|
Roman Personal Weapons
Roman military personal equipment was produced in large numbers to established patterns, and used in an established manner. These standard patterns and uses were called the ''res militaris'' or ''disciplina''. Its regular practice during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire led to military excellence and victory. The equipment gave the Romans a very distinct advantage over their "barbarian" enemies, especially so in the case of armour. This does not mean that every Roman soldier had better equipment than the richer men among his opponents. Roman equipment was not of a better quality than that used by the majority of Rome's adversaries. Other historians and writers have stated that the Roman army's need for large quantities of "mass produced" equipment after the so-called "Marian Reforms" and subsequent civil wars led to a decline in the quality of Roman equipment compared to the earlier Republican era: Initially, they used weapons based on Greek and Etruscan models. On encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Folks' History Of Rome Illus064
Young may refer to: * Offspring, the product of reproduction of a new organism produced by one or more parents * Youth, the time of life when one's age is low, often meaning the time between childhood and adulthood Music * The Young, an American rock band * ''Young'', an EP by Charlotte Lawrence, 2018 Songs * Young (Baekhyun and Loco song), "Young" (Baekhyun and Loco song), 2018 * Young (The Chainsmokers song), "Young" (The Chainsmokers song), 2017 * Young (Hollywood Undead song), "Young" (Hollywood Undead song), 2009 * Young (Kenny Chesney song), "Young" (Kenny Chesney song), 2002 * Young (Place on Earth song), "Young" (Place on Earth song), 2018 * Young (Tulisa song), "Young" (Tulisa song), 2012 * "Young", by Ella Henderson discography#Singles, Ella Henderson, 2019 * "Young", by Lil Wayne from ''Dedication 6'', 2017 * "Young", by Nickel Creek from ''This Side'', 2002 * "Young", by Sam Smith from ''Love Goes'', 2020 * "Young", by Silkworm from ''Italian Platinum'', 2002 * "Young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
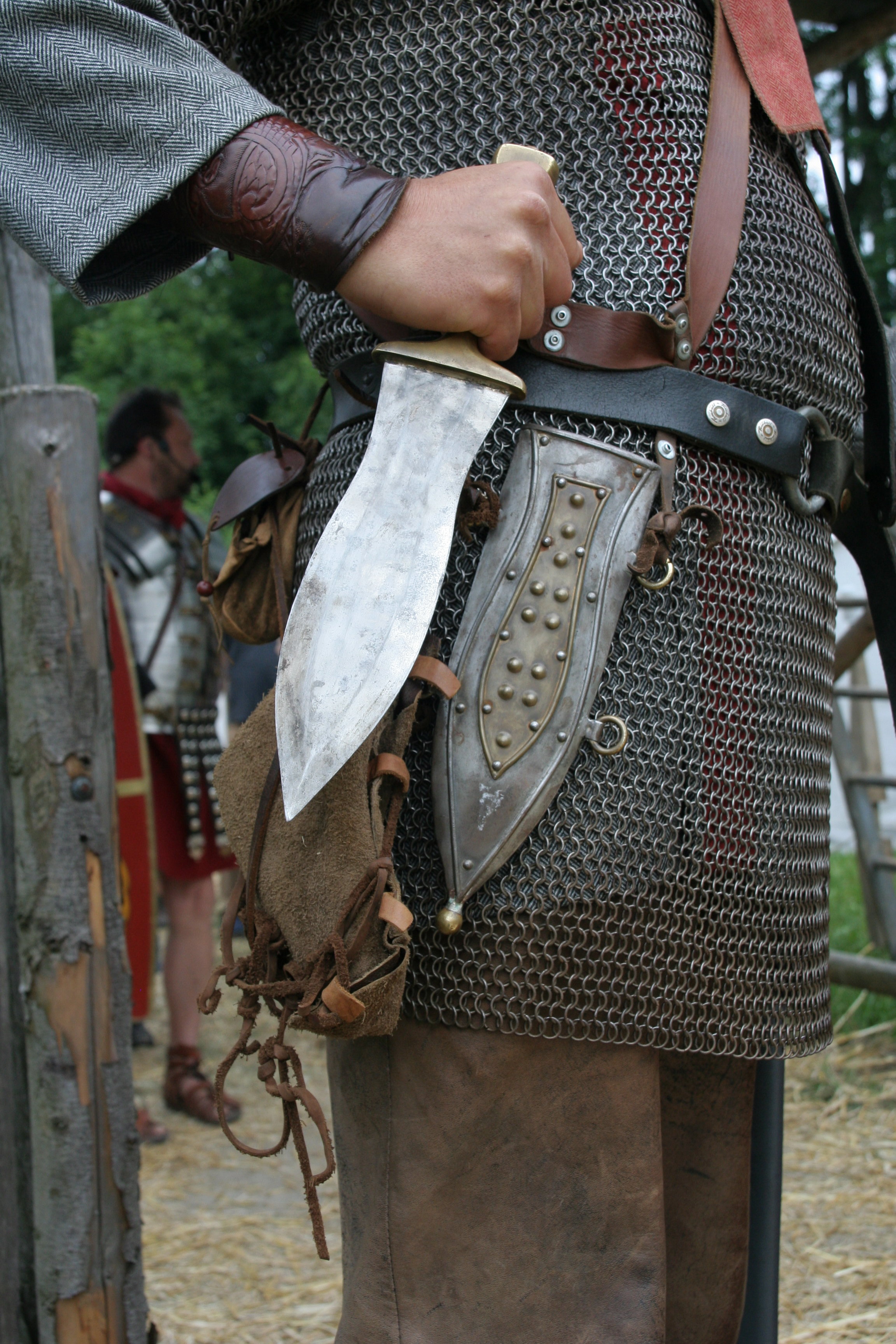
Spatha End Of Second Century 1
The spatha was a type of straight and long sword, measuring between , with a handle length of between , in use in the territory of the Roman Empire during the 1st to 6th centuries AD. Later swords, from the 7th to 10th centuries, like the Viking swords, are recognizable derivatives and sometimes subsumed under the term ''spatha''. The Roman ''spatha'' was used in war and in gladiatorial fights. The ''spatha'' of literature appears in the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD as a weapon used by presumably Celtic auxiliaries and gradually became a standard heavy infantry weapon by the 3rd century AD, relegating the ''gladius'' to use as a light infantry weapon. The ''spatha'' apparently replaced the ''gladius'' in the front ranks, giving the infantry more reach when thrusting. While the infantry version had a long point, versions carried by the cavalry had a rounded tip that prevented accidental stabbing of the cavalryman's own foot or horse. Archaeologically many instances of the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetius
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also referred to as '' De re militari''), and the lesser-known ''Digesta Artis Mulomedicinae'', a guide to veterinary medicine. He identifies himself in the opening of his work ''Epitoma rei militaris'' as a Christian. Dating of work The latest event alluded to in his ''Epitoma rei militaris'' is the death of the Emperor Gratian (383); the earliest attestation of the work is a ''subscriptio'' by Flavius Eutropius, writing in Constantinople in 450, which appears in one of two families of manuscripts, suggesting that a division of the manuscript tradition had already occurred. Despite Eutropius' location in Constantinople, the scholarly consensus is that Vegetius wrote in the Western Roman Empire.Walter Goffart. "The date and purposes of Vegetius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
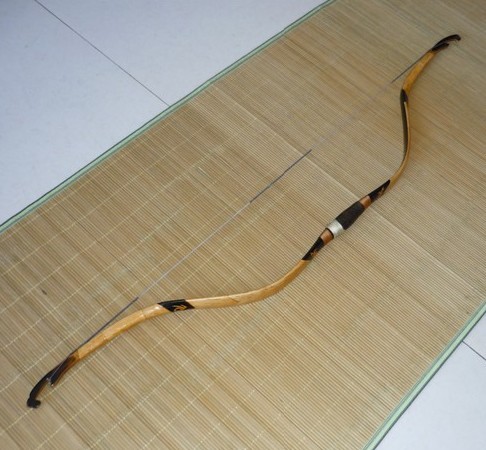
Composite Bow
A composite bow is a traditional bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together, a form of laminated bow. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the outer side of a wooden core. When the bow is drawn, the sinew (stretched on the outside) and horn (compressed on the inside) store more energy than wood for the same length of bow. The strength can be made similar to that of all-wood "self" bows, with similar draw-length and therefore a similar amount of energy delivered to the arrow from a much shorter bow. However, making a composite bow requires more varieties of material than a self bow, its construction takes much more time, and the finished bow is more sensitive to moisture. Archaeological finds and art indicate composite bows have existed since the second millennium BCE, but their history is not well recorded, being developed by cultures without a written tradition. They originated among Asiatic pastoralists who used them as daily necessities, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Ancient Rome
The military history of ancient Rome is inseparable from its political system, based from an early date upon competition within the ruling elite. Two consuls were elected each year to head the government of the state, and in the early to mid-Republic were assigned a consular army and an area in which to campaign. History From Gaius Marius and Sulla onwards, control of the army began to be tied into the political ambitions of individuals, leading to the political triumvirate of the 1st century BC and its resolution in a civil war that led to the Republic's collapse. The Empire was increasingly plagued by usurpations led or supported by military conspiracies, leading to the Crisis of the Third Century (235–284 AD) in the late empire and eventual final decline. Following is a list of topics on the military history of ancient Rome. * Structural history of the Roman military :The branches of the Roman military at the highest level were the Roman army and the Roman navy. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelin (weapon)
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distances, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiculum
A ''spiculum'' is a late Roman spear that replaced the ''pilum'' as the infantryman's main throwing javelin around 250 AD. Scholars suppose that it could have resulted from the gradual combination of the ''pilum'' and two German spears, the ''angon'' and the ''bebra''. As more and more Germans joined the Roman army, their culture and traditions became a driving force for change. The ''spiculum'' was better than the old ''pilum'' when used as a thrusting spear, but still maintained some of the former weapon's penetrative power when thrown. Vegetius mentions the ''spiculum'' in his military manual, but some scholars maintain that the ''spiculum'' was simply a different name for the ''pilum''. Whatever the case, most historians accept that the ''spiculum'' evolved from the earlier javelins used by the Roman army. The main difference between the ''spiculum'' and the ''pilum'' was the length of the thin point. The ''spiculum'' tended to have a much shorter iron point. Thus, the ''sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancea (weapon)
The ''lancea'' was a javelin used in ancient Rome. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word originally came from the Celtiberian language, also cf. λόγχη (''lonche''), the Greek term for lance. One kind of ''lancea'', possibly known as the ''lancea pugnatoria'' or "the fighting lance" was used as a thrusting weapon by cavalrymen. This weapon was used by cavalrymen as it was lighter and easier to use than the '' pilum''. The ''lancea'' was also used by auxiliaries. Legionaries would use the ''lancea'' if the occasion called for it. Arrian equipped his army with the weapon during a battle with the Alans. Soldiers that used it were known as '' lancearii''. It is unclear how the ''lancea'' was distinguished from the '' hastae''. Many ''lancea'' had '' amenta'', although not all. This kind of javelin also had short wooden shafts and small leaf-shaped metal heads. Sometimes the heads had elongated points which may have been used to increase the penetration of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verutum
The ''verutum'', plural ''veruta'' (), was a short javelin used in the Roman army. This javelin was used by the ''velites'' for skirmishing purposes, unlike the heavier ''pilum'', which was used by the ''hastati'' and ''principes'' for weakening the enemy before advancing into close combat. The shafts were about long, substantially shorter than the ''pilum'', and the point measured about long. The ''verutum'' had either an iron shank like the ''pilum'' or a tapering metal head. It was sometimes thrown with the aid of a throwing strap, or '' amentum''. The ''verutum'' was probably adopted from the Samnites and the Volsci but there is not enough proof for that. During the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Roman light infantry (''velites'') would carry seven ''veruta'' into combat. It proved to be quite an effective weapon, even against war elephants as proven in the battle of Zama. In the late 2nd century BC, the ''verutum'' was taken out of service along with the ''veles'', but the jav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velites
''Velites'' (; : ) were a class of infantry in the Roman army of the mid-Republic from 211 to 107 BC. ''Velites'' were light infantry and skirmishers armed with javelins (), each with a 75cm (30 inch) wooden shaft the diameter of a finger, with a 25cm (10 inch) narrow metal point, to fling at the enemy. They also carried short thrusting swords, or gladius, ''gladii'', for use in melee. They rarely wore armour as they were the youngest and poorest soldiers in the legion and could not afford much equipment. They did carry small wooden shields called ''Parma (shield), parma'' for protection, and wore headdresses made from wolf skins so their brave deeds could be recognized. The ''velites'' were placed at the front partly for tactical reasons, and also so that they had the opportunity to secure glory for themselves in single combat. ''Velites'' did not form their own units; a number of them were attached to each Maniple (military unit), maniple of ''hastati'', ''principes'' and ''tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triarii
''Triarii'' (: ''triarius'') ("the third liners") were one of the elements of the early Roman military manipular legions of the early Roman Republic (509 BC – 107 BC). They were the oldest and among the wealthiest men in the army and could afford high quality equipment. They wore heavy metal armor and carried large shields, their usual position being the third battle line. They were equipped with spears and were considered to be elite soldiers among the legion. During the Camillan era, they fought in a shallow phalanx formation, supported by light troops. In most battles ''triarii'' were not used because the lighter troops usually defeated the enemy before the ''triarii'' were committed to the battle. They were meant to be used as a decisive force in the battle, thus prompting an old Roman saying: ''res ad triarios venit'', 'it comes down to the triarii', which meant carrying on to the bitter end. History and deployment According to author Pat Southern, ''triarii'' may ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilum
The ''pilum'' (; : ''pila'') was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about long overall, consisting of an iron shank about in diameter and long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft by either a socket or a flat tang. History The ''pilum ''may have originated from an Italic tribe known as the Samnites. It also may have been influenced by Celtiberian and Etruscan weapons. The ''pilum'' may have derived from a Celtiberian weapon known as the'' falarica''. Archaeological excavations have disclosed ''pila'' in tombs at the Etruscan city of Tarquinia. The oldest finds of pila are from the Etruscan settlements of Vulci and Talamone. The first identified written reference to the ''pilum'' comes from ''The Histories'' of Polybius. According to Polybius, more heavily armed Roman military soldiers used a spear called the ''hyssoí''. This may have been the ''pilum''. The precursor to the ''pilum'' was the '' hasta''. It is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |