|
Rietveld Refinement
Rietveld refinement is a technique described by Hugo Rietveld for use in the characterisation of crystalline materials. The neutron diffraction, neutron and x-ray crystallography, X-ray Powder diffraction, diffraction of powder samples results in a pattern characterised by reflections (peaks in intensity) at certain positions. The height, width and position of these reflections can be used to determine many aspects of the material's structure. The Rietveld method uses a least squares approach to refine a theoretical line profile until it matches the measured profile. The introduction of this technique was a significant step forward in the diffraction analysis of powder samples as, unlike other techniques at that time, it was able to deal reliably with strongly overlapping reflections. The method was first implemented in 1967, and reported in 1969 for the diffraction of monochromatic neutrons where the reflection-position is reported in terms of the Bragg's law, Bragg angle, 2''θ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Rietveld
Hugo M. Rietveld (7 March 1932 – 16 July 2016) was a Dutch crystallographer who is famous for single handedly publishing joint work of Loopstra, van Laar and himself on the full profile refinement method in powder diffraction, which became later known as the Rietveld refinement method. The method was developed by Loopstra and van Laar and programmed in Algol by Rietveld to refine neutron diffraction data, but is applicable to other diffraction experiments as well, like X-ray diffraction. The Rietveld refinement uses a least squares approach to refine a theoretical line profile (calculated from a known or postulated crystal structure) until it matches the measured profile. The introduction of this technique which used the full profile instead of individual reflections was a significant step forward in the diffraction analysis of powder samples. Biography Rietveld was born in the Hague. After completing Grammar School in the Netherlands he moved to Australia and studied physics a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
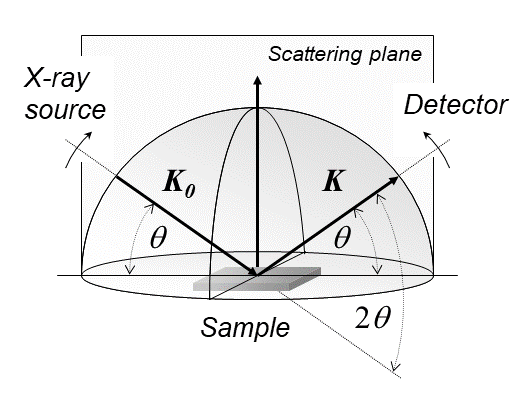
X-ray Diffraction
X-ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of X-ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. It occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. The resulting map of the directions of the X-rays far from the sample is called a diffraction pattern. It is different from X-ray crystallography which exploits X-ray diffraction to determine the arrangement of atoms in materials, and also has other components such as ways to map from experimental diffraction measurements to the positions of atoms. This article provides an overview of X-ray diffraction, starting with the early #History, history of x-rays and the discovery that they have the right spacings to be diffracted by crystals. In many cases these diffraction patterns can be #Introduction to x-ray diffraction theory, Interpreted using a single scattering or kinematical theory with conservation of energy (#Ewald's sphere, wave vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation, propagating wave. Diffraction is the same physical effect as Wave interference, interference, but interference is typically applied to superposition of a few waves and the term diffraction is used when many waves are superposed. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word ''diffraction'' and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660 in science, 1660. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described by the Huygens–Fresnel principle that treats each point in a propagating wavefront as a collection of individual spherical wavelets. The characteristic pattern is most pronounced when a wave from a Coherence (physics), coherent source (such as a laser) encounters a slit/aperture tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two Ray (geometry), rays, called the ''Side (plane geometry), sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex (geometry), vertex'' of the angle. More generally angles are also formed wherever two lines, rays or line segments come together, such as at the corners of triangles and other polygons. An angle can be considered as the region of the plane bounded by the sides. Angles can also be formed by the intersection of two planes or by two intersecting curves, in which case the rays lying tangent to each curve at the point of intersection define the angle. The term ''angle'' is also used for the size, magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or Physical quantity, quantity of these types of geometric figures and in this context an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffractometer
A diffractometer is a measuring instrument for analyzing the structure of a material from the scattering pattern produced when a beam of radiation or particles (such as X-rays or neutrons) interacts with it. Principle A typical diffractometer consists of a source of radiation, a monochromator to choose the wavelength, slits to adjust the shape of the beam, a sample and a detector. In a more complicated apparatus, a goniometer can also be used for fine adjustment of the sample and the detector positions. When an area detector is used to monitor the diffracted radiation, a beamstop is usually needed to stop the intense primary beam that has not been diffracted by the sample, otherwise the detector might be damaged. Usually the beamstop can be completely impenetrable to the X-rays or it may be semitransparent. The use of a semitransparent beamstop allows the possibility to determine how much the sample absorbs the radiation using the intensity observed through the beamstop. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron
A synchrotron is a particular type of cyclic particle accelerator, descended from the cyclotron, in which the accelerating particle beam travels around a fixed closed-loop path. The strength of the magnetic field which bends the particle beam into its closed path increases with time during the accelerating process, being ''synchronized'' to the increasing kinetic energy of the particles. The synchrotron is one of the first accelerator concepts to enable the construction of large-scale facilities, since bending, beam focusing and acceleration can be separated into different components. The most powerful modern particle accelerators use versions of the synchrotron design. The largest synchrotron-type accelerator, also the largest particle accelerator in the world, is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, completed in 2008 by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). It can accelerate beams of protons to an energy of 7 electron volt, teraelectro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide-angle X-ray Scattering
In X-ray crystallography, wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) or wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) is the analysis of Bragg peaks scattered to wide angles, which (by Bragg's law) are caused by sub-nanometer-sized structures. It is an X-ray-diffraction method and commonly used to determine a range of information about crystalline materials. The term WAXS is commonly used in polymer sciences to differentiate it from SAXS but many scientists doing "WAXS" would describe the measurements as Bragg/X-ray/powder diffraction or crystallography. Wide-angle X-ray scattering is similar to small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) but the increasing angle between the sample and detector is probing smaller length scales. This requires samples to be more ordered/crystalline for information to be extracted. In a dedicated SAXS instrument the distance from sample to the detector is longer to increase angular resolution. Most diffractometers can be used to perform both WAXS and limited SAXS in a singl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Scattering Techniques
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy. Note that X-ray diffraction is sometimes considered a sub-set of X-ray scattering, where the scattering is elastic and the scattering object is crystalline, so that the resulting pattern contains sharp spots analyzed by X-ray crystallography (as in the Figure). However, both scattering and diffraction are related general phenomena and the distinction has not always existed. Thus Guinier's classic text from 1963 is titled "X-ray diffraction in Crystals, Imperfect Crystals and Amorphous Bodies" so 'diffraction' was clearly not restricted to crystals at that time. Scattering techniques Elastic scattering * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocal Lattice
Reciprocal lattice is a concept associated with solids with translational symmetry which plays a major role in many areas such as X-ray and electron diffraction as well as the energies of electrons in a solid. It emerges from the Fourier transform of the lattice associated with the arrangement of the atoms. The ''direct lattice'' or ''real lattice'' is a periodic function in physical space, such as a crystal system (usually a Bravais lattice). The reciprocal lattice exists in the mathematical space of spatial frequencies or wavenumbers ''k'', known as reciprocal space or ''k'' space; it is the dual of physical space considered as a vector space. In other words, the reciprocal lattice is the sublattice which is dual to the direct lattice. The reciprocal lattice is the set of all vectors \mathbf_m, that are wavevectors k of plane waves in the Fourier series of a spatial function whose periodicity is the same as that of a direct lattice \mathbf_n. Each plane wave in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |