|
Rolls-Royce Pearl
The Rolls-Royce BR700 is a family of turbofan engines for regional jets and corporate jets. It is manufactured in Dahlewitz, Germany, by Rolls-Royce Deutschland: this was initially a joint venture of BMW and Rolls-Royce plc established in 1990 to develop this engine. The BR710 first ran in 1995. The United States military designation for the BR725 variant is F130. Design and development BR710 The BR710 is a twin shaft turbofan, and entered service on the Gulfstream V in 1997 in aviation, 1997 and the Bombardier Global Express in 1998. This version has also been selected to power the Gulfstream G550. The BR710 comprises a diameter single-stage fan, driven by a two-stage LP turbine, and a ten-stage HP compressor (scaled from the V2500 unit) driven by a two-stage, air-cooled, HP turbine. This engine has a thrust-specific fuel consumption (TSFC) of at static sea level takeoff and at a cruise speed of Mach number, Mach 0.8 and altitude of . In May 2017, the 3,200 engines in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust-specific Fuel Consumption
Thrust-specific fuel consumption (TSFC) is the fuel efficiency of an engine design with respect to thrust output. TSFC may also be thought of as fuel consumption (grams/second) per unit of thrust (newtons, or N), hence ''thrust-specific''. This figure is inversely proportional to specific impulse, which is the amount of thrust produced per unit fuel consumed. TSFC or SFC for thrust engines (e.g. turbojets, turbofans, ramjets, rockets, etc.) is the mass of fuel needed to provide the net thrust for a given period e.g. lb/(h·lbf) (pounds of fuel per hour-pound of thrust) or g/(s·kN) (grams of fuel per second-kilonewton). Mass of fuel is used, rather than volume (gallons or litres) for the fuel measure, since it is independent of temperature. Specific fuel consumption of air-breathing jet engines at their maximum efficiency is more or less proportional to exhaust speed. The fuel consumption ''per mile'' or ''per kilometre'' is a more appropriate comparison for aircraft that travel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
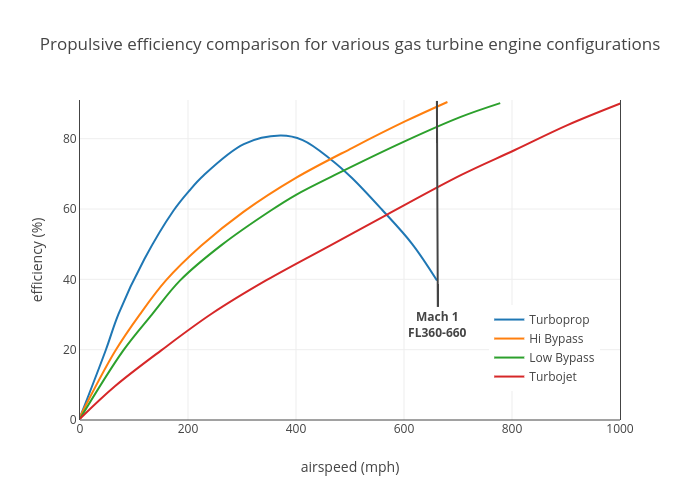
Bypass Ratio
The bypass ratio (BPR) of a turbofan engine is the ratio between the mass flow rate of the bypass stream to the mass flow rate entering the core. A 10:1 bypass ratio, for example, means that 10 kg of air passes through the bypass duct for every 1 kg of air passing through the core. Turbofan engines are usually described in terms of BPR, which together with engine pressure ratio, turbine inlet temperature and fan pressure ratio are important design parameters. In addition, BPR is quoted for turboprop and unducted fan installations because their high propulsive efficiency gives them the overall efficiency characteristics of very high bypass turbofans. This allows them to be shown together with turbofans on plots which show trends of reducing specific fuel consumption (SFC) with increasing BPR. BPR is also quoted for lift fan installations where the fan airflow is remote from the engine and doesn't physically touch the engine core. Bypass provides a lower fuel consumption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Tip-clearance Control
Active clearance control (ACC) is a method used in large aircraft gas turbines to improve fuel efficiency during cruise. This is achieved by setting the turbine tip clearance at more than one operating point and contrasts with passive clearance control which sets it for only one condition and is explained below. As one way to reduce fuel consumption better blade tip sealing has taken on a prominent role in aircraft engine design since the late 1960's. It is used on the CFM International CFM56-5B engine, installed on the Airbus A320, for example. Background Blade tip sealing has been a challenging problem since the development of the gas turbine engine. It is such because the clearance between the blade tips and surrounding casing (shroud) tends to vary due primarily to changes in thermal and mechanical loads on the rotating (turbine wheel) and stationary (stator, turbine casing) structures. Turbine tip clearance is a leakage path for gas which doesn't flow past the turbine blade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Gas, steam, and water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Modern steam turbines frequently employ both reaction and impulse in the same unit, typically varying the degree of reaction and impulse from the blade root to its periphery. History Hero of Alexandria demonstrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combustor
A combustor is a component or area of a gas turbine, ramjet, or scramjet engine where combustion takes place. It is also known as a burner, burner can, combustion chamber or flame holder. In a gas turbine engine, the ''combustor'' or combustion chamber is fed high-pressure air by the compression system. The combustor then heats this air at constant pressure as the fuel/air mix burns. As it burns the fuel/air mix heats and rapidly expands. The burned mix is exhausted from the combustor through the nozzle guide vanes to the turbine. In the case of ramjet or scramjet engines, the exhaust is directly fed out through the nozzle. A combustor must contain and maintain stable combustion despite very high air flow rates. To do so combustors are carefully designed to first mix and ignite the air and fuel, and then mix in more air to complete the combustion process. Early gas turbine engines used a single chamber known as a can-type combustor. Today three main configurations exist: can, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blisk
A blisk (portmanteau of bladed disk) is a turbomachine component comprising both rotor disk and blades as a single part instead of a disk assembled with individual removable blades. Blisks generally have better aerodynamics than conventional rotors with single blades and are lighter. They may be additively manufactured, integrally cast, machined from a solid piece of material, or made by welding individual blades to a rotor disk. The term is used mainly in aerospace engine design. ''Blisks'' may also be known as integrally bladed rotors (IBR). History Blisk manufacturing has been used since the mid-1980s. It was first used by Sermatech-Lehr (now known as GKN Aerospace) in 1985 for the compressors of the T700 helicopter engine. Since then, its use has continued to increase in major applications for both compressors and fan blade rotors. Examples include the Rocketdyne RS-68 rocket engine and the General Electric F110 turbofan. The F-35B variant of the Joint Strike Fighter us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics () is the study of the motion of atmosphere of Earth, air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics, and is an important domain of study in aeronautics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving Aircraft#Heavier-than-air – aerodynes, heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
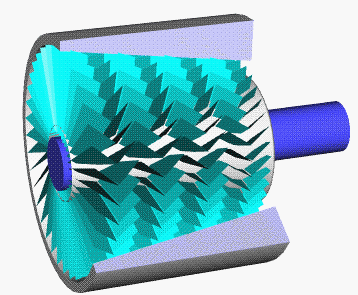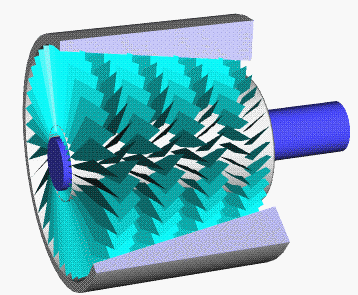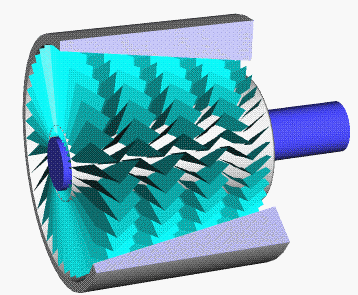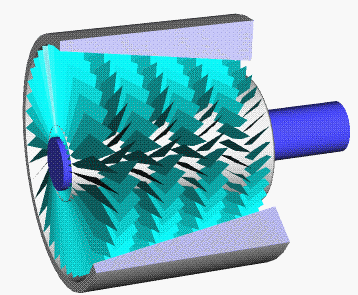
Axial Compressor
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other rotating compressors such as centrifugal compressor, axi-centrifugal compressors and mixed-flow compressors where the fluid flow will include a "radial component" through the compressor. The energy level of the fluid increases as it flows through the compressor due to the action of the rotor blades which exert a torque on the fluid. The stationary blades slow the fluid, converting the circumferential component of flow into pressure. Compressors are typically driven by an electric motor or a steam or a gas turbine. Axial flow compressors produce a continuous flow of compressed gas, and have the benefits of high efficiency and large mass flow rate, particularly in relation to their size and cross-section. They do, however, require several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulfstream G650
The Gulfstream G650, G700, and G800 are large Business jet, business jets produced by the American company Gulfstream Aerospace."Gulfstream Introduces the All-New Gulfstream G650" . Gulfstream, March 13, 2008. The G650 model is designated ''Gulfstream GVI'' in its type certificate. The aircraft can be configured to carry from 11 to 18 passengers over a range of at a top speed of . The aircraft is powered by two Rolls-Royce BR700, Rolls-Royce BR725 turbofans, mounted on the rear fuselage. Gulfstream began the G650 program in 2005 and revealed it to the public in 2008. The G650ER is an extended-range version of the G650, adding about by modifying the fuel system, an upgrade offered for existing G650 aircraft. At its introduction, the G650 was the company's largest and fastest busin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Thrust
Specific thrust is the thrust per unit air mass flowrate of a jet engine (e.g. turbojet, turbofan, etc.) and can be calculated by the ratio of net thrust/total intake airflow. Low specific thrust engines tend to be more efficient of propellant (at subsonic speeds), but also have a lower effective exhaust velocity and lower maximum airspeed. High specific thrust engines are mostly used for supersonic speeds, and high specific thrust engines can achieve hypersonic speeds. Low specific thrust engines A civil aircraft turbofan (with high-bypass ratio) typically has a low specific thrust (~30 lbf/(lb/s)) to reduce noise, and to reduce fuel consumption, because a low specific thrust helps to improve specific fuel consumption (SFC).{{Cite web, url=https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/sfc.html, title=Specific Fuel Consumption, website=www.grc.nasa.gov, access-date=2016-04-25 This is usually achieved with a high bypass ratio. Additionally low specific thrust implies a relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |