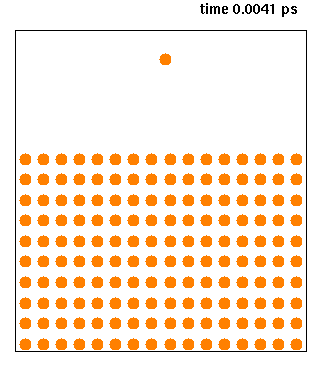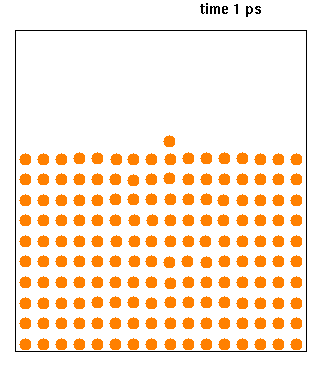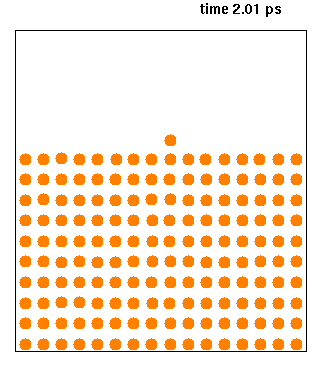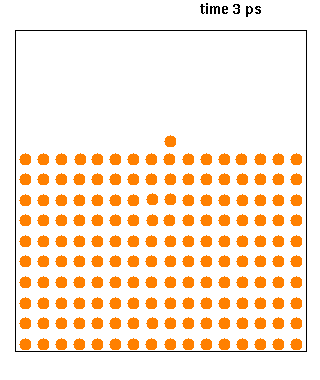
|
Ribosome-nascent Chain Complex
Ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC) refers to the collection of molecules that constitute a ribosome attached to the polypeptide (protein) that it is synthesising. The synthesis of the nascent polypeptide may be stalled by one of several methods. RNCs are produced and purified in laboratories to study the dynamics, biochemistry Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ..., folding and interactions of both the ribosome and proteins undergoing synthesis. References Protein complexes Protein biosynthesis {{Protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all List of life sciences, areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research.#Voet, Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biomolecule, biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living Cell (biology), cells and between cells,#Karp, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissue (biology), tissues and organ (anatomy), organs as well as organism structure and function.#Miller, Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after Protein biosynthesis, synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of Amino acid, amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. This structure permits the protein to become biologically functional or active. The folding of many proteins begins even during the translation of the polypeptide chain. The amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, known as the protein's native state. This structure is determined by the amino-acid sequence or primary structure. The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins Intrinsically unstructured proteins, may remain unfolded, indicating that protein dynamics are important. Failure to fold into a native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances, misfolded proteins have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein–protein Interaction
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by interactions that include electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and the hydrophobic effect. Many are physical contacts with molecular associations between chains that occur in a cell or in a living organism in a specific biomolecular context. Proteins rarely act alone as their functions tend to be regulated. Many molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from numerous protein components organized by their PPIs. These physiological interactions make up the so-called Interactome, interactomics of the organism, while aberrant PPIs are the basis of multiple aggregation-related diseases, such as Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, Creutzfeldt–Jakob and Alzheimer's diseases. PPIs have been studied with Methods to investigate protein–protein interactions, many methods and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Complexes
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multidomain enzymes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain. Protein complexes are a form of quaternary structure. Proteins in a protein complex are linked by non-covalent protein–protein interactions. These complexes are a cornerstone of many (if not most) biological processes. The cell is seen to be composed of modular supramolecular complexes, each of which performs an independent, discrete biological function. Through proximity, the speed and selectivity of binding interactions between enzymatic complex and substrates can be vastly improved, leading to higher cellular efficiency. Many of the techniques used to enter cells and isolate proteins are inherently disruptive to such large complexes, complicating the task of determining the components of a complex. Examples of protein complexes include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |