|
Richland Airport (Washington)
Richland Airport is a public airport in the northwest United States, located northwest of the central business district of Richland, a city in Benton County, Washington. It is owned by the Port of Benton. History The airport, originally named Atomic Energy Field, was constructed in 1943 by the United States Atomic Energy Commission for use by personnel at the Hanford Site. The Port of Benton acquired the airport in December 1961, opening it for public use. Facilities and aircraft Richland Airport covers an area of which contains two asphalt paved runways: 1/19 measuring 4,009 x 75 ft (1,222 x 23 m) and 8/26 measuring 3,995 x 100 ft (1,218 x 30 m). For the 12-month period ending July 31, 2007, the airport had 29,000 general aviation aircraft operations, an average of 79 per day. There are 202 aircraft based at this airport: 87% single-engine, 2% multi-engine, 1% helicopter, 4% glider and 6% ultralight. Accidents *1978: Flight 23 of Richland-based Columbia Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benton County, Washington
Benton County is a County (United States), county in the south-central portion of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, its population was 206,873. The county seat is Prosser, Washington, Prosser, and its most populous city is Kennewick, Washington, Kennewick. The Columbia River demarcates the county's north, south, and east boundaries. Benton County was created from what were then larger versions of Klickitat County, Washington, Klickitat County and Yakima County, Washington, Yakima County on March 8, 1905, and was named after Missouri statesman Thomas Hart Benton (senator), Thomas Hart Benton. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (3.4%) is water. The highest point of land elevation within the county is the summit of Rattlesnake Mountain at 3,527 feet; and the lowest point of land elevation is along the southwestern shore of Crow Butte at 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations except for commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services for other purposes. However, for statistical purposes, ICAO uses a definition of general aviation which includes aerial work. General aviation thus represents the " private transport" and recreational components of aviation, most of which is accomplished with light aircraft. Definition The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines civil aviation aircraft operations in three categories: General Aviation (GA), Aerial Work (AW) and Commercial Air Transport (CAT). Aerial work operations are separated from general aviation by ICAO by this definition. Aerial work is when an aircraft is used for specialized services such as agriculture, construction, photography, surveying, observation and patrol, search and rescue, and aerial adver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
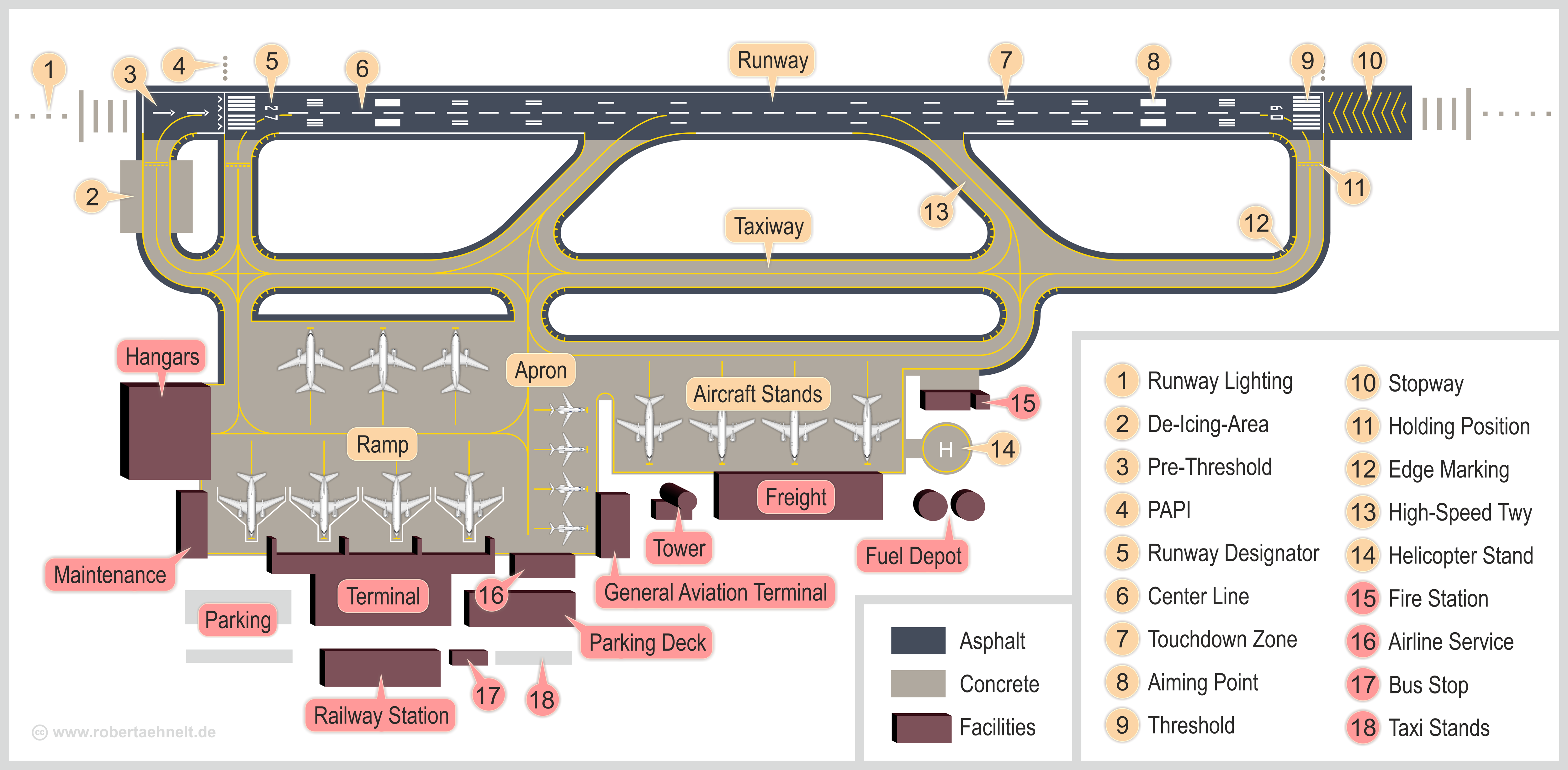
Airports In Washington (state)
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Airport operations are extremely complex, with a complicated system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington State DOT
The Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT or WashDOT, both ) is a governmental agency that constructs, maintains, and regulates the use of transportation infrastructure in the U.S. state of Washington. Established in 1905, it is led by a secretary and overseen by the governor. WSDOT is responsible for more than 20,000 lane-miles of roadway, nearly 3,000 vehicular bridges and 524 other structures. This infrastructure includes rail lines, state highways, state ferries (considered part of the highway system) and state airports. History Department of Highways WSDOT was founded as the Washington State Highway Board and the Washington State Highways Department on March 13, 1905, when then-governor Albert Mead signed a bill that allocated $110,000 to fund new roads that linked the state. The State Highway Board was managed by State Treasurer, State Auditor, and Highway Commissioner Joseph M. Snow and the Board first met on April 17, 1905, to plan the 12 original sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Airports In Washington (state)
Washington, a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States, has 132 public use airports that are used for general aviation, commercial flights, and other purposes. The state also has several military airports and private airfields. Public airports owned by municipal corporations, including public port districts, were authorized by the Washington State Legislature in 1941. This list contains all public-use and military airports in the state, grouped by type and sorted by location. Some private-use and former airports may be included where notable, such as airports that were previously public-use, those with commercial enplanements recorded by the FAA or airports assigned an IATA airport code. Airports See also * Essential Air Service * Washington World War II Army Airfields References General Federal Aviation Administration (FAA): FAA Airport Data (Form 5010)from National Flight Data Center (NFDC), also available froAirportIQ 5010National Plan of Integrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seattle–Tacoma International Airport
Seattle–Tacoma International Airport is the primary international airport serving Seattle and its surrounding metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Washington. It is in the city of SeaTac, which was named after the airport's nickname Sea–Tac, approximately south of downtown Seattle and north-northeast of downtown Tacoma. The airport is the busiest in the Pacific Northwest region of North America and is owned by the Port of Seattle. The entire airport covers an area of and has three parallel runways. It is the primary hub for Alaska Airlines, whose headquarters are near the airport. The airport is also a hub and international gateway for Delta Air Lines, which has expanded at the airport since 2011. , 31 airlines operate at Sea–Tac, serving 91 domestic and 28 international destinations in North America, Oceania, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. Sea–Tac was developed in the 1940s to replace Boeing Field, which had been converted to military use during World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beechcraft Model 99
The Beechcraft Model 99 is a civilian aircraft produced by American manufacturer Beechcraft. It is also known as the Beech 99 Airliner and the Commuter 99. The 99 is a twin-engine, unpressurized, 15 to 17 passenger seat turboprop aircraft, derived from the earlier Beechcraft King Air and Queen Air. It uses the wings of the Queen Air, the engines and nacelles of the King Air, and sub-systems from both, with a specifically designed nose structure. Design and development Designed in the 1960s as a replacement for the Beechcraft Model 18, it first flew in July 1966. It received type certification on May 2, 1968, and 62 aircraft were delivered by the end of the year. In 1984, the Beechcraft 1900, a pressurized 19-passenger airplane, was introduced as the follow-on aircraft. Production ended in early 1987 with 239 airframes completed. Nearly half the Beech 99s in airline service are now operated as freighters by Ameriflight. Variants * : Twin-engined Commuter and cargo transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultralight
Ultralight aviation (called microlight aviation in some countries) is the flying of lightweight, 1- or 2-seat fixed-wing aircraft. Some countries differentiate between weight-shift control and conventional three-axis control aircraft with ailerons, elevator and rudder, calling the former "microlight" and the latter "ultralight". During the late 1970s and early 1980s, mostly stimulated by the hang gliding movement, many people sought affordable powered flight. As a result, many aviation authorities set up definitions of lightweight, slow-flying aeroplanes that could be subject to minimum regulations. The resulting aeroplanes are commonly called "ultralight aircraft" or "microlights", although the weight and speed limits differ from country to country. In Europe, the sporting (FAI) definition limits the maximum stalling speed to and the maximum take-off weight to , or if a ballistic parachute is installed. The definition means that the aircraft has a slow landing speed and sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glider Aircraft
A glider is a fixed-wing aircraft that is supported in flight by the dynamic reaction of the air against its lifting surfaces, and whose gliding flight, free flight does not depend on an engine. Most gliders do not have an engine, although motor-gliders have small engines for extending their flight when necessary by sustaining the altitude (normally a sailplane relies on rising air to maintain altitude) with some being powerful enough to take off by Motor glider, self-launch. There are a wide variety of types differing in the construction of their wings, aerodynamic efficiency, location of the pilot, controls and intended purpose. Most exploit lift (soaring), meteorological phenomena to maintain or gain height. Gliders are principally used for the air sports of gliding, hang gliding and paragliding. However some spacecraft have been designed to descend as gliders and in the past military gliders have been used in warfare. Some simple and familiar types of glider are toys such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which Lift (force), lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning Helicopter rotor, rotors. This allows the helicopter to VTOL, take off and land vertically, to hover (helicopter), hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. The Focke-Wulf Fw 61 was the first successful, practical, and fully controllable helicopter in 1936, while in 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale mass production, production. Starting in 1939 and through 1943, Igor Sikorsky worked on the development of the Vought-Sikorsky VS-300, VS-300, which over four iterations, became the basis for modern helicopters with a single main rotor and a single tail rotor. Although most earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway
In aviation, a runway is an elongated, rectangular surface designed for the landing and takeoff of an aircraft. Runways may be a human-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to manufacture Bréguet Aviation military aircraft. In January 1919, aviation p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richland, Washington
Richland () is a city in Benton County, Washington, United States. It is located in southeastern Washington at the confluence of the Yakima River, Yakima and the Columbia River, Columbia Rivers. As of the 2020 census, the city's population was 60,560. Along with the nearby cities of Pasco, Washington, Pasco and Kennewick, Washington, Kennewick, Richland forms the Tri-Cities, Washington, Tri-Cities metropolitan area. The townsite was established in 1905 and incorporated as Richland in 1910. The U.S. Army acquired the city and surrounding areas in 1943 for the establishment of the Hanford site, Hanford nuclear site, part of the Manhattan Project during World War II. Richland was transformed into a bedroom community for Hanford workers and grew to 25,000 residents by the end of the war. The city remained under control of Hanford contractors until it was re-incorporated as a city in 1958. History For centuries, the village of Chemna stood at the mouth of the current Yakima River. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |