|
Rohrbach, Birkenfeld
Rohrbach () is an ''Ortsgemeinde (Germany), Ortsgemeinde'' – a Municipalities of Germany, municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld (district), Birkenfeld Districts of Germany, district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Baumholder (Verbandsgemeinde), ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Baumholder, whose seat is in the Baumholder, like-named town. Geography Location The municipality lies on the like-named Rohrbach south of the Nahe (Rhine), Nahe at the foot of the 548.5 m-high Wüschberg. Neighbouring municipalities Rohrbach borders in the north on the municipality of Berglangenbach, in the east on the municipalities of Fohren-Linden and Berschweiler bei Baumholder, in the south on the municipality of Freisen in the Saarland and in the west on the municipality of Rückweiler. History Names The villages of Rohrbach, Rückweiler, Hahnweiler and Leitzweiler bear the tag ''Auf der Heide'', although it is unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ortsgemeinde (Germany)
A (; plural ) is a low-level administrative division, administrative unit in the Germany, German States of Germany, federal states of Brandenburg, Rhineland-Palatinate and Saxony-Anhalt. A is typically composed of a small group of Municipalities of Germany, municipalities. Rhineland-Palatinate The state of Rhineland-Palatinate is divided into 163 , which are municipal associations grouped within the 24 Districts of Germany, districts of the state and subdivided into 2,257 Ortsgemeinden (singular Ortsgemeinde) which comprise single settlements. Most of the were established in 1969. Formerly the name for an administrative unit was ''Amt (political division), Amt''. Most of the functions of municipal government for several municipalities are consolidated and administered centrally from a larger or more central town or municipality among the group, while the individual municipalities (Ortsgemeinden) still maintain a limited degree of local autonomy. Saxony-Anhalt The 11 distric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leitzweiler
Leitzweiler is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Baumholder, whose seat is in the like-named town. Geography Location Leitzweiler lies near the state boundary with the Saarland, roughly 3 km southeast of Hoppstädten-Weiersbach and 9 km west of Baumholder. The municipal area measures 3.02 km2, of which 30% is wooded. Constituent communities Also belonging to Leitzweiler is the outlying homestead of Lindenhof. Municipality’s name Leitzweiler was founded in the 8th or 9th century by nobility. At that time, all the places ending in ''—weiler'' were founded as a result of the growth in population. In Leitzweiler's case, the leading syllable would give a clue as to the founder's name. It was likely ''Leudoin'', for this was a very common name in the Early Middle Ages. History In 1440 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salian Dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty () was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125). After the death of the last Ottonian emperor in 1024, the Kingdom of Germany and later the entire Holy Roman Empire passed to Conrad II, a Salian. He was followed by three more Salian rulers: Henry III, Henry IV, and Henry V. They established their monarchy as a major European power. The Salian dynasty developed a permanent administrative system based on a class of public officials answerable to the crown. Origins and name Modern historians suppose that the Salians descended from the Widonids, a prominent noble kindred emerging in the 7th century. Their estates were located at the confluence of rivers Moselle and Saar and they supported the Carolingians. The Widonids' eastward expansion towards the river Rhine started after they founded Hornbach Abbey in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Franks, Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Pippinids, Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The dynasty consolidated its power in the 8th century, eventually making the offices of mayor of the palace and ''dux et princeps Francorum'' hereditary, and becoming the ''de facto'' rulers of the Franks as the real powers behind the Merovingian throne. In 751 the Merovingian dynasty which had ruled the Franks was overthrown with the consent of the Papacy and the aristocracy, and Pepin the Short, son of Martel, was crowned King of the Franks. The Carolingian dynasty reached its peak in 800 with the crowning of Charlemagne as the first Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans in the West in over three centuries. Nearly every monarch of France from Charlemagne's son Louis the Pious until the pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gau (country Subdivision)
''Gau'' ( German: ; ; or ) is a Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu. Middle Ages Etymology The Germanic word is reflected in Gothic ''gawi'' (neuter; genitive ''gaujis'') and early Old High German ''gewi, gowi'' (neuter) and in some compound names ''-gawi'' as in Gothic (e.g. ''Durgawi'' " Canton of Thurgau", ''Alpagawi'' " Allgäu"), later ''gâi, gôi'', and after loss of the stem suffix ''gaw, gao'', and with motion to the feminine as ''gawa'' besides ''gowo'' (from ''gowio''). Old Saxon shows further truncation to ''gâ, gô''. As an equivalent of Latin ''pagus'', a ''gau'' is analogous with a ''pays'' of the Kingdom of France, or of Loth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse through Combustion, burning. Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India, Nepal, and Syria, cremation on an Pyre, open-air pyre is an ancient tradition. Starting in the 19th century, cremation was introduced or reintroduced into other parts of the world. In modern times, cremation is commonly carried out with a Crematorium, closed furnace (cremator), at a crematorium. Cremation leaves behind an average of of remains known as ''ashes'' or ''cremains''. This is not all ash but includes unburnt fragments of bone mineral, which are commonly ground into powder. They are inorganic and inert, and thus do not constitute a health risk and may be buried, interred in a memorial site, retained by relatives or scattered in various ways. History Ancient Cremation dates from at least 17,000 years ago in the archaeological record, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
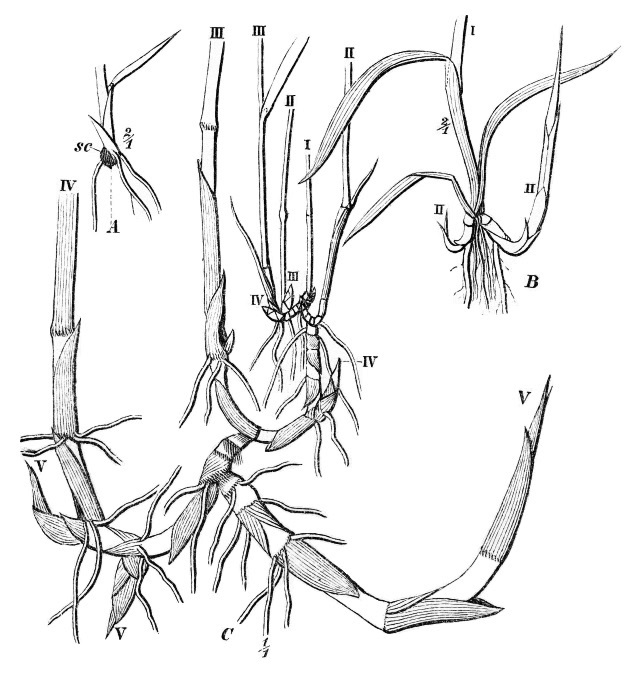
Phragmites
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial plant, perennial reed (plant), reed Poaceae, grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * ''Phragmites australis'' (Antonio José Cavanilles, Cav.) Carl Bernhard von Trinius, Trin. ex Steud. – The cosmopolitan common reed * ''Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * ''Phragmites karka'' (Anders Johan Retzius, Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * ''Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius Wildlife in reed beds ''Phragmites'' stands can provide food and shelter resources for a number of birds, insects, and other animals. Habitat benefits are often optimal when stands are thinner, and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |