|
Rivers Of Armenia
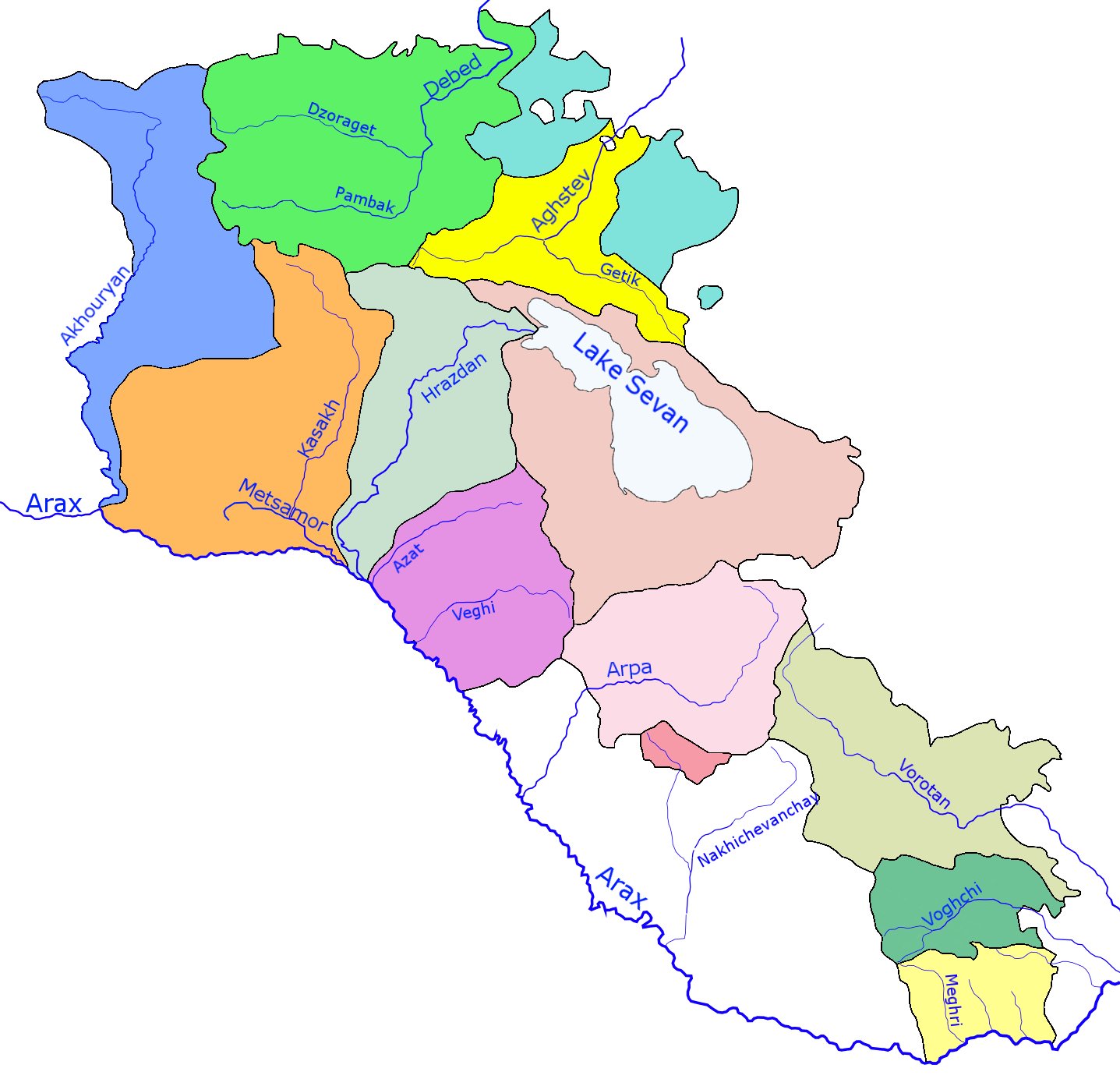
The rivers of Armenia are part of either the Caspian Sea or Lake Sevan watersheds. Throughout history, Armenia has been called Nairi by the ancient Assyrians, Assyrians meaning the "Land of the lakes and rivers". There are 16 rivers over long in or bordering Armenia. The longest river, Aras (river), Aras, has been mentioned in the Old Testament as one of the four sacred rivers of the Garden of Eden. There are about 9480 rivers and small streams in Armenia. List of rivers Approximately 4.7 percent of the territory of Armenia consists of rivers. The longest river of Armenia is the Aras (river), Aras (also called Araks, Arax), which lies on the country's border with Iran and a large part of the border with Turkey. Its major tributaries are the Akhuryan (river), Akhuryan, Kasagh (river), Kasagh, Hrazdan (river), Hrazdan, Azat (river), Azat, Arpa (river), Arpa, Vorotan (river), Vorotan and Voghji (river), Voghji rivers. The longest rivers in northwest part of the country are the De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrazdan (river)
The Hrazdan (, ) is a major river and the second largest in Armenia. It originates at the northwest extremity of Lake Sevan and flows south through the Kotayk Province and Armenia's capital, Yerevan; the lake in turn is fed by several streams. In the Ararat plain it joins the Aras river along the border with Turkey. It joins as a left tributary the Kura river, which then flows into the Caspian Sea. A series of hydro-electric projects have been constructed on the Hrazdan. Its waters are in demand to irrigate crops. Names The river is called Ildaruni in Urartian inscriptions. The name ''Hrazdan'' derives from a Middle Iranian form of Avestan , which in Zoroastrian mythology is the body of water by which Vishtaspa converted to Zoroastrianism. is composed of the elements 'elevated, high' and 'river'. derives from the same Iranian root as a number of hydronyms in Europe, such as Don, Dnieper, Danube and Dniester. The change of word-initial to can be seen in a number of Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakari (river)
The Hakari (, ) is a left tributary of the Aras in Azerbaijan, geographically located in the Armenian Highlands. The river is long and flows through the Lachin, Qubadli and Zangilan districts of Azerbaijan. In a small area, it serves as a border with Armenia. Its largest right tributary is the Vorotan (called ''Bazarchay'' in Azerbaijan), which joins the Hakari in its lowermost section. Populated places along the river, include Aganli (left bank), Alibayli (right bank), Mammadbayli (left bank) and Yenikend (right bank). The elevation difference between the source and mouth is . The river's water is used for irrigation and drinking. Fish like trout and Arctic cisco The Arctic cisco (''Coregonus autumnalis''), also known as Arctic omul (), is an anadromy, anadromous species of freshwater whitefish that inhabits the Arctic parts of Siberia especially Yenisey Gulf. It can also be found in Alaska and Canada. I ... spawn in the Hikari. References Rivers of Azerbaijan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kura (South Caucasus River)
The Kura, also known in Georgian as Mtkvari ( ), is an east-flowing transboundary river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus, while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, the Kura flows through to Georgia, then into Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and finally enters the Caspian Sea. The total length of the river is . People have inhabited the Caucasus region for thousands of years and first established agriculture in the Kura Valley over 4,500 years ago. Large, complex civilizations eventually grew on the river, but by 1200 CE most were reduced to ruin by natural disasters and foreign invaders. The increasing human use, and eventual damage, of the watershed's forests and grasslands, contributed to a rising intensity of floods through the 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Research Division
The Federal Research Division (FRD) is the research and analysis unit of the United States Library of Congress. The Federal Research Division provides directed research and analysis on domestic and international subjects to agencies of the United States government, the District of Columbia, and authorized federal contractors. As expert users of the vast English and foreign-language collections of the Library of Congress, the Division's area and subject specialists employ the resources of the world's largest library and other information sources worldwide to produce impartial and comprehensive studies on a cost-recovery basis. The Federal Research Program is run by the Federal Research Division (FRD), the fee-for-service research and analysis unit within the Library of Congress. The Federal Research Program of the Library of Congress was authorized by the United States Congress in accordance with the Library of Congress Fiscal Operations Improvement Act of 2000 (2 U.S.C. 182c). FR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrazdan
Hrazdan ( ) is a town and urban municipal community in Armenia serving as the administrative centre of Kotayk Province, located northeast of the capital Yerevan. As of the 2011 census, the population of the town is 44,231. During the Soviet Union, Soviet period, Hrazdan was one of the industrialized centres of the Armenian SSR. The prelacy of the Diocese of Kotayk of the Armenian Apostolic Church is headquartered in Hrazdan. Etymology The town is named after the Hrazdan River, which flows through the town from north to south. The name ''Hrazdan'' itself is derived from the Middle-Persian name ''Frazdān,'' which is related to the Zoroastrian Persian mythology, mythology. ''Frazdān'' is the name of the lake mentioned in the Avesta while referring to Vishtaspa, Goshtasb's war with two of its enemies. Zoroastrianism in Armenia, Armenians were predominantly Zoroastrian before embracing Christianity, and Zoroastrian names were maintained in the geography of Armenia. History A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araks
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, finally, through Azerbaijan where it flows into the Kura river as a right tributary. It drains the south side of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains, while the Kura drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus. The river's total length is and its watershed covers an area of . The Aras is one of the longest rivers in the Caucasus. Names In classical antiquity, the river was known to the Greeks as Araxes (). Its modern Armenian name is ''Arax'' or ''Araks'' (). Historically, it was called (, in modern pronunciation) by Armenians and its Old Georgian name is ''Rakhsi'' (). In Azerbaijani, the river's name is ''Araz''. In Persian, Kurdish and Turkish its name is (''Aras''). Geography The Aras is supported by the Kocagün stream, Dallı s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pambak River
The Pambak (), is a river in the Lori Province in Northern Armenia. It is a tributary of the Debed river. It originates in the Pambak Mountains and flows west to east through spectacular gorges around Bazum Mountains. It finally feeds into the Debed near Dzoragyugh, which ultimately discharges from the left into the Khrami The Khrami ( ka, ხრამი, ), in its upper course ''Ktsia'', is a river in eastern Georgia and western Azerbaijan, and a right tributary of the Kura (''Mtkvari''). It is long, and has a drainage basin of . References Rivers of Armenia {{Armenia-river-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzoraget River
The Dzoraget () is a river in the Lori region in Northern Armenia. It originates in the Bazum Mountains and flows west to east through spectacular gorges around Stepanavan. It finally feeds into the river Debed near Dzoragyugh, which ultimately drains to the Kura. ''Dzoraget'' is a compound word in Armenian meaning ''Gorge-river'' and formed with the lexemes ձոր ('gorge') and գետ ('river') joined by the interfix ա . In certain places (e.g. at Kurtan), the gorge is over deep. Rafting The Armenian Travel Bureau considers the Dzoraget River the only Armenian river suitable for rafting. The commonest rafting route begins at the Dzoraget bridge, near the town of Stepanavan. Rafting on the river is concentrated in the Dzoraget Canyon, which is in some places as deep as 300 meters. Towns and villages Towns and villages along the river include: Stepanavan, Amrakits, Lori Berd, Agarak, Vardablur, Kurtan, Arevatsag, and Dzoragyukh. Gallery Image:Dzoragetatste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aghstafa (river)
The Aghstafa (also, ''Aghstafachay'' ()) or Aghstev () is a river in Armenia and Azerbaijan, and a right tributary of the Kura. It is long, and has a drainage basin.classification of world regions places Armenia in West Asia; the CIA World ... * Geography of Azerbaijan References Rivers of Armenia Rivers of Azerbaijan International rivers of Europe International rivers of Asia {{Armenia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debed
The Debed () or Debeda ( ka, დებედა) is a river in Armenia and Georgia. It also serves as a natural boundary between Armenia and Georgia at the village Sadakhlo, Georgia. The Debed is long, and has a drainage basin. The river originates in Armenia and is formed at the confluence of the Dzoraget and Pambak near Dzoragyugh. It ends in Georgia where it discharges from the left into the Khrami, a tributary of the Kura.classification of world regions places Armenia in West Asia; the CIA World ... * Geography of Georgia References Rivers of Armenia Rivers of Georgia (country) International rivers of Asia International rivers of Europe Armenia–Georgia (country) border Border rivers {{Georgia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voghji (river)
The Voghji () or Okchuchay () is a river on the south slopes of the Lesser Caucasus range, and is a left tributary of the Aras. It flows through the territory of Armenia and Azerbaijan. In its upper reaches, the Voghji has formed a deep canyon which, near the city of Kapan, turns into a wide valley. It is fed by a range of sources. The cities of Zangilan and Mincivan in Azerbaijan and Kajaran and Kapan in Armenia lie along the banks of the river. The Kapan and Voghji hydroelectric power stations are located along the section of the river in Armenia. See also *List of rivers of Armenia *List of lakes of Armenia *Rivers and lakes in Azerbaijan *Geography of Armenia *Geography of Azerbaijan Azerbaijan is a country in the Caucasus region, situated at the juncture of Eastern Europe and West Asia. Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the Greater Caucasus ... References * * Rivers of Azerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |