|
Rockwell PPS-4
The Rockwell PPS-4, short for "Parallel Processing System, 4-bit", was an early 4-bit microprocessor from Rockwell International, released in late 1972. Although practically unknown today, the PPS series was widely used in calculators, games and toys, and other embedded applications. Updated versions continued to be produced into the 1980s. The original version was implemented in a three-chip set, consisting of the CPU, a clock generator, and a user ROM. In 1975, the clock generator was integrated to produce the PPS-4/2 with a variety of ROM and RAM support chips. In 1976, the PPS-4/1 added user-customized ROM to produce a single-chip solution, running at a lower speed. The release of the PPS-4/1 coincided with the release of the Rockwell PPS-8, a more advanced 8-bit processor. Support chips released for the PPS-8 also worked with the PPS-4/1. These versions of the lineup continued to be produced into the 1980s. The PPS-8, however, was abandoned shortly after its introduction as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quad In-line Package
QUaD, an acronym for QUEST at DASI, was a ground-based cosmic microwave background (CMB) Polarization (waves), polarization experiment at the South Pole. QUEST (Q and U Extragalactic Sub-mm Telescope) was the original name attributed to the bolometer detector instrument, while Degree Angular Scale Interferometer, DASI is a famous CMB interferometry experiment credited with the first detection of CMB polarization. QUaD used the existing DASI mechanical infrastructure but replaced the DASI interferometric array with a bolometer detector at the end of a Cassegrain reflector, cassegrain optical system. The mount has housed the Keck Array since 2011. See also * Cosmic microwave background radiation * Cosmic microwave background experiments References External links * http://www.stanford.edu/~schurch/quad.html * http://find.spa.umn.edu/quad/ Submillimetre telescopes Radio telescopes Cosmic microwave background experiments Astronomical experiments in the Antarctic {{phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMOS Logic
PMOS or pMOS logic, from p-channel metal–oxide–semiconductor, is a family of digital circuits based on p-channel, enhancement mode metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In the late 1960s and early 1970s, PMOS logic was the dominant semiconductor technology for large-scale integrated circuits before being superseded by NMOS and CMOS devices. History and application Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng manufactured the first working MOSFET at Bell Labs in 1959. They fabricated both PMOS and NMOS devices but only the PMOS devices were working. It would be more than a decade before contaminants in the manufacturing process (particularly sodium) could be managed well enough to manufacture practical NMOS devices. Compared to the bipolar junction transistor, the only other device available at the time for use in an integrated circuit, the MOSFET offers a number of advantages: *Given semiconductor device fabrication processes of similar precision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMOS Logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. NMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type transistor body. This inversion layer, called the n-channel, can conduct electrons between n-type ''source'' and ''drain'' terminals. The n-channel is created by applying voltage to the third terminal, called the ''gate''. Like other MOSFETs, nMOS transistors have four modes of operation: cut-off (or subthreshold), triode, saturation (sometimes called active), and velocity saturation. NMOS AND-by-default logic can produce unusual glitches or buggy behavior in NMOS components, such as the 6502 "illegal opcodes" which are absent in CMOS 6502s. In some cases such as Commodore's VIC-II chip, the bugs present in the chip's logic were extensively exploited by programmers for graphics effects. For many years, NMOS ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170. In 1953, a second NTSC standard was adopted, which allowed for color television broadcast compatible with the existing stock of black-and-white receivers. It is one of three major color formats for analog television, the others being PAL and SECAM. ''NTSC color'' is usually associated with the System M; this combination is sometimes called NTSC II. The only other broadcast television system to use NTSC color was the System J. Brazil used System M with PAL color. Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos used System M with SECAM color – Vietnam later started using PAL in the early 1990s. The NTSC/System M standard was used in most of the Americas (except Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay), Myanmar, South Korea, Taiwan, Philippines, Japan, and some Pacific Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
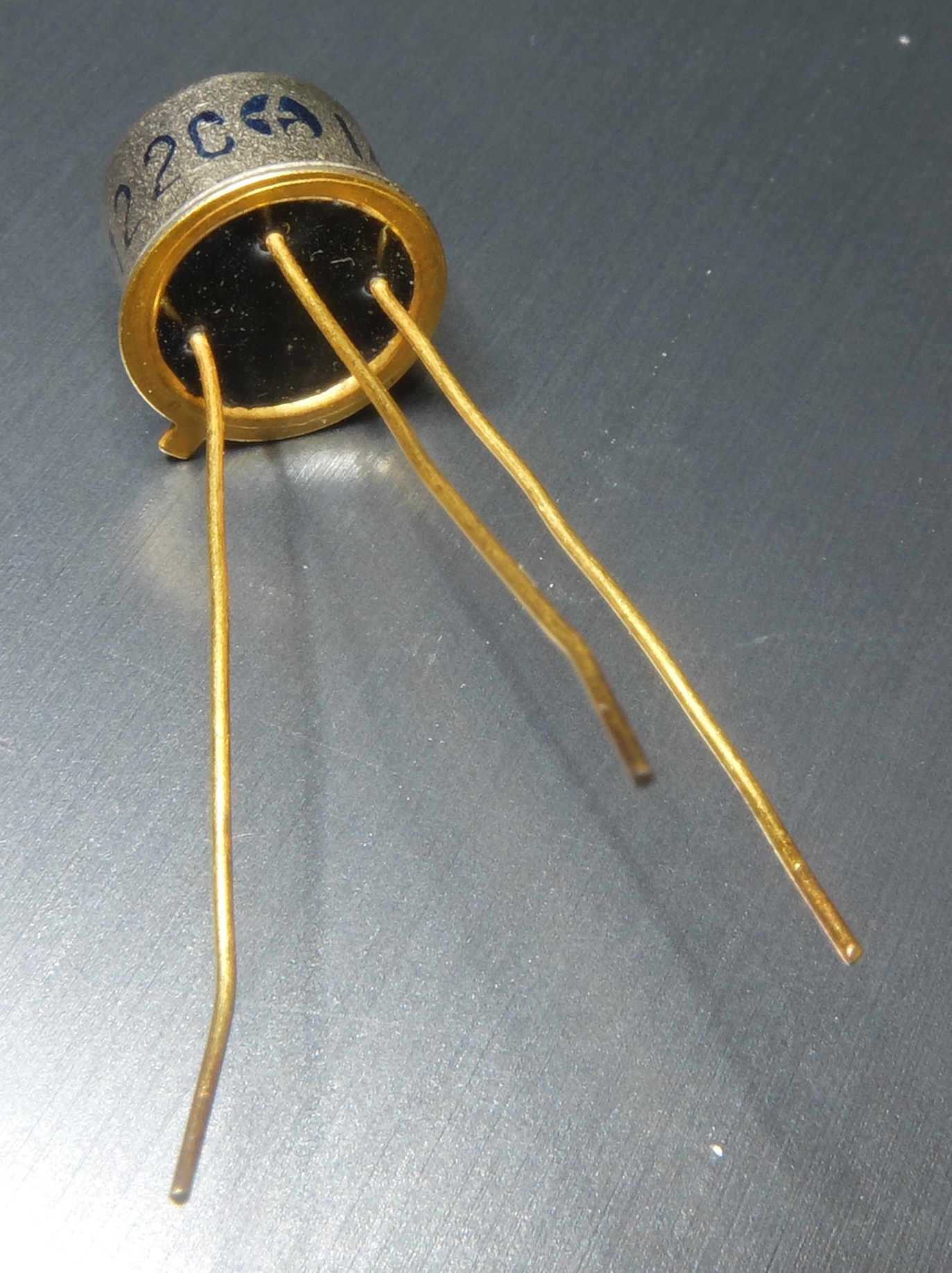
TO-5
In electronics, TO-5 (Transistor Outline 5) is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for transistors and some integrated circuits. The ''TO'' element stands for "transistor outline" and refers to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC. The first commercial silicon transistors, the 2N696 and 2N697 from Fairchild Semiconductor, came in a TO-5 package. Construction and orientation The tab is located 45° from pin 1, which is typically the emitter. The typical TO-5 package has a base diameter of , a cap diameter of , a cap height of . The pins are isolated from the package by individual glass-metal seals, or by a single resin potting. Sometimes one pin is connected directly to the metal case. Variants Several variants of the original TO-5 package have the same cap dimensions but differ in the number and length of the leads (wires). Somewhat incorrectly, TO-5 and TO-39 are often used in manufacturer's literature as synonyms for any package wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, flip-flops and latches are electronic circuit, circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will output its state (often along with its logical complement too). It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements to store a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state (computer science), state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, i/o, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, such as another computer system, peripherals, or a human operator. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation. are the pieces of hardware used by a human (or other system) to communicate with a computer. For instance, a keyboard or computer mouse is an input device for a computer, while monitors and printers are output devices. Devices for communication between computers, such as modems and network cards, typically perform both input and output operations. Any interaction with the system by an interactor is an input and the reaction the system responds is called the output. The designation of a device as either input or output depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Bus
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called a data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers. It encompasses both hardware (e.g., wires, optical fiber) and software, including communication protocols. At its core, a bus is a shared physical pathway, typically composed of wires, traces on a circuit board, or busbars, that allows multiple devices to communicate. To prevent conflicts and ensure orderly data exchange, buses rely on a communication protocol to manage which device can transmit data at a given time. Buses are categorized based on their role, such as system buses (also known as internal buses, internal data buses, or memory buses) connecting the CPU and memory. Expansion buses, also called peripheral buses, extend the system to connect additional devices, including peripherals. Examples of widely used buses include PCI Express (PCIe) for high-speed internal connections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-aligned Gate
In semiconductor electronics fabrication technology, a self-aligned gate is a transistor manufacturing approach whereby the gate electrode of a MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) is used as a mask for the doping of the source and drain regions. This technique ensures that the gate is naturally and precisely aligned to the edges of the source and drain. The use of self-aligned gates in MOS transistors is one of the key innovations that led to the large increase in computing power in the 1970s. Self-aligned gates are still used in most modern integrated circuit processes. Introduction IC construction Integrated circuits (ICs, or "chips") are produced in a multi-step process that builds up multiple layers on the surface of a disk of silicon known as a " wafer". Each layer is patterned by coating the wafer in photoresist and then exposing it to ultraviolet light being shone through a stencil-like "mask". Depending on the process, the photoresist that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-bit
4-bit computing is the use of computer architectures in which integer (computer science), integers and other data (computer science), data units are 4 bits wide. 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on processor register, registers or bus (computing), data buses of that size. A group of four bits is also called a nibble and has 24 = 16 possible values, with a range of 0 to 15. 4-bit computation is obsolete, i.e. CPUs supporting 4-bit as the maximum size. However, 4-bit integers (or smaller), and 4-bit floating point is gaining ground for AI, large-language models. 4-bit processors were widely used in electronic calculators and other roles where decimal math was used, like electronic cash registers, microwave oven timers, and so forth. This is because a 4-bit value holds a single binary-coded decimal (BCD) digit, making it a natural size for directly processing decimal values. As a 4-bit value is generally too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 was part of the 4 chip MCS-4 micro computer set, released by the Intel, Intel Corporation in November 1971; the 4004 being part of the first commercially marketed microprocessor chipset, and the first in a long line of List of Intel processors, Intel central processing units (CPUs). Priced at , the chip marked both a technological and economic milestone in computing. The 4-bit computing, 4-bit 4004 CPU was the first significant commercial example of large-scale integration, showcasing the abilities of the Self-aligned gate, MOS silicon gate technology (SGT). Compared to the existing technology, SGT enabled twice the transistor density and five times the operating speed, making future single-chip CPUs feasible. The MCS-4 chip set design served as a model on how to use SGT for complex logic and memory circuits, accelerating the adoption of SGT by the world's semiconductor industry. The project originated in 1969 when Busicom, Busicom Corp. commissioned Intel to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |