|
Richard Lewisohn
Richard Lewisohn (July 12, 1875 in Hamburg – August 11, 1961 in New York) was a German-American surgeon. At Mount Sinai Hospital in Manhattan, he developed procedures that made blood transfusion practical. Life and career Lewisohn was born to German-Jewish parents in Hamburg and was educated at the local Gymnasium from where he entered medical school in Kiel in 1893. As was typical for German medical students, he attended several different medical schools, before receiving his doctorate from the University of Freiburg in 1899 with a thesis on malignant kidney tumors. He then served for two years as an assistant to Karl Weigert at the Senckenberg Institute in Frankfurt. In 1904 he became an assistant to Geheimrat Czerny in Heidelberg. In 1906 he emigrated to New York, where he became a gastroenterologist and surgeon; from 1928 to 1936 he was chief of the general surgical service at Mount Sinai. Scientific career Blood transfusion Following early speculation and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg, Germany
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin, as well as the overall List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th largest city and largest non-capital city in the European Union with a population of over 1.85 million. Hamburg's urban area has a population of around 2.5 million and is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, which has a population of over 5.1 million people in total. The city lies on the River Elbe and two of its tributaries, the River Alster and the Bille (Elbe), River Bille. One of Germany's 16 States of Germany, federated states, Hamburg is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The official name reflects History of Hamburg, Hamburg's history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Hustin
Albert Hustin (1882–1967) was a Belgian medical doctor. Hustin was born in Ethe and died in Uccle ( Uccle Brussels – Belgium). In 1914, he was the first person to successfully practice non-direct blood transfusions with sodium citrate used as an anticoagulant Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the .... He added sodium citrate and glucose to the blood to preserve it, and stop it from clotting. References 1882 births 1967 deaths 20th-century Belgian physicians People from Virton {{Belgium-med-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Board Of Surgery
The American Board of Surgery (ABS) is an independent, non-profit organization located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, founded for the purpose of certifying surgeons who have met a defined standard of education, training and knowledge. Surgeons certified by the ABS, known as diplomates, have completed a minimum of five years of surgical residency training following medical school and successfully completed a written and oral examination process administered by the ABS. The ABS provides board certification in general surgery, vascular surgery, pediatric surgery, surgical critical care, surgery of the hand, hospice and palliative medicine, and complex general surgical oncology. The ABS is composed of a board of directors representing the principal surgical organizations in the U.S. and is one of the 24 member boards of the American Board of Medical Specialties. History The American Board of Surgery was officially organized on January 9, 1937. The formation of the ABS was the result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Gastroenterological Association
The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) is a medical association of gastroenterologists. Approximately 16,000 scientists and physicians are members of the organization. Overview The American Gastroenterological Association is a professional association for gastroenterologists. The AGA was founded in 1897 and has grown to include 16,000 members worldwide who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice, and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programs of the organization. The AGA, a 501(c)(6) organization, administers all membership and public policy activities, while the AGA Institute, a 501(c)(3) organization, runs the organization's practice, research, and educational programs. On a monthly basis, the AGA Institute publishes two journals, ''Gastroenterology'' and '' Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology''. The organization's annual meeting is Digestive Disease Week, which is held each M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Surgeons
The American College of Surgeons is an educational association of surgeons created in 1913.American College of Surgeons Online "What is the American College of Surgeons?"/ref> See also *American College of Physicians The American College of Physicians (ACP) is a national organization of internists, who specialize in the diagnosis, treatment, and care of adults.Sokanu "What is an Internist?" Retrieved October 20, 2014 With 161,000 members, ACP is the largest ... References External links *ACS Foundation [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award
The Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award is a scientific award given by the American Association of Blood Banks (AABB) to scientists with "an international reputation in transfusion medicine or cellular therapies" "whose original research resulted in an important contribution to the body of scientific knowledge". Recipients give a lecture at the AABB Annual Meeting and receive a $7,500 honorarium. The prize was initiated in 1954 to honor Karl Landsteiner, whose research laid the foundation for modern blood transfusion therapy. Recipients * 1954 Reuben Ottenberg * 1955 Richard Lewisohn * 1956 Philip Levine, Alexander Solomon Wiener * 1957 Ruth Sanger, Robert Russell Race * 1958 Oswald Hope Robertson, Francis Peyton Rous, J. R. Turner * 1959 Ernest Witebsky * 1960 Patrick L. Mollison * 1961 Robert R. A. Coombs * 1962 William C. Boyd * 1963 Fred H. Allen Jr., Louis K. Diamond * 1964 J. J. van Loghem * 1965 Ruggero Ceppellini * 1966 Elvin A. Kabat * 1967 Walter Morgan, Winifred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folic Acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is required for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids necessary for cell division. As humans cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an essential nutrient. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements. Folate in the form of folic acid is used to treat anemia caused by folate deficiency. Folic acid is also used as a supplement by women during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in the baby. Low levels in early pregnancy are believed to be the cause of more than half of babies born with NTDs. More than 80 countries use either mandatory or voluntary fortification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Von Haberer
Hans may refer to: __NOTOC__ People * Hans (name), a masculine given name * Hans Raj Hans, Indian singer and politician ** Navraj Hans, Indian singer, actor, entrepreneur, cricket player and performer, son of Hans Raj Hans ** Yuvraj Hans, Punjabi actor and singer, son of Hans Raj Hans * Hans clan, a tribal clan in Punjab, Pakistan Places * Hans, Marne, a commune in France * Hans Island, administrated by Greenland and Canada Arts and entertainment * ''Hans'' (film) a 2006 Italian film directed by Louis Nero * Hans (Frozen), the main antagonist of the 2013 Disney animated film ''Frozen'' * ''Hans'' (magazine), an Indian Hindi literary monthly * ''Hans'', a comic book drawn by Grzegorz Rosiński and later by Zbigniew Kasprzak Other uses * Clever Hans, the "wonder horse" * ''The Hans India'', an English language newspaper in India * HANS device, a racing car safety device *Hans, the ISO 15924 code for Simplified Chinese script See also * Han (other) *Hans im Glück ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
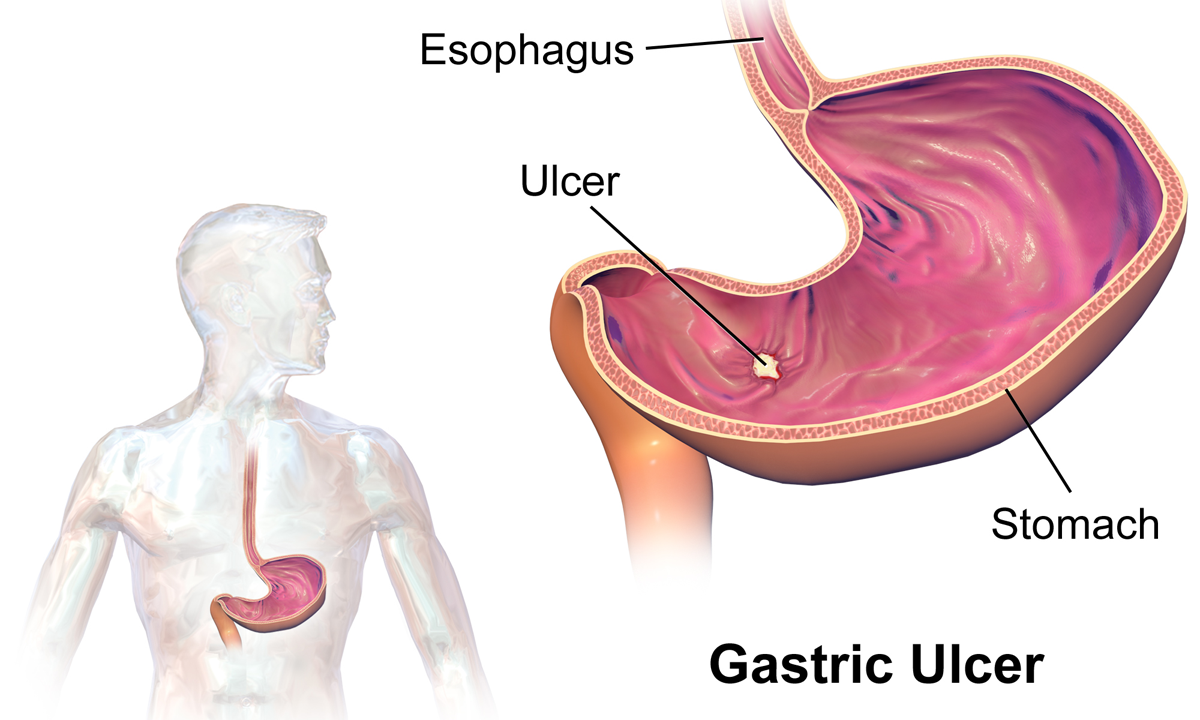
Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrectomy
A gastrectomy is a partial or total surgical removal of the stomach. Indications Gastrectomies are performed to treat stomach cancer and perforations of the stomach wall. In severe duodenal ulcers it may be necessary to remove the lower portion of the stomach called the pylorus and the upper portion of the small intestine called the duodenum. If there is a sufficient portion of the upper duodenum remaining a Billroth I procedure is performed, where the remaining portion of the stomach is reattached to the duodenum before the bile duct and the duct of the pancreas. If the stomach cannot be reattached to the duodenum a Billroth II is performed, where the remaining portion of the duodenum is sealed off, a hole is cut into the next section of the small intestine called the jejunum and the stomach is reattached at this hole. As the pylorus is used to grind food and slowly release the food into the small intestine, removal of the pylorus can cause food to move into the small int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Berg (surgeon)
Albert Ashton Berg (August 10, 1872 in New York – July 1, 1950) was an American surgeon of Hungarian heritage. He had three sisters and four brothers. Berg attended New York public schools, City College and Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. Berg trained at Mount Sinai Hospital in Manhattan from 1894 to 1896, before being appointed to its staff as an adjunct surgeon in 1899. He was later promoted to associate surgeon (1911) and attending surgeon (1914). Berg was chief of the gastrointestinal service there between 1915 and 1934, when he retired from active service, becoming a consulting surgeon. At the behest of his colleague Richard Lewisohn, Berg performed the first subtotal gastric resection for peptic ulcer in the United States. Berg was "a strong advocate of the procedure and reported more than 500 cases, in which a recurrence rate of slightly over 1% was compared to a recurrence rate of 34% after gastroenterostomy alone". Berg "gain dnationwide renow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |