|
Riotinto Railway
The Riotinto Railway was a Spain, Spanish narrow-gauge railway line, predominantly used for mining and industry, that operated between 1875 and 1984. During this time it became one of the main railways in the province of Huelva, gaining a large fleet of rolling stock. The railway was built between 1873 and 1875 by the British Rio Tinto Company Limited (RTC), that sought to provide maritime access to the minerals extracted from ore deposits in the Riotinto-Nerva mining basin. For much of its route, the track ran parallel to the course of the Rio Tinto (river), Tinto River, although in its last stage it ran alongside the Iberian-gauge railways, Iberian-gauge Línea Sevilla-Huelva, Seville-Huelva railway. For over a century, it was one of the most heavily-used mining railways in Spain,. Likewise it had a large fleet of cars and engines, to the point of becoming the second largest in the country after the Renfe. The route closed to public traffic in 1984. After several years the aba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothschild Family
The Rothschild family ( , ) is a wealthy Ashkenazi Jewish family originally from Frankfurt that rose to prominence with Mayer Amschel Rothschild (1744–1812), a court factor to the German Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel in the Free City of Frankfurt, Holy Roman Empire, who established his banking business in the 1760s. Unlike most previous court factors, Rothschild managed to bequeath his wealth and established an international banking family through his five sons, who established businesses in London, Paris, Frankfurt, Vienna, and Naples. The family was elevated to noble rank in the Holy Roman Empire and the United Kingdom. The family's documented history starts in 16th century Frankfurt; its name is derived from the family house, Rothschild, built by Isaak Elchanan Bacharach in Frankfurt in 1567. During the 19th century, the Rothschild family possessed the largest private fortune in the world, as well as in modern world history.''The House of Rothschild: Money's prophets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3 Ft 6 In Gauge Railways
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
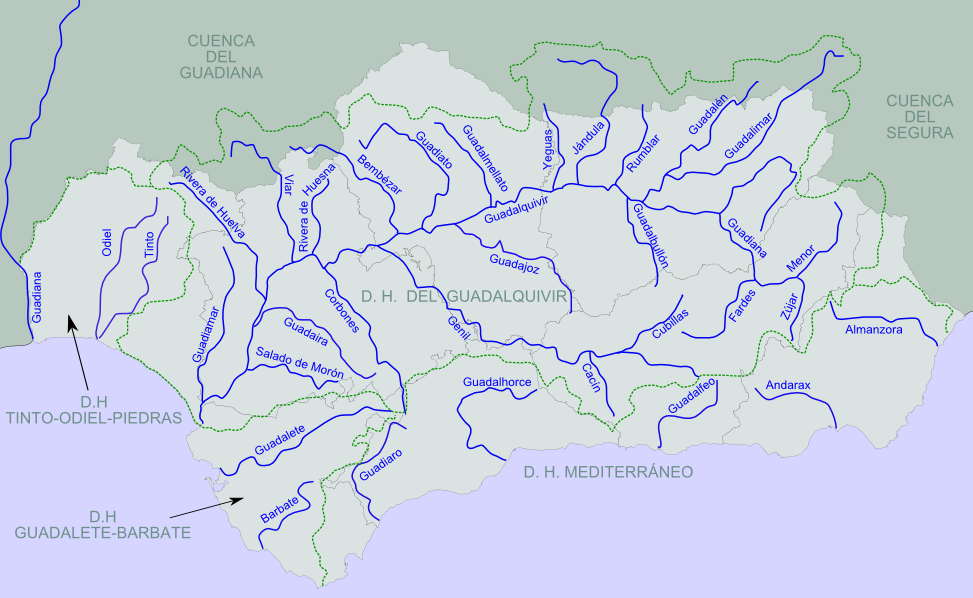
Odiel
The Odiel ( es, Río Odiel) is a river in the Atlantic basin in southern Spain, more precisely in the province of Huelva, Andalusia. It originates at Marimateos in the Sierra de Aracena at an elevation of above sea level. At the Punta del Sebo, it joins the Rio Tinto to form the Huelva Estuary. Its principal tributaries are the Escalada, Meca, Olivargas, Oraque, Santa Eulalia, and El Villar. Its basin covers . In Roman times it was known as the ''Urius'', although some scholars have proposed to identify the Odiel with another ancient name normally associated with the Río Tinto (''Luxia''). Even before the Romans, its mouth was an important place of commerce, as can be seen by archaeological remnants from Phoenicians and Ancient Greeks, known as the "Huelva Estuary Deposit" ( es, Depósito de la Ría de Huelva), dated 1000 BCE. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
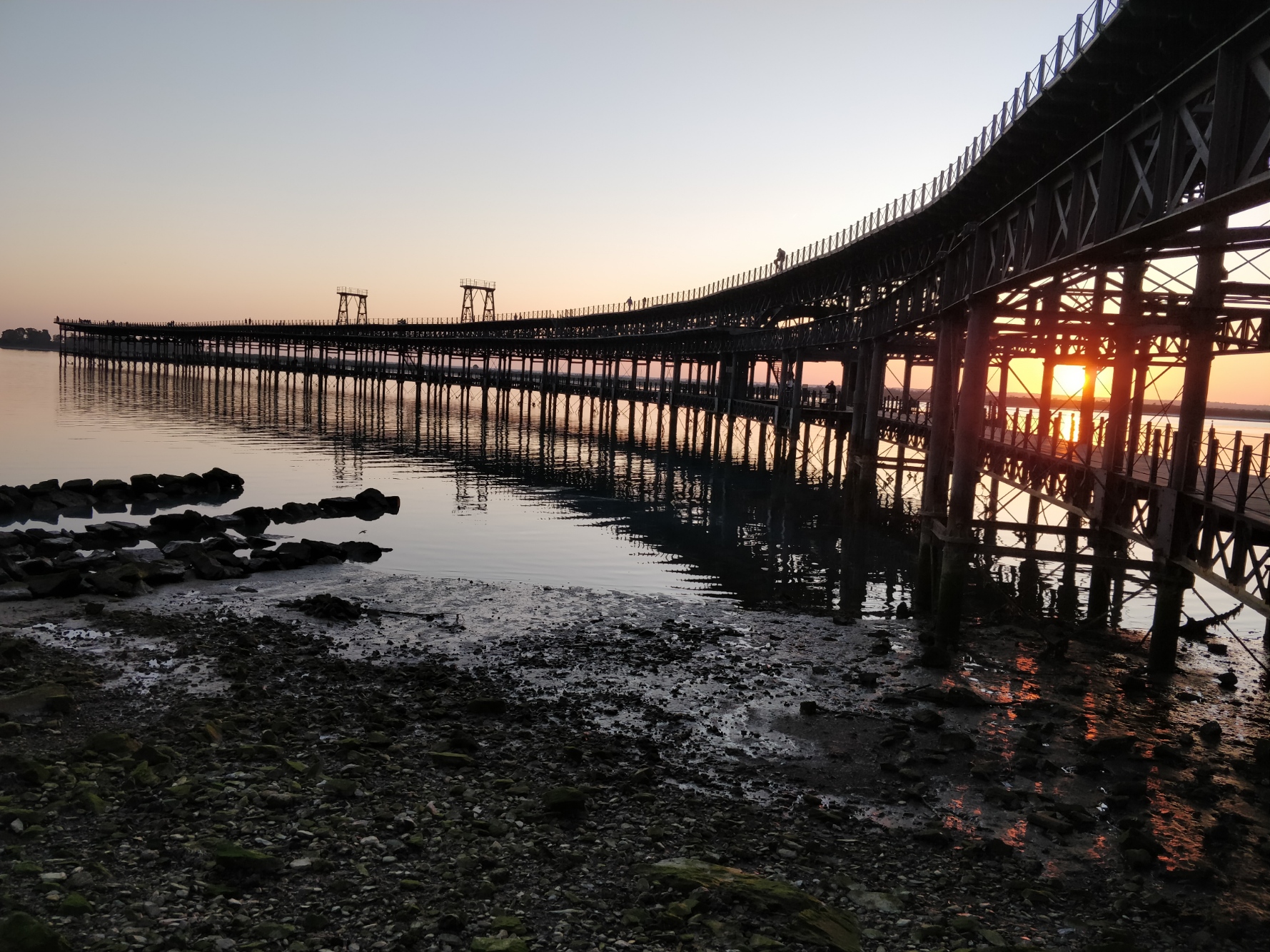
Rio Tinto Pier (Huelva, Spain)
The Rio Tinto Pier ( es, Muelle de Rio Tinto) was a commercial pier formerly used for the trade of material from the mines of the Rio Tinto Company in Andalusia, Spain. It is situated on the River Odiel in the city of Huelva. An estimated 150 million tons of ore were shipped from the pier over its life. Closed in 1975, it is now a popular tourist attraction and fishing spot. The pier is 1165 meters long, although part of that is built on reclaimed marshland. History A site along the Rio Tinto had been mined since 3000 BCE. Over time, mining activities fell into neglect, until 1724 when the Spanish government began mining again. However, mining operations were inefficient, and the government itself was distracted by political and financial crises, leading it to sell the mines by auction in 1873.The syndicate purchasing the mine was led by Matheson and Company and, following purchase of the mine, the buyers launched the Rio Tinto Company. At the end of the 1880s, control of the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound Sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO 4217, ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of #Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories, its associated territories. The Pound (currency), pound (pound sign, sign: £) is the main unit of account, unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. Sterling is the world's oldest currency that is still in use and that has been in continuous use since its inception. It is currently the fourth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen. Together with those three currencies and Renminbi, it forms the basket of currencies which special drawing rights#Value definition, calculate the value of International Monetary Fund, IMF special drawing rights. As of mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Tinto-Estación 1892
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil. Rio or Río may also refer to: Geography Brazil * Rio de Janeiro * Rio do Sul, a town in the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil Mexico * Río Bec, a Mayan archaeological site in Mexico * Río Bravo, Tamaulipas, a city in Mexico United States * Rio, a location in Deerpark, New York, US * Rio, Florida, a census-designated place in Martin County, US * Rio, Georgia, an unincorporated community in Spalding County, US * Rio, Illinois, a village in Knox County, US * Rio, Virginia, a community in Albemarle County, US * Rio, West Virginia, a village in Hampshire County, US * Rio, Wisconsin, a village in Columbia County, US * El Río, Las Piedras, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Añasco, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Arecibo, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Vega Baja, Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Ballast
Track ballast forms the trackbed upon which railroad ties (sleepers) are laid. It is packed between, below, and around the ties. It is used to bear the load from the railroad ties, to facilitate drainage of water, and also to keep down vegetation that might interfere with the track structure. Ballast also holds the track in place as the trains roll over it. A variety of materials have been used as track ballast, including crushed stone, washed gravel, bank run (unwashed) gravel, torpedo gravel (a mixture of coarse sand and small gravel), slag, chats, coal cinders, sand, and burnt clay. The term "ballast" comes from a nautical term for the stones used to stabilize a ship. Construction The appropriate thickness of a layer of track ballast depends on the size and spacing of the ties, the amount of traffic on the line, and various other factors. Track ballast should never be laid down less than thick, and high-speed railway lines may require ballast up to thick.Bell 2004, p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western part of Tarraconensis was split off, first as Hispania Nova, later renamed "Callaecia" (or Gallaecia, whence modern Galicia). From Diocletian's Tetrarchy (AD 284) onwards, the south of the remainder of Tarraconensis was again split off as Carthaginensis, and all of the mainland Hispanic provinces, along with the Balearic Islands and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana, were later grouped into a civil diocese headed by a '' vicarius''. The name Hispania was also used in the period of Visigothic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
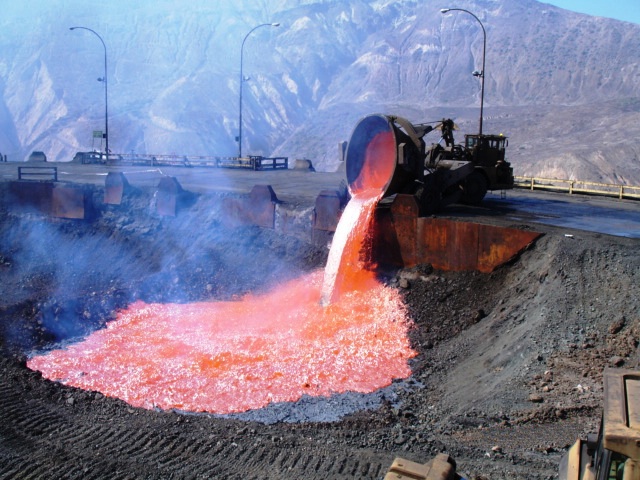
Slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting ( pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/ base metals (by-products of recovering non-ferrous materials like copper, nickel, zinc and phosphorus). Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions (e.g., Blast furnace (BF) slags, air-cooled blast furnace (ACBF) slag, basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag, and electric arc furnace (EAF) slag) . Due to the large demand for these materials, slag production has also significantly increased throughout the years despite recycling (most notably in the iron and steelmaking industries) and upcycling efforts. The World Steel Association (WSA) estimates that 600 kg of by-products (~90 wt% is slags) are generated per tonne of steel produced. Composition Slag is usually a mixture of metal oxides and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_02.jpg)
