by narcotic cartels, organized crime, by multinational corporations, and also the effects of natural disasters. Governments rely on a range of measures, including political, economic, and military power, as well as diplomacy, to safeguard the security of a state. They may also act to build the conditions of security regionally and internationall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their Enterprise life cycle, life cycles. At its core, systems engineering utilizes systems thinking principles to organize this body of knowledge. The individual outcome of such efforts, an engineered system, can be defined as a combination of components that work in synergy to collectively perform a useful Function (engineering), function. Issues such as requirements engineering, Reliability engineering, reliability, logistics, coordination of different teams, testing and evaluation, maintainability, and many other Discipline (academia), disciplines, aka List of system quality attributes, "ilities", necessary for successful system design, development, implementation, and ultimate decommission become more difficult when dealing with large or complex projects. Systems engineering deals with work processes, optimizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cybersecurity
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and networks from threats that can lead to unauthorized information disclosure, theft or damage to hardware, software, or data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the services they provide. The significance of the field stems from the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards. Its importance is further amplified by the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most significant new challenges facing the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societies they support. Security is particularly crucial for systems that govern large-scale sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington University
The George Washington University (GW or GWU) is a Private university, private University charter#Federal, federally-chartered research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Originally named Columbian College, it was chartered in 1821 by the United States Congress and is the first university founded under Washington, D.C.'s jurisdiction. It is one of the nation's six University charter#Federal, federally chartered universities. GW is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among List of research universities in the United States#Universities classified as "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity", "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity." It is a member of the Association of American Universities. The university offers degree programs in seventy-one disciplines, enrolling around 11,500 Undergraduate education, undergraduate and 15,000 Graduate school, graduate students. The school's athletic teams, the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College ( ) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, Dartmouth is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Emerging into national prominence at the turn of the 20th century, Dartmouth has since been considered among the most prestigious undergraduate colleges in the United States. Although originally established to educate Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in Christian theology and the Anglo-American way of life, the university primarily trained Congregationalism in the United States, Congregationalist ministers during its early history before it gradually secularized. While Dartmouth is now a research university rather than simply an undergraduate college, it continues to go by "Dartmouth College" to emphasize its focus on undergraduate education. Following a liberal arts curriculum, Dartmouth provides unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and science. In response to the increasing Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialization of the United States, William Barton Rogers organized a school in Boston to create "useful knowledge." Initially funded by a land-grant universities, federal land grant, the institute adopted a Polytechnic, polytechnic model that stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT moved from Boston to Cambridge in 1916 and grew rapidly through collaboration with private industry, military branches, and new federal basic research agencies, the formation of which was influenced by MIT faculty like Vannevar Bush. In the late twentieth century, MIT became a leading center for research in compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth List of governors of California, governor of and then-incumbent List of United States senators from California, United States senator representing California) and his wife, Jane Stanford, Jane, in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., Leland Jr. The university admitted its first students in 1891, opening as a Mixed-sex education, coeducational and non-denominational institution. It struggled financially after Leland died in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, university Provost (education), provost Frederick Terman inspired an entrepreneurship, entrepreneurial culture to build a self-sufficient local industry (later Silicon Valley). In 1951, Stanfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |