|
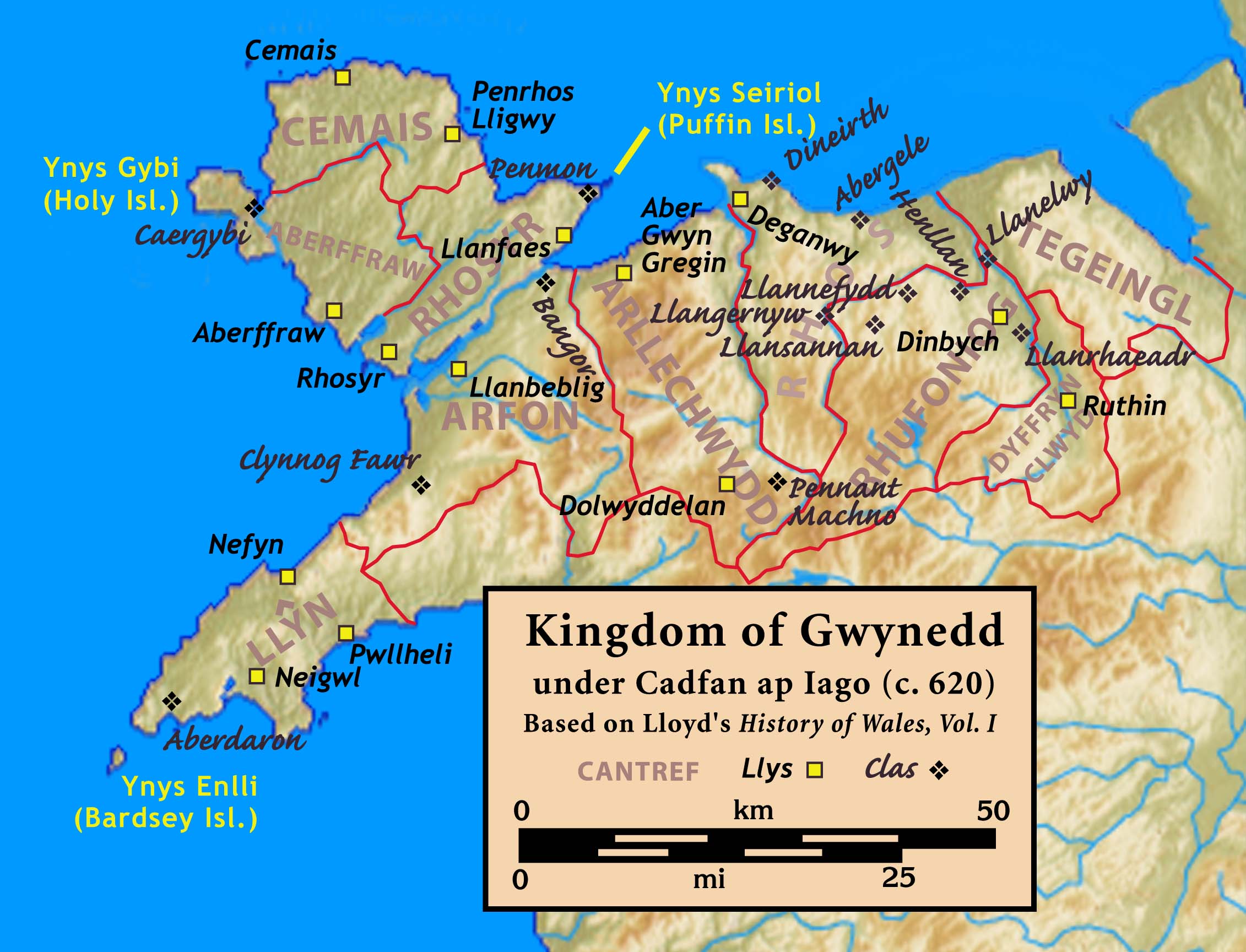
Rhufoniog
{{coord, 52.950, -3.275, display=title, region:GB_scale:20000 Rhufoniog was a small sub-kingdom of the Dark Ages Gwynedd, and later a cantref in medieval Wales. Geography The cantref Rhos lay between it and the Irish Sea. Sometimes the two cantrefi were linked together as "Rhos and Rhufeiniog", which roughly corresponds to the territory of the old county of Denbighshire. The rivers Elwy, Clwyd and Clywedog formed a natural border to the north and east. As today, the countryside was bleak and isolated. There were three commotes in Rhufoniog, namely Upper Aled, Lower Aled and River Aled as a border between them, and the commote Ceinmerch (also known as 'Cymeirch' or 'Ystrad') in the north-east between the River Lliwen and the River Clywedog. History The early history of the cantref is unclear. According to tradition, it was ruled by its eponymous founder Rhufon, the third son of the first King of Gwynedd, Cunedda, and his direct descendants from the year 445 until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
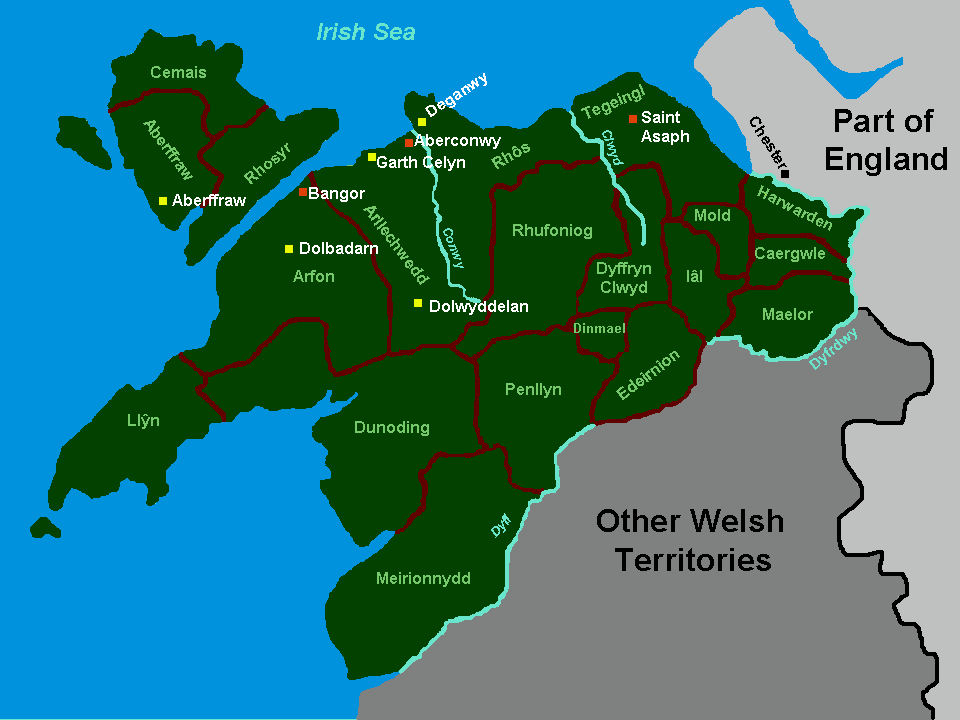
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfeddwlad
Perfeddwlad or Y Berfeddwlad was an historic name for the territories in Wales lying between the River Conwy and the River Dee. comprising the cantrefi of Rhos, Rhufoniog, Dyffryn Clwyd and Tegeingl. Perfeddwlad thus was also known as the Four Cantrefs. Early history For much of its history the area had been known as ''Tegeingl'', after the Celtic tribe '' Deceangli'' which inhabited North East Wales since the Iron Age. This was also the name of the most easterly cantref of the region. As the Kingdom of Gwynedd emerged as the dominant power in North Wales, the area also became known as ''Gwynedd Is Conwy'' (Gwynedd "below" the Conwy River). The name Y Berfeddwlad appears in the High Middle Ages, as the rivalries between Gwynedd, Powys, and the Anglo-Saxon England (and later Normans) intensified. The name is a contraction ofPerfedd andgwlad meaning ''heart-land'' or ''middle-country'' as the area became a centre of conflict. Later history Shortly after the death of Owain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commote
A commote (Welsh ''cwmwd'', sometimes spelt in older documents as ''cymwd'', plural ''cymydau'', less frequently ''cymydoedd'')'' Geiriadur Prifysgol Cymru'' (University of Wales Dictionary), p. 643 was a secular division of land in Medieval Wales. The word derives from the prefix ''cym-'' ("together", "with") and the noun ''bod'' ("home, abode"). The English word "commote" is derived from the Middle Welsh ''cymwt''. Medieval Welsh land organisation The basic unit of land was the ''tref'', a small village or settlement. In theory, 100 ''trefi'' made up a '' cantref'' (literally, "one hundred settlements"; plural: ''cantrefi''), and half or a third of a ''cantref'' was a ''cymwd'', although in practice the actual numbers varied greatly. Together with the ''cantrefi'', commotes were the geographical divisions through which defence and justice were organised. In charge of a commote would be a chieftain probably related to the ruling Prince of the Kingdom. His court would have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denbighshire (historic)
, HQ= Denbigh and Ruthin , Arms= , Map= , Code= DEN , CodeName= Chapman code , Government= Denbighshire County Council (1889-1974) , PopulationFirst= 83,629Vision of Britain 1831 Census/ref> , PopulationFirstYear= 1831 , AreaFirst= , AreaFirstYear= 1831 , DensityFirst= 0.2/acre , DensityFirstYear= 1831 , PopulationSecond= 144,783Vision of Britain Denbighshire population an density , PopulationSecondYear= 1911 , AreaSecond= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunedda
Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda ''Wledig'' ( 5th century), was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of western Europe. Name The name ''Cunedda'' (spelled ''Cunedag'' in the AD 828 pseudo-history ''Historia Brittonum'') derives from the Brythonic word ', meaning "Good Hound/Warrior" or "Having Good Hounds/Warriors". Genealogy His genealogy is traced back to a grandfather living in late Roman Britain named Padarn Beisrudd. His name literally translates as Paternus of the "red tunic" or the scarlet cloak, a color attributed to Roman officers during the Roman Empire. One traditional interpretation identifies Padarn as a Roman ( Romano-British) official of reasonably high rank who had been placed in command of the Votadini troops stationed in the Clackmannanshire region of Scotland in the 380s or earlier by the Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. Alternatively, he may have been a frontier chieftain who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantref
A cantref ( ; ; plural cantrefi or cantrefs; also rendered as ''cantred'') was a medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law. Description Land in medieval Wales was divided into ''cantrefi'', which were themselves divided into smaller ''cymydau'' (commotes). The word ''cantref'' is derived from ''cant'' ("a hundred") and ''tref'' ("town" in modern Welsh, but formerly used for much smaller settlements). The ''cantref'' is thought to be the original unit, with the commotes being a later division. ''Cantrefi'' could vary considerably in size: most were divided into two or three commotes, but the largest, the ''Cantref Mawr'' (or "Great Cantref") in Ystrad Tywi (now in Carmarthenshire) was divided into seven commotes. History The antiquity of the ''cantrefi'' is demonstrated by the fact that they often mark the boundary between dialects. Some were originally kingdoms in their own right; others may have been artificial units created later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moreith Ap Aidan
Moreith ap Aidan was king of Rhufoniog {{coord, 52.950, -3.275, display=title, region:GB_scale:20000 Rhufoniog was a small sub-kingdom of the Dark Ages Gwynedd, and later a cantref in medieval Wales. Geography The cantref Rhos lay between it and the Irish Sea. Sometimes the two ... around 520. Nothing is known about his life, aside from rumour that he lived in Castle Greynus. 5th-century Welsh monarchs {{Wales-bio-stub fr:Moreith ap Aidan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
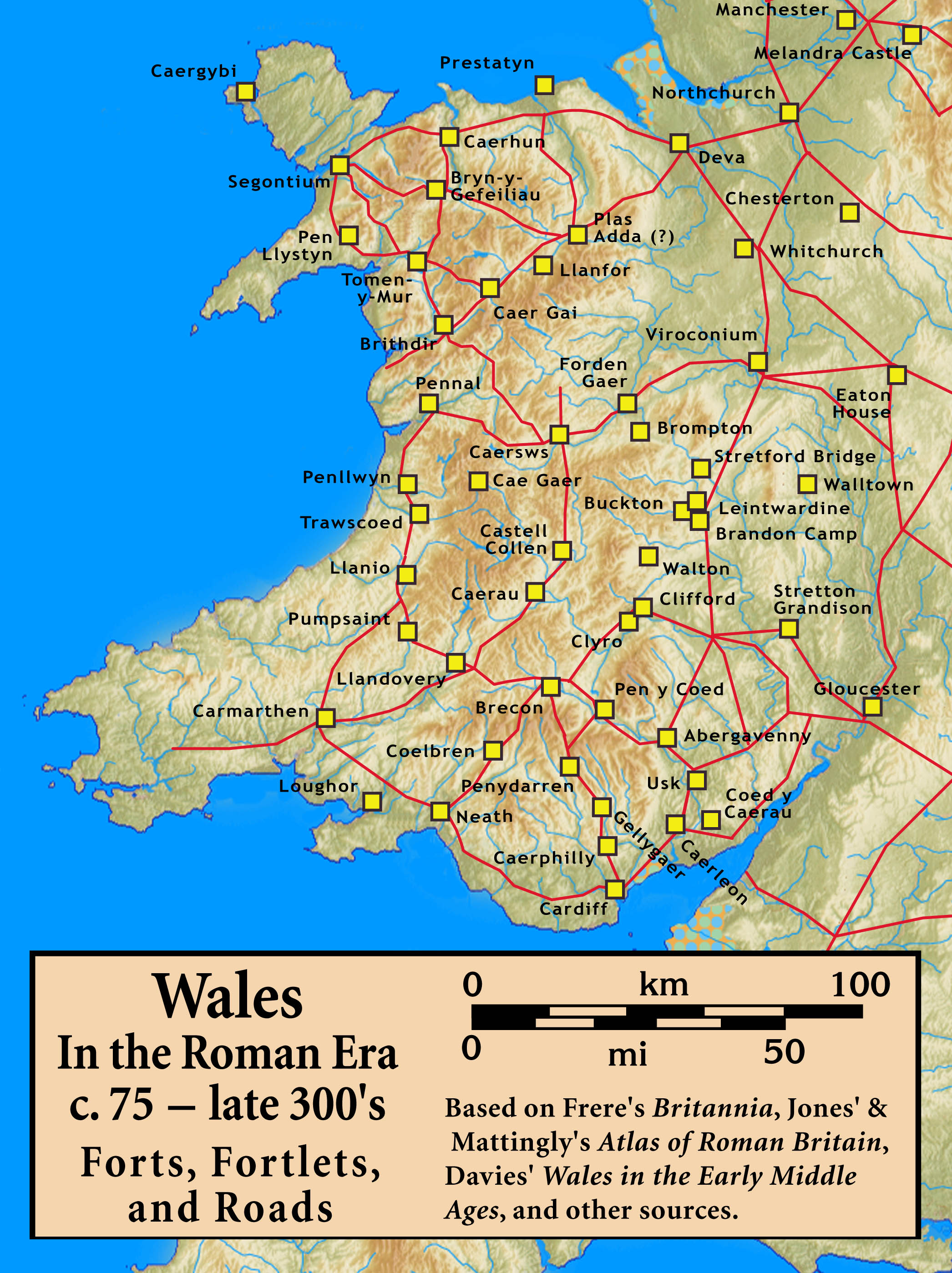
Wales In The Roman Era
The Roman era in the area of modern Wales began in 48 AD, with a military invasion by the imperial governor of Roman Britain. The conquest was completed by 78 AD, and Roman rule endured until the region was abandoned in 383 AD. The Roman Empire held a military occupation in most of Wales, except for the southern coastal region of South Wales, east of the Gower Peninsula, where there is a legacy of Romanisation in the region, and some southern sites such as Carmarthen, which was the civitas capital of the Demetae tribe. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is located in South Wales. Wales was a rich source of mineral wealth, and the Romans used their engineering technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper, and lead, as well as modest amounts of some other metals such as zinc and silver. The Roman campaigns of conquest in Wales appear in surviving ancient sources, who record in particular the resistance and ultimate conquest of two of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangor, Gwynedd
Bangor (; ) is a cathedral city and community in Gwynedd, North Wales. It is the oldest city in Wales. Historically part of Caernarfonshire, it had a population of 18,322 in 2019, according to the Office for National Statistics. Landmarks include Bangor Cathedral, Bangor University, Garth Pier, and the Menai Suspension Bridge and Britannia Bridge which connect the city to the Isle of Anglesey. History The origins of the city date back to the founding of a monastic establishment on the site of Bangor Cathedral by the Celtic saint Deiniol in the early 6th century AD. itself is an old Welsh word for a wattled enclosure, such as the one that originally surrounded the cathedral site. The present cathedral is a somewhat more recent building and has been extensively modified throughout the centuries. While the building itself is not the oldest, and certainly not the biggest, the bishopric of Bangor is one of the oldest in the UK. In 973, Iago, ruler of the Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanelwy
St Asaph (; cy, Llanelwy "church on the Elwy") is a city and community on the River Elwy in Denbighshire, Wales. In the 2011 Census it had a population of 3,355, making it the second-smallest city in Britain in terms of population and urban area. It is in the historic county of Flintshire. The city of St Asaph is surrounded by countryside and views of the Vale of Clwyd. It is situated close to a number of busy coastal towns such as Rhyl, Prestatyn, Abergele, Colwyn Bay and Llandudno. The historic castles of Denbigh and Rhuddlan are also nearby History The earliest inhabitants of the vale of Elwy lived at the nearby Paleolithic site of Pontnewydd (Bontnewydd), which was excavated from 1978 by a team from the University of Wales, led by Stephen Aldhouse Green. Teeth and part of a jawbone excavated in 1981 were dated to 225,000 years ago. This site is the most north-western site in Eurasia for remains of early hominids and is considered of international importance. Based on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early ..., High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry De Lacy, 3rd Earl Of Lincoln
Henry de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln (c. 1251February 1311), Baron of Pontefract, Lord of Bowland, Baron of Halton and hereditary Constable of Chester, was an English nobleman and confidant of King Edward I. He served Edward in Wales, France, and Scotland, both as a soldier and a diplomat. Through his mother he was a great-grandson of Amadeus IV, Count of Savoy. He is the addressee, or joint composer, of a poem (a ''tenson'') by Walter of Bibbesworth about crusading, ''La pleinte par entre missire Henry de Lacy et sire Wauter de Bybelesworthe pur la croiserie en la terre seinte''. Origins Henry was the son and heir of Edmund de Lacy, Baron of Pontefract (c. 1230–1258) (eldest son and heir apparent of John de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln (c. 1192–1240) and his wife Margaret de Quincy suo jure Countess of Lincoln (c. 1206–1266)) by his wife Alice of Saluzzo, a Savoyard noblewoman descended from Amadeus IV, Count of Savoy. Inheritance Henry's father died in 1258 when he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)