|
Robert Marcus Gunn
Robert Marcus Gunn (1850, Dunnet – 29 November 1909, Hindhead) was a Scotland, Scottish ophthalmologist remembered for AV nicking, Gunn's sign and the Marcus Gunn pupil. Early life and education Gunn went to school in Golspie, then studied medicine at the University of St Andrews and the University of Edinburgh, graduating with distinction Master of Arts (Scotland), M.A. in 1871 and Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery, M.B.,C.M. in 1873. He was influenced by James Syme, Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister and Douglas Argyll Robertson during his studies. He taught himself direct ophthalmoscopy, a skill for which he would later become particularly noted. Career Gunn was a Pre-registration house officer, house physician at Moorfields Eye Hospital and then worked in comparative anatomy at University College Hospital. He worked at the Perth District Asylum during the summers of 1874 and 1875, where he examined the fundus (eye), fundi of all the patients. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorfields Eye Hospital
Moorfields Eye Hospital is a specialist National Health Service (NHS) eye hospital in Finsbury in the London Borough of Islington in London, England run by Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Together with the UCL Institute of Ophthalmology, which is adjacent to the hospital, it is the oldest and largest centre for ophthalmic treatment, teaching and research in Europe. History Moorfields Eye Hospital was founded at Charterhouse Square in 1805 as the London Dispensary for curing diseases of the Eye and Ear, by John Cunningham Saunders, assisted by John Richard Farre. It moved to a site on the former Moorfields in 1822, before moving to its present site in 1899, and became part of the National Health Service in 1948. These anniversaries gave it the unique ability to celebrate a centenary in 1999 and a bicentenary in 2005. The new Richard Desmond Children's Eye Centre (RDCEC), was endowed by the publisher, Richard Desmond, and was opened by Queen Elizabeth II in Febru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Scottish Medical Doctors
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of The University Of Edinburgh
This is a list of notable graduates as well as non-graduate former students, academic ranks in the United Kingdom, academic staff, and university officials of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland. It also includes those who may be considered alumni by extension, having studied at institutions that later merged with the University of Edinburgh. The university is associated with 20 Nobel Prize laureates, three Turing Award winners, an Abel Prize laureate and Fields Medallist, four Pulitzer Prize winners, three List of prime ministers of the United Kingdom by education, Prime Ministers of the United Kingdom, and several Olympic Games, Olympic gold medallists. Government and politics Heads of state and government United Kingdom Cabinet and Party Leaders Scottish Cabinet and Party Leaders Current Members of the House of Commons * Douglas Alexander, MP for Lothian East (UK Parliament constituency), Lothian East * Catherine Atkinson, MP for Derby North (UK Parliament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Ophthalmologists
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English *Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland * Scots language, a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland *Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also *Scotch (other) *Scotland (other) *Scots (other) *Scottian (other) *Schottische The schottische is a partnered country dance that apparently originated in Bohemia. It was popular in Victorian-era ballrooms as a part of the Bohemian folk-dance craze and left its traces in folk music of countries such as Argentina (Spanish ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Medical Association
The British Medical Association (BMA) is a registered trade union and professional body for physician, doctors in the United Kingdom. It does not regulate or certify doctors, a responsibility which lies with the General Medical Council. The BMA has a range of representative and scientific committees and is recognised by National Health Service (NHS) employers alongside the Hospital Consultants and Specialists Association as one of two national contract negotiators for doctors. The BMA's stated aim is "to promote the medical and allied sciences, and to maintain the honour and interests of the medical profession". History Provincial Medical and Surgical Association and Webster's Medical Association The British Medical Association traces its origins to the Provincial Medical and Surgical Association (PMSA), founded by Sir Charles Hastings (English physician), Charles Hastings on 19 July 1832, and to the "British Medical Association" founded by George Webster (medical practitioner) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hospital For Neurology And Neurosurgery
The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery (informally the National Hospital or Queen Square) is a neurological hospital in Queen Square, London. It is part of the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It was the first hospital to be established in England dedicated exclusively to treating the diseases of the nervous system. It is closely associated with University College London (UCL) and in partnership with the UCL Institute of Neurology, which occupies the same site, is a major centre for neuroscience research. History The hospital was founded by Johanna Chandler as the National Hospital for the Paralysed and Epileptic at Queen Square in 1859. The hospital was completely rebuilt in the early 1880s: the East Wing was re-opened by Princess Helena in 1881 and the West Wing was re-opened by the Prince of Wales in 1885. In 1904, it adopted the name National Hospital for the Relief and Cure of the Paralysed and Epileptic. The hospital served as a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Ormond Street Hospital
Great Ormond Street Hospital (informally GOSH, formerly the Hospital for Sick Children) is a children's hospital located in the Bloomsbury area of the London Borough of Camden, and a part of Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust. The hospital is the largest centre for child heart surgery in Britain and one of the largest centres for heart transplantation in the world. In 1962 it developed the first heart and lung bypass machine for children. With children's book author Roald Dahl, it developed an improved shunt valve for children with hydrocephalus, and non-invasive (percutaneous) heart valve replacements. Great Ormond Street performed the first UK clinical trials of the rubella vaccine, and the first bone marrow transplant and gene therapy for severe combined immunodeficiency.Breakthroughs The hospital is the largest centre for research and postgraduate teaching in children's health in Europe. In 1929, J. M. Barrie donated the copyright ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellowship Of The Royal College Of Surgeons
Fellowship of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons (FRCS) is a professional qualification to practise as a senior surgeon in Ireland or the United Kingdom. It is bestowed on an intercollegiate basis by the four Royal Colleges of Surgeons (the Royal College of Surgeons of England, Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (chartered 1784), Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (chartered 1505), and Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow). The initials may be used as post-nominal letters. Several Commonwealth countries have organisations that bestow similar qualifications, among them the FRCSC in Canada, FRACS in Australia and New Zealand, FCS(SA) in South Africa, FCSHK in Hong Kong, FCPS by College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan in Pakistan and FCPS by College of Physicians & Surgeons of Mumbai in India. The intercollegiate FRCS examinations are administered by two committees, the JCIE (Joint Committee on Intercollegiate Examinations, which handles domestic exami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challenger Expedition
The ''Challenger'' expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific programme that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, . The expedition, initiated by William Benjamin Carpenter, was placed under the scientific supervision of Sir Charles Wyville Thomson—of the University of Edinburgh and Merchiston Castle School—assisted by five other scientists, including Sir John Murray (oceanographer), John Murray, a secretary-artist and a photographer. The Royal Society of London obtained the use of ''Challenger'' from the Royal Navy and in 1872 modified the ship for scientific tasks at Sheerness, equipping it with separate laboratories for natural history and chemistry. The expedition, led by Captain George Nares, sailed from Portsmouth, England, on 21 December 1872. Other naval officers included Commander John Maclear. – pages 19 and 20 list the civilian staff and naval officers and crew, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
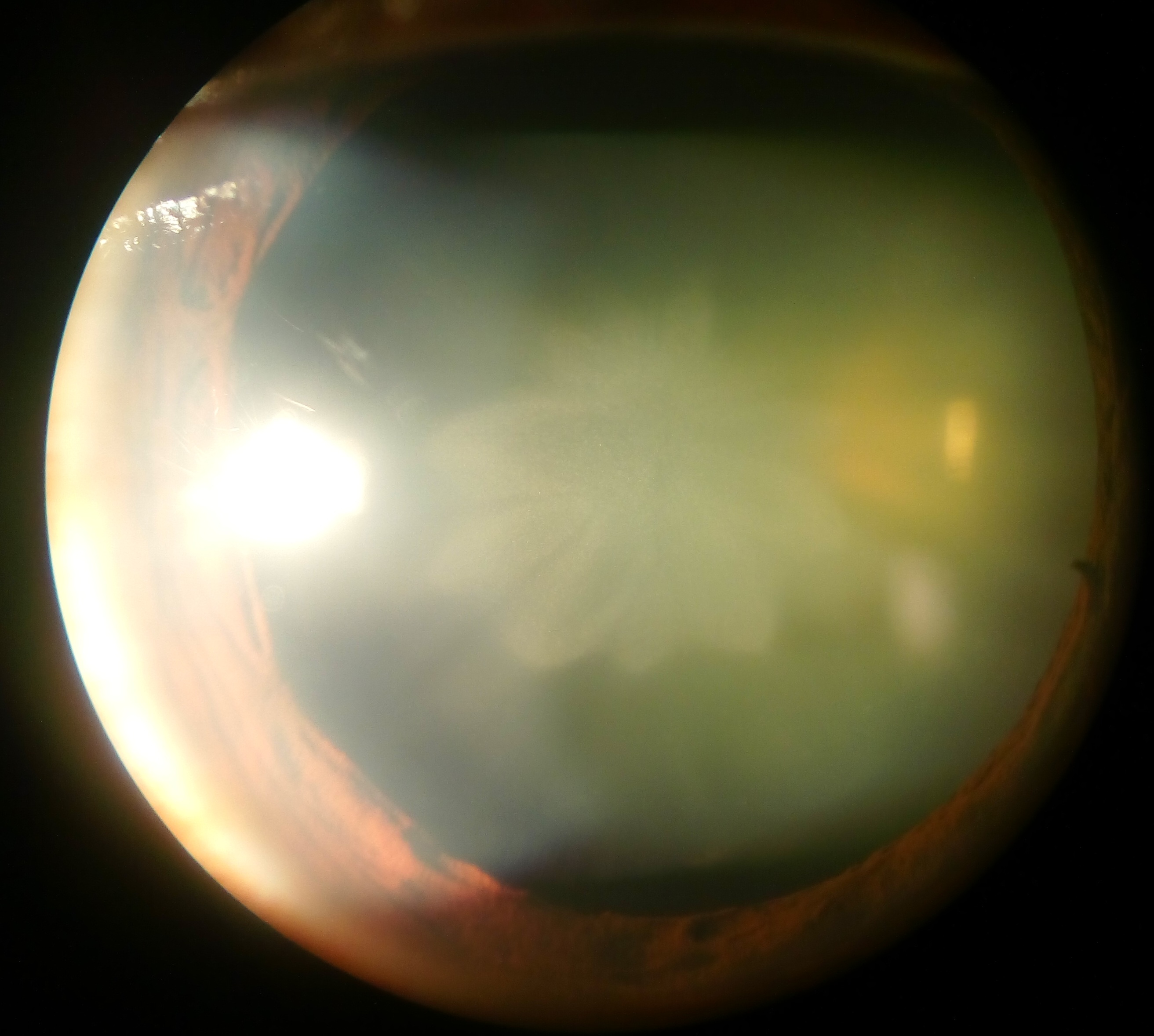
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and Nyctalopia, difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of Falling (accident), falling and Depression (mood), depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to senescence, aging but may also occur due to Trauma (medicine), trauma or radiation exposure, be congenital cataract, present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Jäger Von Jaxtthal
Eduard Jäger von Jaxtthal (25 June 1818 in Vienna – 5 July 1884 in Vienna) was an Austrian ophthalmologist who was a native of Vienna. He was a professor at the University of Vienna, and was son to oculist Friedrich Jäger von Jaxtthal (1784-1871), and grandson to Georg Joseph Beer (1763-1821). Jäger is remembered for his work involving eye operations, and for his research of ophthalmic disorders. He was an early practitioner of the ophthalmoscope, and was among the first to use ophthalmoscopy to determine refractive error in the eye. Also, he is credited with providing the first description of retinal appearances associated with diabetes. In the 1850s Jäger made improvements to eye chart test types that were earlier developed by Heinrich Küchler (1811-1873). In 1862 Dutch ophthalmologist Hermann Snellen introduced the popular "Snellen chart" for testing visual acuity.H. Snellen, Probebuchstaben zur Bestimmung der Sehschärfe, Utrecht 1862. Selected writings * ''Bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |