|
Richard Stovin
Lieutenant General Richard Stovin (1761 – 1825) was a British Army officer during the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. He originally joined the army as an ensign in 1780, and saw service in the American War of Independence, where he may have been taken prisoner after the Battle of Yorktown. After the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars, he saw service with a force sent to invade French colonies in the Caribbean, and was taken prisoner in 1794 at Guadeloupe. Released after two years in captivity, he later commanded his regiment in the Netherlands, in the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland of 1799, and on garrison duties in the Mediterranean and in India. In the War of 1812 he was appointed to command a division in the forces in Canada, where an island in the St. Lawrence river was named after him. Family and early career Stovin was born at Whitgift, in the West Riding of Yorkshire (now the East Riding of Yorkshire), the son of James Stovin. His elder broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitgift, East Riding Of Yorkshire
Whitgift is a small linear village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Twin Rivers, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England approximately east of Goole. It is located alongside the River Ouse and north of the A161 road between Goole and Scunthorpe. Ousefleet and Reedness are to the east and west respectively. Historically Whitgift was part of the West Riding of Yorkshire. In 1961 the parish had a population of 191. Features There was for many years a Whitgift ferry, which may originally have predated the village. Between November 1606 and February 1607, a persistent cold weather spell froze the River Ouse, and the ferry could not operate. However, records indicate that ".. men, women and children, horses and wagons loaded went on ye water at Ouse here at Whitgift ferrie and son continued until ye xiiii day of Februarie...". Church The Church of Mary Magdalene (on the Whitgift side of the border between Whitgift and Reedness) dates from 1304 (replacing an earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of King George III of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and representatives of the United States on September 3, 1783, officially ended the American Revolutionary War and recognized the Thirteen Colonies, which had been part of colonial British America, to be free, sovereign and independent states. The treaty set the Demarcation line, boundaries between British North America, later called Canada, and the United States, on lines the British labeled as "exceedingly generous", although exact boundary definitions in the far-northwest and to the south continued to be subject to some controversy. Details included fishing rights and restoration of property and Prisoners of war in the American Revolutionary War, prisoners of war. This treaty and the separate peace treaties between Great Britain and the nations that supported the American cause, including Kingdom of France, France, History of Spain (1700–1808), Spain, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
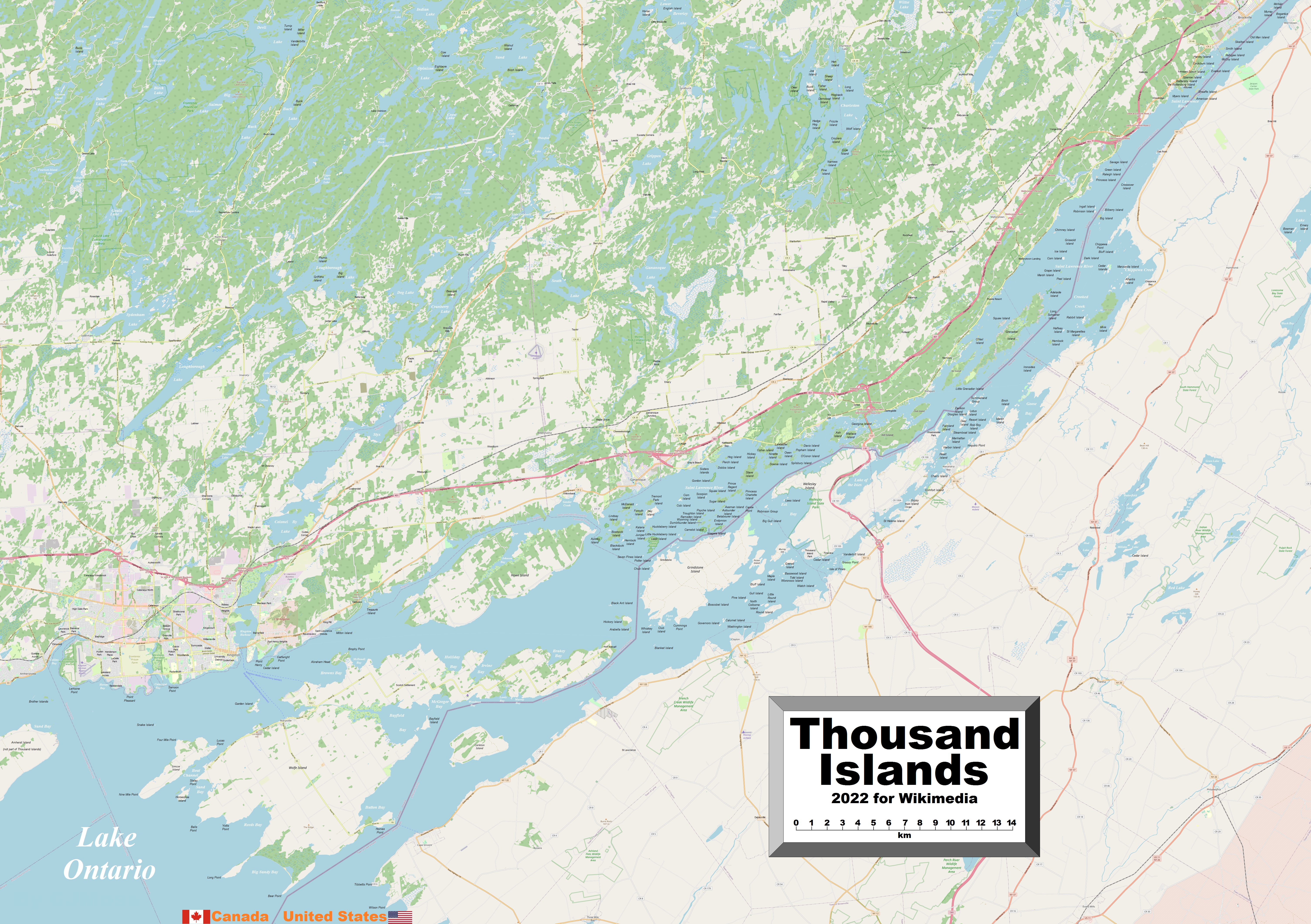
Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (, ) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for about downstream from Kingston, Ontario. The Canadian islands are in the province of Ontario and the U.S. islands in the state of New York. The islands range in size from over to smaller islands occupied by a single residence, or uninhabited outcroppings of rocks. To count as one of the Thousand Islands, emergent land within the river channel must have at least of land above water level year-round, and support at least two living trees. Geography The Thousand Islands archipelago is at the outlet of Lake Ontario at the head of the Saint Lawrence River. The region is bisected by the Canada–United States border and covers portions of Jefferson and St. Lawrence counties in the U.S. state of New York, in addition to parts of the United Counties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France, the Spanish Empire, and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it set the stage for the Napoleonic Wars. Britain gave up most of its recent conquests; France was to evacuate Naples and Egypt. Britain retained Ceylon (Sri Lanka) and Trinidad. It was signed in the Hôtel de Ville (City Hall) of Amiens on 25 March 1802 (4 Germinal X in the French Revolutionary calendar) by Joseph Bonaparte and Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis as a "Definitive Treaty of Peace". The consequent peace lasted only one year (18 May 1803) and was the only period of general peace in Europe between 1793 and 1814. Under the treaty, Britain recognised the French Republic. Together with the Treaty of Lunéville (1801), the Treaty of Amiens marked the end of the Second Coalition, which had waged war against Revolutionary Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bergen (1799)
The Battle of Bergen was fought on 19 September 1799 and resulted in a Franco-Batavian victory under Generals Guillaume Brune and Herman Willem Daendels against Anglo-Russian forces under the Duke of York who had landed in North Holland. The battlefield is marked by the Russisch Monument (1902). Order of battle The Duke of York landed on 15 September, and assumed the command of the army, which now amounted to about 30,000 men with 1,200 light cavalry. On 19 September the forces, under the Duke of York, formed in four columns, moved forward from Schagerbrug. At this period the Allies possessed a superiority of force with which it was decided to strike a decisive blow as early as possible. The Dutch, numbering 12,000, were in a strong position around Langedijk, somewhat in advance of the French, who, by drawing in all detachments, had raised their field strength to 10,000 men, who were positioned in Alkmaar, Bergen, Schoorl, and Egmond aan Zee. Anglo-Russian Forces Prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Krabbendam (1799)
The Battle of Krabbendam (also called the Battle of Zijpedijk) of 10 September 1799 was fought during the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland between forces of the French Republic and her ally, the Batavian Republic, under the command of French general Guillaume Marie Anne Brune on one side, and a British division under general Sir Ralph Abercromby on the other. The British division had established a bridgehead in the extreme north of the North-Holland peninsula after the Battle of Callantsoog (1799). Brune tried to dislodge them before they could be reinforced by further Anglo-Russian forces, but the British prevailed. This enabled the British and their Russian allies to land their expeditionary force and to break out of the bridgehead during the Battle of Bergen (1799). Background After the Battle of Callantsoog General Herman Willem Daendels with the 1st Batavian Division had fallen back all the way to the Schermer polder, as he deemed the ''Zijpe'' polder indefensible, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Hugues
Jean-Baptiste Victor Hugues (July 20, 1762 – August 12, 1826) was a French politician and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Guadeloupe from 1794 to 1798. He is best known for his actions during the French Revolutionary Wars, where Hugues played a major role in implementing the Law of 4 February 1794 which abolished slavery in France's colonies. Early life Jean-Baptiste Victor Hugues was born on 20 July 1762 in Marseille into a wealthy family. His father, Jean-François Hugues, was a merchant, and Hugues's mother Catherine Fodrin was born into family of silk traders from Saint-Étienne. Hugues moved along with his family to the French colony of Saint-Domingue during the early 1780s, where he eventually acquired ownership of a number of slave plantations. During the 1790s, Hugues was forced to return to France as a result of the Haitian Revolution. There, he was appointed as prosecutor of the Committee of Public Safety in La Rochelle with the support of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Grey, 1st Earl Grey
Charles Grey, 1st Earl Grey, (circa 23 October 1729 – 14 November 1807) was a British Army officer. He was a distinguished soldier in a generation of exceptionally capable military personnel, serving crucially in the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the American Revolutionary War, and the French Revolutionary Wars. He served in the American War of Independence (1775–1783), rising to be Commander-in-Chief of the British forces in America. Following the Battle of Paoli in Pennsylvania in 1777 he became known as "No-flint Grey" for reputedly ordering his men to extract the flints from their muskets during a night approach and to fight with bayonets only. He later fought in the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802), capturing Martinique as leverage to force the Treaty of Amiens, and was appointed as Governor of Guernsey. Early life Grey was born at his family estate Howick Hall, 30 miles north of Newcastle upon Tyne and one mile from the North Sea. His exact birthdate is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Guadeloupe (1794)
The invasion of Guadeloupe was a British attempt in 1794 to take and hold the island of Guadeloupe in the French West Indies during the French Revolutionary Wars. The British had negotiated with the French planters, Ignace-Joseph-Philippe de Perpignan and Louis de Curt, who wished to gain British protection, as France's National Convention was passing a law abolishing slavery on 4 February 1794. The Whitehall Accord was signed on 19 February 1794 while the British were securing Martinique in the Battle of Martinique (1794). Troops led by General Charles Grey landed in Guadeloupe on 11 April 1794, assisted by a fleet led by Admiral Sir John Jervis. On 24 April French general Victor Collot surrendered the last stronghold at Basse-Terre, leaving the island in the hands of the British and their French Royalist allies. On 4 June a French fleet landed troops under the command of Victor Hugues who, with the assistance of French Republican locals, helped by the effect of yellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique. It covers a land area of with an estimated population of over 180,000 people as of 2018. The nation's capital and largest city is Castries. The first proven inhabitants of the island, the Arawaks, are believed to have been the first to settle on the island in 200–400 AD. In 800 AD, the island was taken over by the Kalinago. The French people, French were the first European colonization of the Americas, European colonists to settle on the island, and they signed a treaty with the native Caribs in 1660. The English people, English took control of the island in 1663. In ensuing years, Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France fought 14 times for control of the island; conseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |