|
Richard Risby
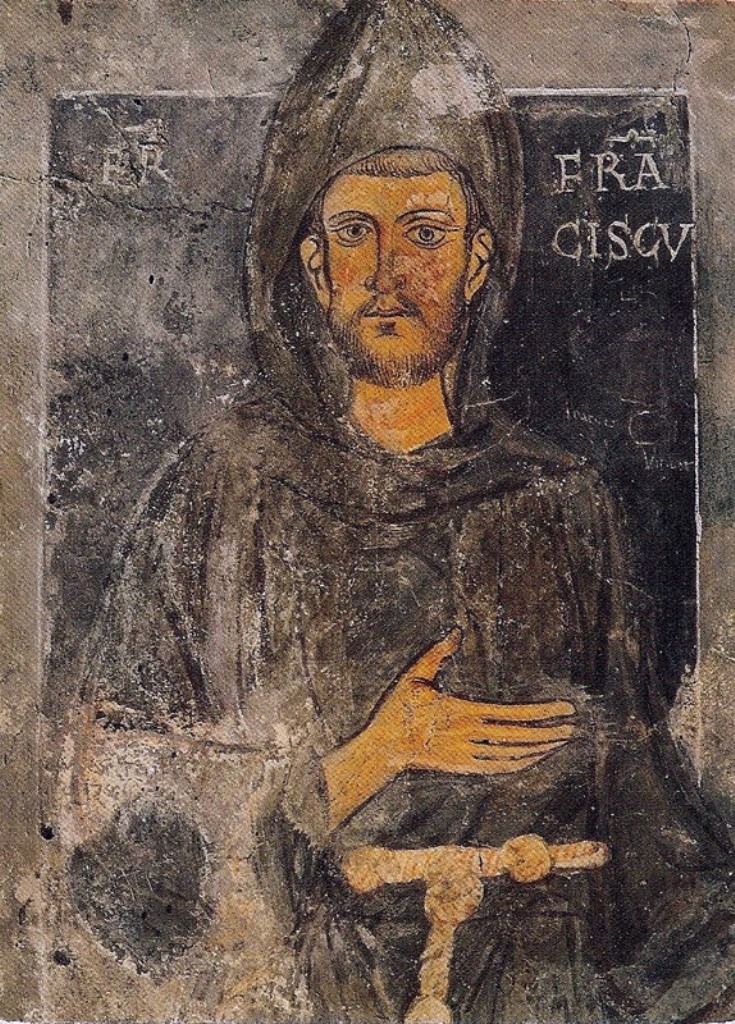
Richard Risby, O.F.M., (1489 - 20 April 1534) was an English Catholic Franciscan friar who was executed for treason during the reign of King Henry VIII. Life Risby was born in the parish of St. Lawrence, Reading, in 1489, and entered Winchester College in 1500. He was subsequently a fellow of New College, Oxford, taking his degree in 1510. He resigned in 1513 to enter the Franciscan Order, and eventually became guardian of the Observant friary at Canterbury. Risby became a supporter of Dame Elizabeth Barton, O.S.B., widely known as the "Holy Maid of Kent", who had the reputation of being a visionary. When she declared that King Henry would soon die if he continued his actions against the papacy, a prophecy that failed to come to pass within the time she predicted, the king turned against her and she was condemned to death by an Act of Attainder (25 Hen. 8. c. 12), together with several of her supporters: Hugh Rich, O.F.M., guardian of the Observant friary at Richmond, Edward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (commonly called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; Post-nominal letters, postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a Mendicant orders, mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary, among many others. The Order of Friars Minor is the largest of the contemporary Religious institute#Categorization, First Orders within the Franciscan movement. Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval of his order from Pope Innocent III in 1209. The original Rule of Saint Francis approved by the pope disallowed ownership of property, requiring members of the order to beg for food while preaching. The austerity was meant to emulate the life and ministry of Jesus Christ. Franciscans traveled and preached in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parson
A parson is an ordained Christian person responsible for a small area, typically a parish. The term was formerly often used for some Anglican clergy and, more rarely, for ordained ministers in some other churches. It is no longer a formal term denoting a specific position within Anglicanism, but has some continued historical and colloquial use. In the pre-Reformation church, a parson was the priest of an independent parish church, that is, a church not under the control of a larger ecclesiastical or monastic organization. The term is similar to rector and is in contrast to a vicar, a cleric whose revenue is usually, at least partially, appropriated by a larger organisation. Today the term is normally used for some parish clergy of non-Roman Catholic churches, in particular in the Anglican tradition in which a parson is the incumbent of a parochial benefice: a parish priest or a rector; in this sense a parson can be compared with a vicar. The title ''parson'' can be applied to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Educated At Winchester College
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1534 Deaths
Year 1534 (Roman numerals, MDXXXIV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 15 – The Parliament of England passes the ''Act Respecting the Oath to the Succession'', recognising the marriage of Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, and their children as the legitimate heirs to the throne. * February 23 – A group of Anabaptists, led by Jan Matthys, Münster Rebellion, seize Münster, Westphalia and declare it ''The New Jerusalem'', begin to exile dissenters, and forcibly baptize all others. *March 10 – The Portuguese Empire, Portuguese crown divides Colonial Brazil into fifteen Captaincies of Brazil, donatory captaincies, hereditary titles similar to duchy, duchies. * March 30 – The Submission of the Clergy Act 1533 becomes law in England, requiring Submission of the Clergy, submission of the clergy, that is, churchmen are to submit to the king and the publication of ecclesiasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1489 Births
Year 1489 ( MCDLXXXIX) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * March 14 – The Queen of Cyprus, Catherine Cornaro, sells her kingdom to the Republic of Venice. * March 26 – The Treaty of Medina del Campo between England and Spain includes provision for a marriage between Arthur, the son of King Henry VII of England, and Infanta Catherine of Aragon. *June 29 – King James IV grants Andrew, Lord Gray, the lands and Barony of Lundie in Scotland. * July 17 – Delhi Sultanate: Sikandar Lodi succeeds Bahlul Khan Lodi as sultan. * November 29 – Arthur Tudor is named Prince of Wales. * December 11 – Jeannetto de Tassis is appointed Chief Master of Postal Services in Innsbruck; his descendants, the Thurn und Taxis Family, later run much of the postal system of Europe. Date unknown * Typhus first appears in Europe, during the Siege of Baza in the Granada War. * A gold coin equa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Aidan Gasquet
Francis Aidan Cardinal Gasquet (born Francis Neil Gasquet; 5 October 1846 – 5 April 1929) was an English Benedictine monk and historical scholar. He controversially challenged what he regarded as the anti-Catholic narrative of the English history of his age, and uncovered the extent of the Black Death in England. He was created Cardinal in 1914. Life Gasquet was the third of six children of Raymond Gasquet, a physician whose French naval officer father had emigrated to England during the British evacuation of Toulon in 1793. His mother was a Yorkshirewoman. He was born at 26 Euston Place, Somers Town, London. Educated at Downside School, he entered the Benedictines in 1865 at Belmont Priory. He moved to Downside Abbey where he was professed and, on 19 December 1871, ordained a priest. From 1878 to 1885 he was prior of Downside Abbey, resigning because of ill health; but he retained a life long interest in the development of the monastic buildings, in particular the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
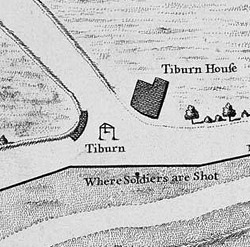
Tyburn
Tyburn was a Manorialism, manor (estate) in London, Middlesex, England, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne (stream), Bourne, means 'boundary stream'.Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. The parish, and probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street). The junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For many centuries the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment: it was the principal place for execution for London and Middlesex criminals and convicted Treason, traitors, including many religious martyrs. In the 18th century it was also known as "God's Tribunal". Hangings at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich
Greenwich ( , , ) is an List of areas of London, area in south-east London, England, within the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London, east-south-east of Charing Cross. Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Prime meridian (Greenwich), Greenwich Meridian (0° longitude) and Greenwich Mean Time. The town became the site of a royal palace, the Palace of Placentia, from the 15th century and was the birthplace of many House of Tudor, Tudors, including Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. The palace fell into disrepair during the English Civil War and was demolished, eventually being replaced by the Greenwich Hospital (London), Royal Naval Hospital for Sailors, designed by Sir Christopher Wren and his assistant Nicholas Hawksmoor. These buildings became the Old Royal Naval College, Royal Naval College in 1873, and they remained a military education establishment until 1998, when they passed into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Habit
A religious habit is a distinctive set of clothing worn by members of a religious order. Traditionally, some plain garb recognizable as a religious habit has also been worn by those leading the religious Hermit, eremitic and Anchorite, anchoritic life, although in their case without conformity to a particular uniform style. Uniformity and distinctiveness by order often evolved and changed over time. Interpretation of terms for clothes in religious rules could change over centuries. Furthermore, every time new communities gained importance in a cultural area the need for visual separation increased for new as well as old communities. Thus, modern habits are rooted in historic forms, but do not necessarily resemble them in cut, color, material, detail or use. In Christian monasticism, Christian monastic orders of the Catholic church, Catholic, Lutheranism, Lutheran and Anglicanism, Anglican Churches, the habit often consists of a tunic covered by a scapular and cowl, with a hood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Bourchier (Franciscan)
Thomas Bourchier (''d.'' 1586?) was an English Observantine Franciscan and martyologist. Life He was probably educated at Magdalen Hall, Oxford, but there is no record of his having graduated in that university. When Queen Mary attempted to re-establish the friars in England, Bourchier became a member of the new convent at Greenwich; but on the queen's death he left the country. After spending some years in Paris, where the theological faculty of the Sorbonne conferred on him the degree of doctor, he travelled to Rome. He at first joined the convent of the Reformed Franciscans at the church of S. Maria di Ara Coeli, and taught at Genoa and Turin. Subsequently he became penitentiary in the church of S. Giovanni in Laterano, where John Pits, his biographer, speaks of having sometimes seen him. Bourchier died, according to Pits, at Rome about 1586. Works He wrote several books, but the only one that survives is the ''Historia Ecclesiastica de Martyrio Fratrum Ordinis Divi Franci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rector (ecclesiastical)
A rector is, in an ecclesiastical sense, a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations. In contrast, a vicar is also a cleric but functions as an assistant and representative of an administrative leader. Ancient usage In ancient times bishops, as rulers of cities and provinces, especially in the Papal States, were called rectors, as were administrators of the patrimony of the Church (e.g. '). The Latin term ' was used by Pope Gregory I in '' Regula Pastoralis'' as equivalent to the Latin term ' (shepherd). Roman Catholic Church In the Roman Catholic Church, a rector is a person who holds the ''office'' of presiding over an ecclesiastical institution. The institution may be a particular building—such as a church (called his rectory church) or shrine—or it may be an organization, such as a parish, a mission or quasi-parish, a seminary or house of studies, a university, a hospital, or a community of clerics or religious. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |