|
Rieterpark
The Rieterpark is a park in central Zurich, Switzerland. Richard Wagner lived at Villa Wesendonck in Reiterpark from 1849 to 1858 where he worked on ''Tristan''.Millington (undated a) History In the 19th century it was bought by the German merchant Otto Wesendonck in an independent municipality near Zurich. Through the well-known architect Leonhard Zeugheer, he established the Villa Wesendonck and hired the gardener Theodor Froebel to design the extensive park and gardens. As a great patron of the arts, the Wesendoncks granted the house to Richard Wagner in 1849. Wagner had an affair there with Mathilde Wesendonck and finished in 1858 when he fled from Zurich. In 1871, the Wesendoncks eventually sold the mansion to the industrialist Rieter family along with the park grounds. After the death of Adolf Rieter Rotpletz in 1882, he left it to his son Fritz Rieter. Alfred Friedrich Bluntschli was hired to develop part of the property. In 1912, the German Emperor William II stay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rietberg Museum
The Rietberg Museum is a museum in Zürich, Switzerland, displaying Asian, African, American and Oceanian art. It is the only art museum focusing on non-European art and design in Switzerland, the third-largest museum in Zürich, and the largest to be run by the city itself. In 2007, it received approximately 157,000 visitors. Location and buildings The Rietberg Museum is situated in the Rieterpark in central Zürich, on the western shores of the Lake Zurich, and consists of several historic buildings: the Wesendonck Villa, the Remise (or "Depot"), the Rieter Park-Villa, and the Schönberg Villa. In 2007 a new building, designed by Alfred Grazioli and Adolf Krischanitz, was opened – the addition of this largely subterranean building, known as "Smaragd", more than doubled the museum's exhibition space.Museum Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belvoirpark
The Villa Belvoir respectively the Belvoirpark is a Cultural Heritage in Zürich- Enge that comprises the mansion built between 1828 and 1831, and one of the largest public parks and arboreta in the city of Zürich in Switzerland. Location Lydia Escher's (1858–1891) grandfather Heinrich Escher (1776–1853) had built the country house ''Belvoir'', situated on the left shore of ''Zürichsee'' in the then village of Enge, as of today being a district of the city of Zürich. The area houses the ''Hotelfachschule Belvoirpark'' and is one of the largest public parks in Zürich. Public transport is provided by the Zürich Tram route 7 and by the bus lines 161 and 165. History Heinrich Escher bought in 1826 the so-called «Wyssbühel», a vine-covered hill on Zürichsee lakeshore. According to his own plans, the top of the hill was removed and the material used for populations on the swampy banks. The area was planted with exotic trees, which partly came from Northern America. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 443,037 inhabitants, the urban area 1.315 million (2009), and the Zurich metropolitan area 1.83 million (2011). Zurich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zurich Airport and Zurich's main railway station are the largest and busiest in the country. Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zurich was founded by the Romans, who called it '. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years (although this only indicates human presence in the area and not the presence of a town that early). During the Middle Ages, Zurich gained the independent and privileged status of imperial immediacy and, in 1519, became a primary centre of the Protestant Reformation in Europe under the leadership of Huldrych Zwingli. The official language of Zurich is Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
; rm, citad federala, links=no). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Lucerne, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zurich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2022 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: link=no, Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: link=no, Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federal assembly-independent directorial republic , leader_title1 = Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Viktor Rossi , legislature = Federal Assembly , upper_house = Counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
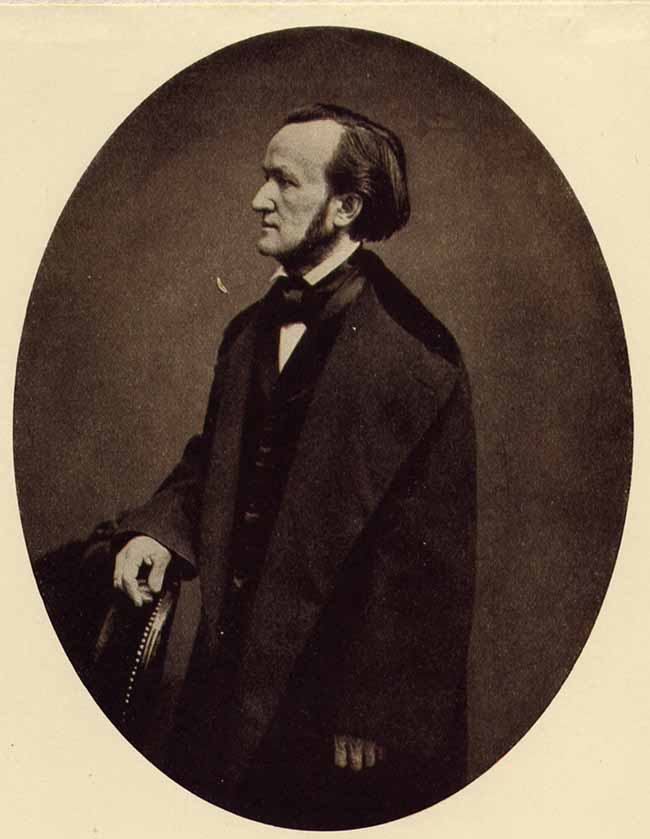
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the music for each of his stage works. Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works in the romantic vein of Carl Maria von Weber and Giacomo Meyerbeer, Wagner revolutionised opera through his concept of the '' Gesamtkunstwerk'' ("total work of art"), by which he sought to synthesise the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, with music subsidiary to drama. He described this vision in a series of essays published between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised these ideas most fully in the first half of the four-opera cycle '' Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (''The Ring of the Nibelung''). His compositions, particularly those of his later period, are notable for their complex textur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Wesendonck
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', ''Odo'', ''Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity". The name is recorded from the 7th century ( Odo, son of Uro, courtier of Sigebert III). It was the name of three 10th-century German kings, the first of whom was Otto I the Great, the first Holy Roman Emperor, founder of the Ottonian dynasty. The Gothic form of the prefix was ''auda-'' (as in e.g. '' Audaþius''), the Anglo-Saxon form was ''ead-'' (as in e.g. ''Eadmund''), and the Old Norse form was '' auð-''. The given name Otis arose from an English surname, which was in turn derived from ''Ode'', a variant form of ''Odo, Otto''. Due to Otto von Bismarck, the given name ''Otto'' was strongly associated with the German Empire in the later 19th century. It was comparatively frequently given in the United States (presumably in German American families) during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Zeugheer (1921-2014), German author & historian
{{disambiguation ...
Leonhard may refer to: * Leonhard Euler (1707–1783), Swiss mathematician and physicist * Leonhard Hutter (1563–1616), German theologian * Karl Leonhard (1904–1988), German psychiatrist * Jim Leonhard (1982– ), American football safety * LEONHARD (2009– ), Oslo-based DJ collective * Leonhard Rauwolf (1535–1596), German physician and botanist *Leonhard Stejneger (1851–1943), American herpetologist *Wolfgang Leonhard Wolfgang Leonhard (16 April 1921 – 17 August 2014) was a German political author and historian of the Soviet Union, the German Democratic Republic and Communism. A German Communist whose family had fled Hitler's Germany and who was educated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Froebel
Theodor is a masculine given name. It is a German form of Theodore. It is also a variant of Teodor. List of people with the given name Theodor * Theodor Adorno, (1903–1969), German philosopher * Theodor Aman, Romanian painter * Theodor Blueger, Latvian professional ice hockey forward for the Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League (NHL) * Theodor Burghele, Romanian surgeon, President of the Romanian Academy * Theodor Busse, German general during World War I and World War II * Theodor Cazaban, Romanian writer * Theodor Fischer (fencer), German Olympic épée and foil fencer * Theodor Fontane, (1819–1898), German writer * Theodor Geisel, American writer and cartoonist, known by the pseudonym Dr. Seuss * Theodor W. Hänsch (born 1940), German physicist * Theodor Herzl, (1860–1904), Austrian-Hungary Jewish journalist and the founder of modern political Zionism * Theodor Heuss, (1884–1963), German politician and publicist * Theodor Innitzer, Austrian Catho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Friedrich Bluntschli
Alfred Friedrich Bluntschli (29 January 1842, Zürich - 27 July 1930, Zürich) was a Swiss architect and educator. Life and work Son of a distinguished legal scholar, Johann Caspar Bluntschli, A. F. "Fritz" Bluntschli commenced his architectural education in 1860 at the Zürich Polytechnikum (now ETH Zurich) under Gottfried Semper, and later (1864) attended the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris in the ''atelier'' of Charles-Auguste Questel. By 1866, Bluntschli was shuttling between Heidelberg and Konstanz, and in 1870 he settled in Frankfurt-am-Main where he met (1839-1883), with whom he established a successful architectural practice. One of their first successful commissions was for the layout of Vienna's Zentralfriedhof in 1871, though none of the planned structures were built. In 1876, Mylius and Bluntschli won an international competition for the new Hamburg City Hall, though it was not executed to their designs. In 1881, Bluntschli was called to assume the leadership of the De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William II, German Emperor
, house = Hohenzollern , father = Frederick III, German Emperor , mother = Victoria, Princess Royal , religion = Lutheranism ( Prussian United) , signature = Wilhelm II, German Emperor Signature-.svg Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until his abdication on 9 November 1918. Despite strengthening the German Empire's position as a great power by building a powerful navy, his tactless public statements and erratic foreign policy greatly antagonized the international community and are considered by many to be one of the underlying causes of World War I. When the German war effort collapsed after a series of crushing defeats on the Western Front in 1918, he was forced to abdicate, thereby marking the end of the German Empire and the House of Hohenzollern's 300-year reign in Prussia and 500-year reign in Brandenburg. Wilhelm II was the son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
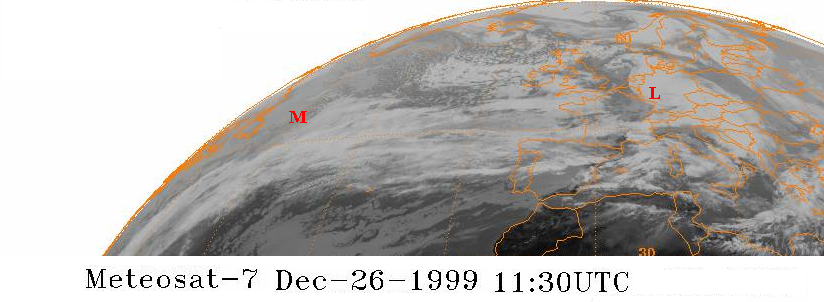
Lothar (storm)
Cyclone Lothar is regarded as the worst European windstorm recorded during the 20th century. Crossing France, Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany between 25 December and 27 December 1999, Cyclone Lothar resulted in 110 fatalities (including 88 in France alone) and more than €15 billion in damage, becoming the costliest European windstorm ever recorded. Cyclone Lothar was the second of a series of devastating European windstorms which made landfall in December 1999, occurring around three weeks after Cyclone Anatol, which caused severe damage in Denmark and nearby parts of Sweden and Germany. The day after Lothar moved over western Europe, another intense European windstorm, Cyclone Martin, caused severe damage to the south of Lothar's track. Meteorological history December 1999 saw a series of heavy winter storms cross the North Atlantic and western Europe. In early December, Denmark was hit by Cyclone Anatol which caused severe damage there and in neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristan Und Isolde
''Tristan und Isolde'' (''Tristan and Isolde''), WWV 90, is an opera in three acts by Richard Wagner to a German libretto by the composer, based largely on the 12th-century romance Tristan and Iseult by Gottfried von Strassburg. It was composed between 1857 and 1859 and premiered at the Königliches Hoftheater und Nationaltheater in Munich on 10 June 1865 with Hans von Bülow conducting. Wagner referred to the work not as an opera, but called it "" (literally ''a drama'', ''a plot'', or ''an action''). Wagner's composition of ''Tristan und Isolde'' was inspired by the philosophy of Arthur Schopenhauer (particularly '' The World as Will and Representation''), as well as by Wagner's affair with Mathilde Wesendonck. Widely acknowledged as a pinnacle of the operatic repertoire, ''Tristan'' was notable for Wagner's unprecedented use of chromaticism, tonal ambiguity, orchestral colour, and harmonic suspension. The opera was enormously influential among Western classical comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |