|
Roger Blench
Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and works as a consultant. Career Blench is known for his wide-ranging interests and has made important contributions to African linguistics, Southeast Asian linguistics, anthropology, ethnomusicology, ethnobotany, and various other related fields. He has done significant research on the Niger–Congo, Nilo-Saharan, and Afroasiatic families, as well as the Arunachal languages. Additionally, Blench has published extensively on the relationship between linguistics and archaeology. Blench is currently engaged in a long-term project to document the languages of central Nigeria. He has also expressed concern about ranching in Nigeria. Blench collaborated with the late Professor Kay Williamson, who died in January 2005, and is now a trustee of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also known as diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of how languages change over time. It seeks to understand the nature and causes of linguistic change and to trace the evolution of languages. Historical linguistics involves several key areas of study, including the reconstruction of ancestral languages, the classification of languages into families, ( comparative linguistics) and the analysis of the cultural and social influences on language development. This field is grounded in the uniformitarian principle, which posits that the processes of language change observed today were also at work in the past, unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Historical linguists aim to describe and explain changes in individual languages, explore the history of speech communities, and study the origins and meanings of words ( etymology). Development Modern historical linguistics dates to the late 18th century, having originally grown o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kay Williamson
Kay Williamson (January 26, 1935, Hereford, United Kingdom – January 3, 2005, Brazil), born Ruth Margaret Williamson, was a linguist who specialised in the study of African languages, particularly those of the Niger Delta in Nigeria, where she lived for nearly fifty years. She has been called "The Mother of Nigerian Linguistics" and is also notable for proposing the Pan-Nigerian alphabet. Early life Kay Williamson was born in Hereford, England, where she lived for the first 18 years of her life. She was the eldest of six children. Her father, Alfred Henry Williamson, also known as Harry, was the founder of Wyevale Nurseries. Her father and mother, Harriett Eileen Williamson, turned the Wyevale nurseries into one of the largest garden center chains in Europe. Williamson was educated at Hereford girls' high school and St Hilda's College, Oxford, where she took a BA in English in 1956, followed by an MA in 1960. Career Her many publications include a grammar and dictionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
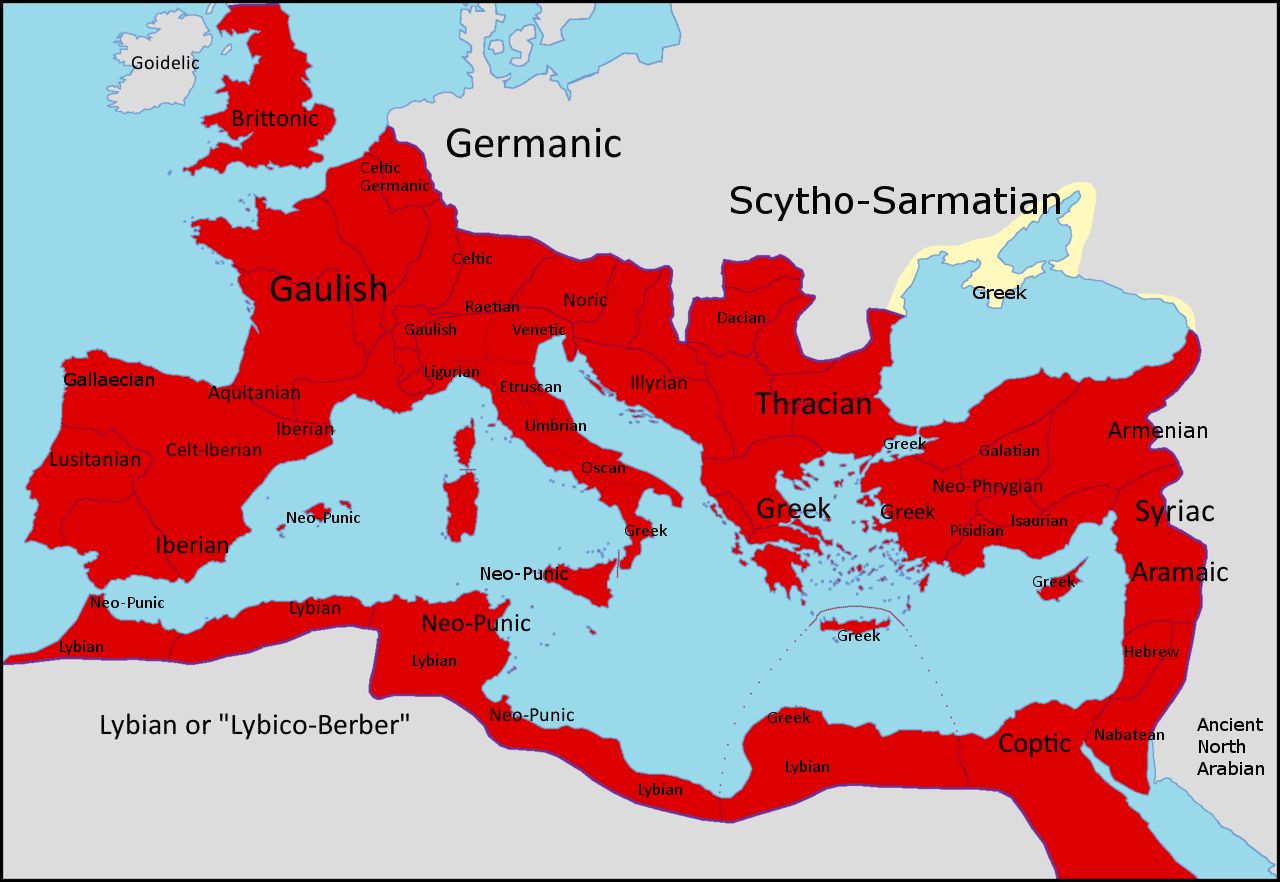
Tartessian Language
Tartessian is an extinct Paleo-Hispanic languages, Paleo-Hispanic language found in the Southwest Paleohispanic script, Southwestern inscriptions of the Iberian Peninsula, mainly located in the south of Portugal (Algarve and southern Alentejo), and the southwest of Spain (south of Extremadura and western Andalusia). There are 95 such inscriptions; the longest has 82 readable signs. Around one third of them were found in Early Iron Age necropolises or other Iron Age burial sites associated with rich complex burials. It is usual to date them to the 7th century BC and to consider the southwestern script to be the most ancient Paleohispanic scripts, Paleo-Hispanic script, with characters most closely resembling specific Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter forms found in inscriptions dated to ''c.'' 825 BC. Five of the inscriptions occur on ''stele, stelae'' that have been interpreted as Late Bronze Age carved warrior gear from the Urnfield culture. Name Most researchers use the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprising most of the region, as well as the tiny adjuncts of Andorra, Gibraltar, and, pursuant to the traditional definition of the Pyrenees as the peninsula's northeastern boundary, a small part of France. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second-largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula. Etymology The Iberian Peninsula has always been associated with the River Ebro (Ibēros in ancient Greek and Ibērus or Hibērus in Latin). The association was so well known it was hardly necessary to state; for example, Ibēria was the country "this side of the Ibērus" in Strabo. Pliny goes so far as to assert that the Greeks had called "the whole of the peninsula" Hiberia beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Language
The Punic language, also called Phoenicio-Punic or Carthaginian, is an extinct variety of the Phoenician language, a Canaanite languages, Canaanite language of the Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic branch of the Semitic languages. An offshoot of the Phoenician language of coastal West Asia (modern Lebanon and north western Syria), it was principally spoken on the Mediterranean coast of Northwest Africa, the Iberian Peninsula and several List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean islands, such as Malta, Sicily, and Sardinia by the Punic people, or western Phoenicians, throughout classical antiquity, from the 8th century BC to the 6th century AD. History Early history Punic is considered to have gradually separated from its Phoenician parent around the time that Carthage became the leading Phoenician city under Mago I of Carthage, Mago I, but scholarly attempts to delineate the dialects lack precision and generally disagree on the classification. The Punics s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea coast in the east. The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, and Western Sahara, the territory territorial dispute, disputed between Morocco and the list of states with limited recognition, partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The United Nations’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan. The African Union defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania. The Sahel, south of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Extinct Languages Of Africa
This is a list of extinct languages of Africa, languages which have undergone language death, have no native speakers and no spoken descendant. There are 73 languages listed. List See also *Languages of Africa * List of endangered languages in Africa Notes : These languages can still be spoken today, but are only used liturgically. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Extinct languages of Africa Africa Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ... Extinct languages of Africa Africa-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric North Africa
The prehistory of North Africa spans the period of earliest human presence in the region to gradual onset of historicity in the Maghreb during classical antiquity. Early anatomically modern humans are known to have been present at Jebel Irhoud, in what is now Morocco, approximately 300,000 years ago. The Nile Valley region, via ancient Egypt, contributed to the Neolithic, Bronze Age and Iron Age periods of the Old World, along with the ancient Near East. Climate Human habitation in North Africa has been greatly influenced by the climate of the Sahara (currently the world's largest warm desert), which has undergone enormous variations between wet and dry over the last few hundred thousand years. This is due to a 41,000-year Axial tilt cycle in which the tilt of the earth changes between 22° and 24.5°. At present (2000 AD), we are in a dry period, but it is expected that the Sahara will become green again in 15,000 years (17,000 AD). During the last glacial period, the Sah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berber Languages
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight, are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related but mostly mutually unintelligible languages spoken by Berbers, Berber communities, who are indigenous to North Africa.Hayward, Richard J., chapter ''Afroasiatic'' in Heine, Bernd & Nurse, Derek, editors, ''African Languages: An Introduction'' Cambridge 2000. . The languages are primarily spoken and not typically written. Historically, they have been written with the ancient Libyco-Berber script, which now exists in the form of Tifinagh. Today, they may also be written in the Berber Latin alphabet or the Arabic script, with Latin being the most pervasive. The Berber languages have a similar level of variety to the Romance languages, although they are sometimes referred to as a single collective language, often as "Berber", "Tamazight", or "Amazigh". The languages, with a few exceptions, form a dialect continuum. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechta-Afalou
Mechta-Afalou, also known as Mechtoid or Paleo-Berber, are a population that inhabited parts of North Africa during the late Paleolithic and Mesolithic. They are associated with the Iberomaurusian archaeological culture. The name Mechta-Afalou comes from the large number of skeletons found in the Afalou bou Rhummel site in Béjaïa in Algeria. Ginette Aumassip. '' 4. L’homme de Mechta el-Arbi, dernier descendant de l’Atlanthrope ? '', in ''L'Algérie des premiers hommes''. Éditions de la Maison des sciences de l’homme. 31 March 2017. Bioanthropology Mechtoids are believed to have been assimilated during the Neolithic and early Bronze Age by the makers of the ensuing Capsian culture. In 1999, the anthropologists Colin Groves & Alan Thorne in studying three Northern African samples from the Pleistocene/Holocene, found Taforalt was morphologically "Caucasoid" and resembled late Pleistocene Europeans, while Afalou was more intermediate in traits. In contrast to both, the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |